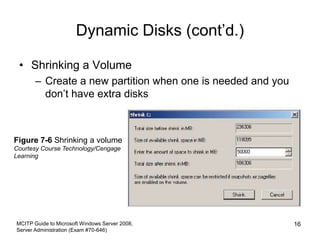
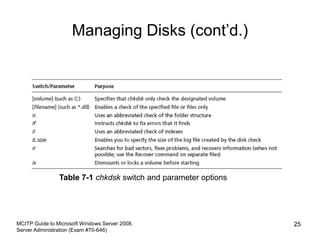
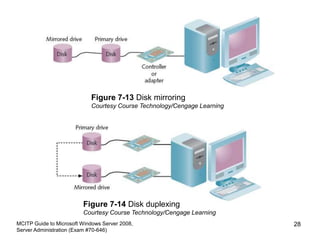
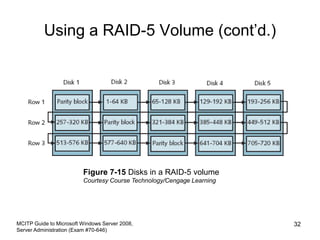
This chapter discusses data storage and backup options in Windows Server 2008. It covers configuring basic and dynamic disks, using RAID for fault tolerance, and the new Windows Server Backup tool. Disk storage can be configured as basic or dynamic disks. RAID 0 provides striping for performance, RAID 1 uses mirroring for redundancy, and RAID 5 offers striping with parity. The Windows Server Backup tool allows scheduling full, incremental, and custom backups locally or over the network. Developing a regular backup and off-site disaster recovery strategy is also recommended.