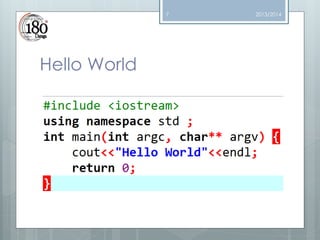
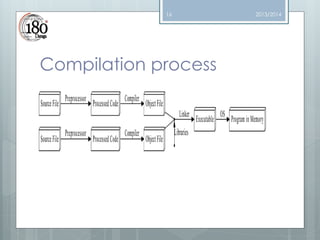
The document provides an outline and introduction to a C++ course. The outline lists topics that will be covered including variables, data types, control statements, functions, arrays, structures, files, pointers, recursion, and STL. The introduction explains that programming languages allow communication with computers. The document then discusses the evolution of programming languages from machine code to assembly to high-level languages. It provides reasons for using C++, including maintainability and portability. It also lists tools that will be used like Eclipse, Codeblocks, Dev C++, and Netbeans. The rest of the document dives deeper into concepts like I/O streams, the main function, and the compilation process.