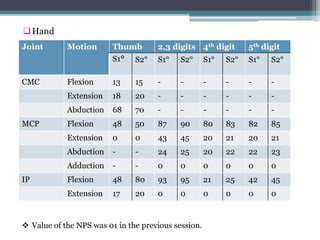
This document presents a case study of a 61-year-old male electrician who injured his right hand in a motorcycle accident. He has limited extension of his right 4th and 5th fingers. On examination, deformities and swelling were observed in the 4th and 5th fingers. Range of motion was restricted in the fingers but normal elsewhere. Tests indicated a boutonniere deformity in the 4th and 5th fingers. The physiotherapy diagnosis was decreased range of motion, joint mobility, and muscle performance in the fingers. The treatment plan focuses on pain management, maintaining joint and tendon mobility, increasing range of motion and muscle strength through various exercises over several weeks. Progress will be measured by monitoring range of motion