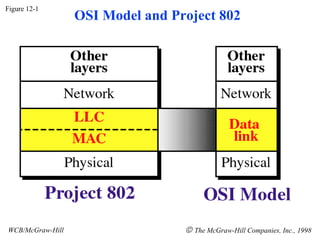
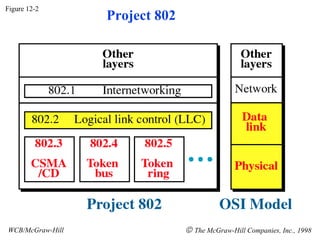
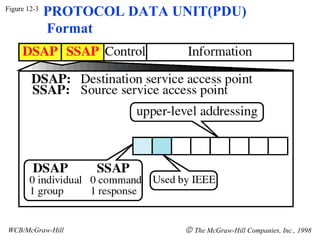
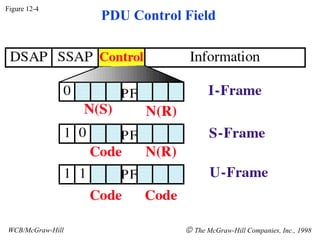
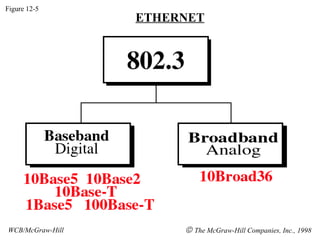
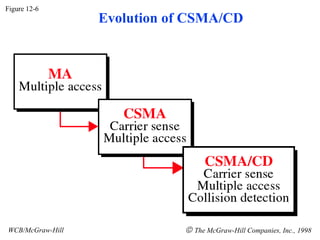
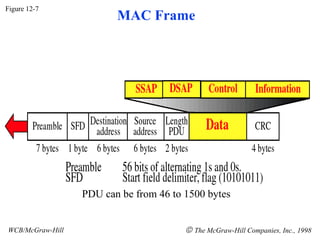
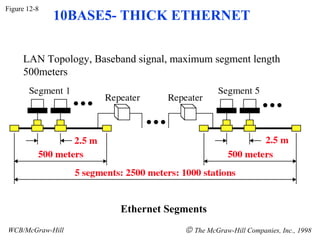
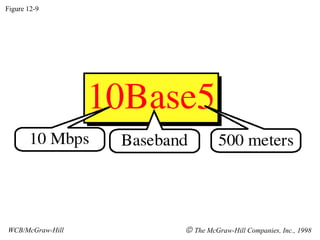
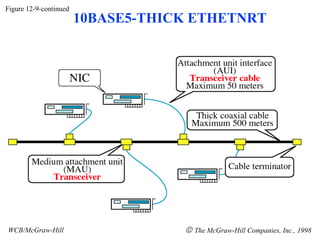
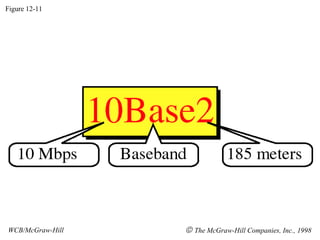
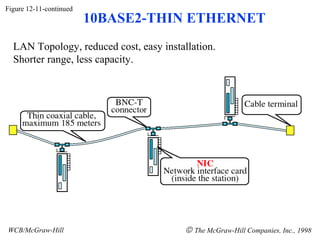
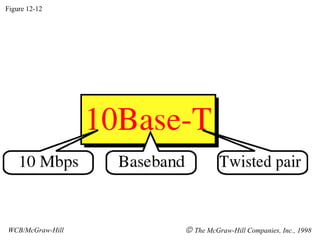
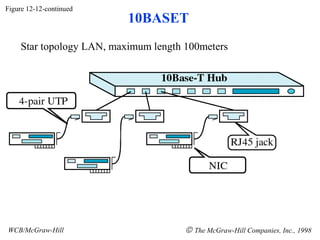
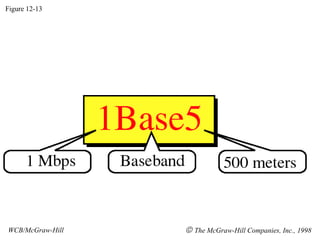
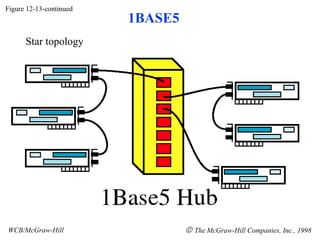
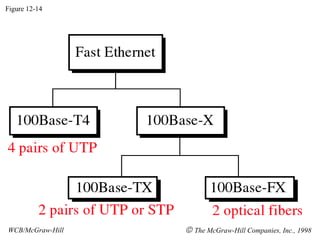
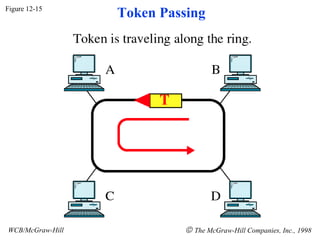
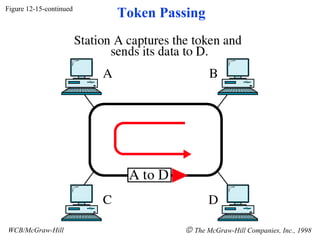
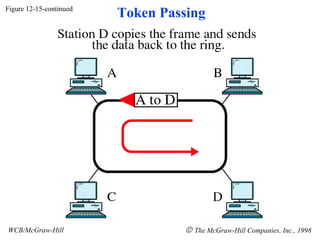
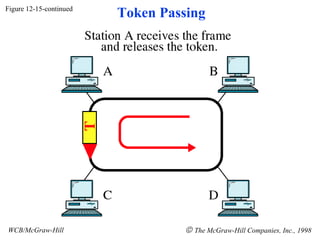
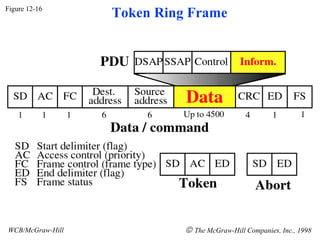
