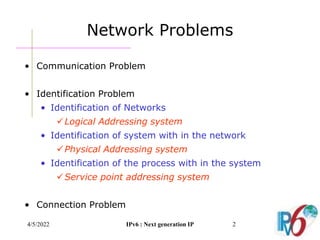
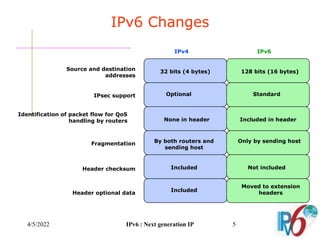
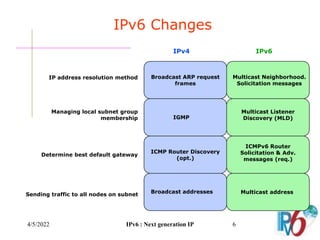
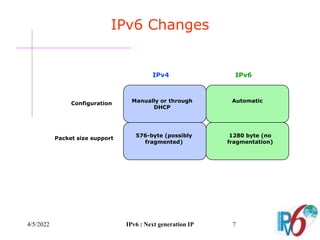
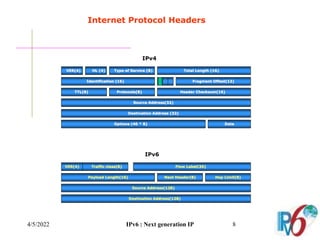
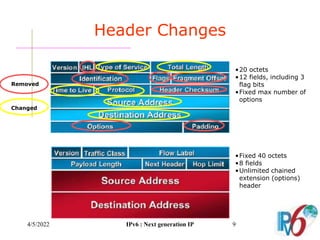
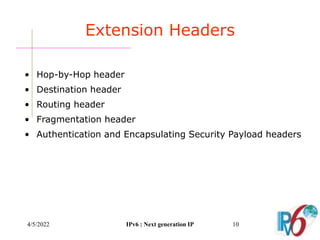
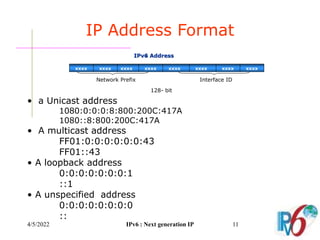
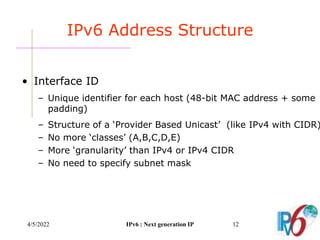
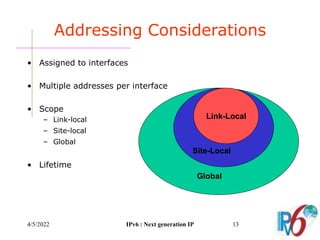
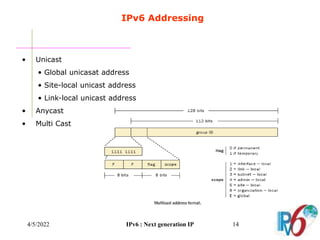
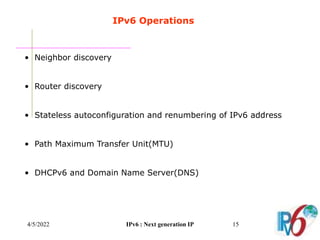
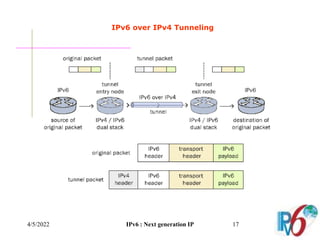
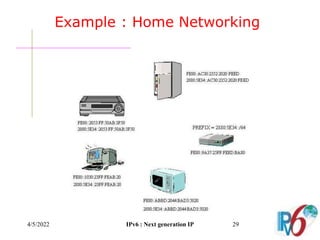
The document discusses IPv6, the next generation Internet Protocol. It addresses network problems like identification that IPv6 aims to solve through a larger 128-bit address space and built-in security features. The document outlines key changes in IPv6 like larger addresses, stateless autoconfiguration, and built-in header fields for quality of service and security. It also covers address formats, extension headers, deployment methods, and the overall benefits and challenges around transitioning to IPv6.