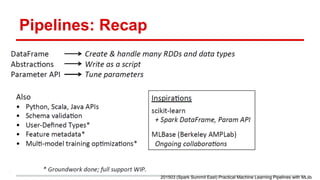
(1) The document describes building an email classifier using Spark MLlib. It loads spam and ham email datasets, trains a logistic regression model on tokenized and hashed features, and evaluates the model on test data.
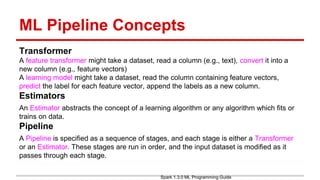
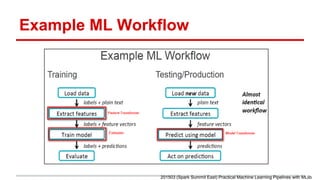
(2) It then shows how to implement the same workflow as a machine learning pipeline in Spark, including tokenization, feature extraction, model training, validation, and hyperparameter tuning via cross-validation.
(3) The pipeline achieves 99.77% accuracy on test data, outperforming the standalone model implementation from the first part. This demonstrates the benefits of ML pipelines for simplifying, standardizing, and automating machine learning workflows.


![Spam Sample
From 12a1mailbot1@web.de Thu Aug 22 13:17:22 2002
Return-Path: <12a1mailbot1@web.de>
Delivered-To: zzzz@localhost.spamassassin.taint.org
Received: from localhost (localhost [127.0.0.1])
by phobos.labs.spamassassin.taint.org (Postfix) with ESMTP id 136B943C32
for <zzzz@localhost>; Thu, 22 Aug 2002 08:17:21 -0400 (EDT)
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0 Transitional//EN">
<HTML><HEAD>
<META content=3D"text/html; charset=3Dwindows-1252" http-equiv=3DContent-T=ype>
<META content=3D"MSHTML 5.00.2314.1000" name=3DGENERATOR></HEAD>
<BODY><!-- Inserted by Calypso -->
<TABLE border=3D0 cellPadding=3D0 cellSpacing=3D2 id=3D_CalyPrintHeader_ r=
<CENTER>Save up to 70% on Life Insurance.</CENTER></FONT><FONT color=3D#ff=
0000
face=3D"Copperplate Gothic Bold" size=3D5 PTSIZE=3D"10">
<CENTER>Why Spend More Than You Have To?
<CENTER><FONT color=3D#ff0000 face=3D"Copperplate Gothic Bold" size=3D5 PT=
SIZE=3D"10">
<CENTER>Life Quote Savings
Email headers
HTML tags
Email body](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/131-150715013049-lva1-app6891/85/Email-Classifier-using-Spark-1-3-Mlib-ML-Pipeline-3-320.jpg)

![Using Spark Mlib (2)
val validation = testData.map{ lpoint => (lpoint.label, model.predict(lpoint.features)) }
val matirx = validation.map{
ret => ret match {
case (1.0, 1.0) => Array(1, 0, 0, 0) // TP
case (0.0, 1.0) => Array(0, 1, 0, 0) // FP
case (0.0, 0.0) => Array(0, 0, 1, 0) // TN
case (1.0, 0.0) => Array(0, 0, 0, 1) // FN
}
}.reduce{
(ary1, ary2) => Array(ary1(0)+ary2(0), ary1(1)+ary2(1), ary1(2)+ary2(2), ary1(3)+ary2(3))
}
matrix:Array[Int] = Array(37TP, 11FP, 347TN, 36FN)
Accuracy = 89.0951% ( (37+347)/431 ) , vs. 99.5585% using Mahout
Precision = 77.0833% ( 37/(37+11) ) , vs. 98.5714% using Mahout
Recall = 50.6849% ( 37/(37+36) ) , vs. 98.5714% using Mahout
validation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/131-150715013049-lva1-app6891/85/Email-Classifier-using-Spark-1-3-Mlib-ML-Pipeline-5-320.jpg)


![Using ML Pipeline (2)
crossval.setEstimatorParamMaps(paramGrid).setNumFolds(3)
val cvModel = crossval.fit(trainSet)
val validation = cvModel.transform(testSet)
val matrix = validation.select("label","prediction").map{
case Row(label: Double, prediction: Double) => (label, prediction) match {
case (1.0, 1.0) => Array(1, 0, 0, 0) // TP
case (0.0, 1.0) => Array(0, 1, 0, 0) // FP
case (0.0, 0.0) => Array(0, 0, 1, 0) // TN
case (1.0, 0.0) => Array(0, 0, 0, 1) // FN
}
}.reduce{
(ary1, ary2) => Array(ary1(0)+ary2(0), ary1(1)+ary2(1), ary1(2)+ary2(2), ary1(3)+ary2(3))
}
matrix:Array[Int] = Array(84TP, 1FP, 352TN, 0FN)
Accuracy = 99.7712% ( (84+352)/437 ) , vs. 99.5585% using Mahout
Precision = 98.8235% ( 84/(84+1) ) , vs. 98.5714% using Mahout
Recall = 100% ( 84/(84+0) ) , vs. 98.5714% using Mahout
All in One
Tokenization, Featurization, Model Training, Model Validation, and Prediction
cvModel.bestModel.fittingParamMap = {
LogisticRegression-3cb51fc7-maxIter: 20,
HashingTF-cb518e45-numFeatures: 1000,
LogisticRegression-3cb51fc7-regParam: 0.1 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/131-150715013049-lva1-app6891/85/Email-Classifier-using-Spark-1-3-Mlib-ML-Pipeline-10-320.jpg)