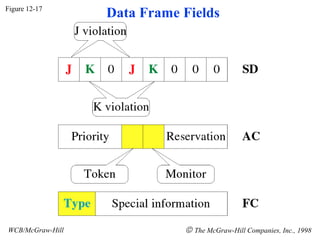
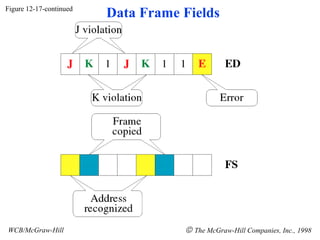
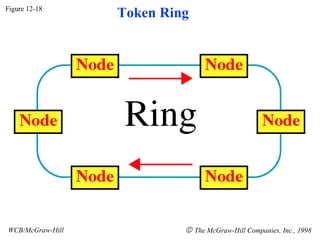
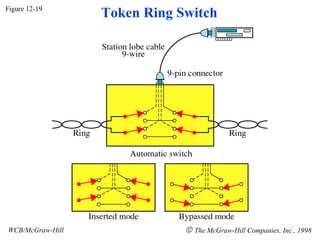
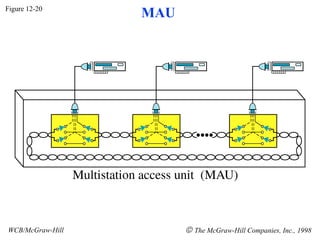
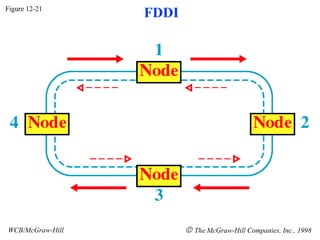
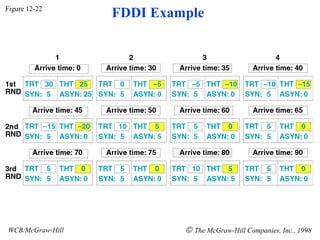
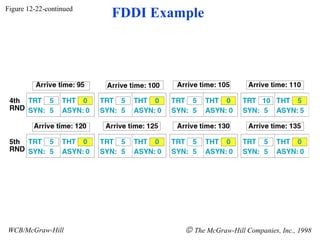
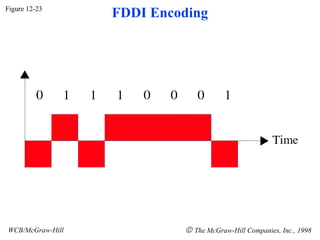
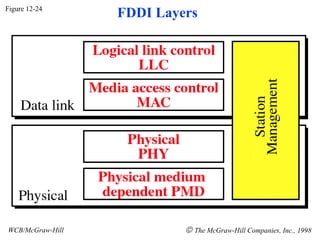
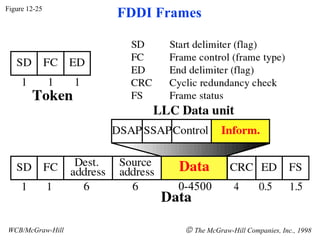
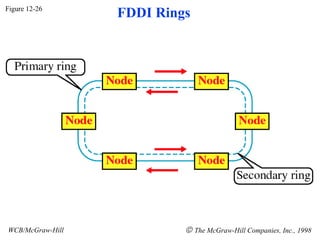
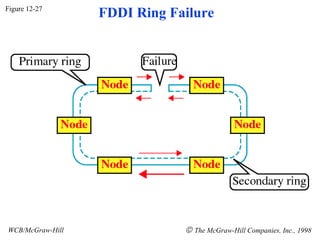
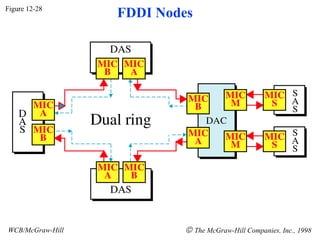
The document discusses local area network (LAN) technologies including Ethernet, Token Ring, and FDDI. It describes the OSI model and Project 802 which established standards for LANs. Ethernet uses CSMA/CD access method and has evolved from thick to thin to twisted-pair cable. Token Ring uses a token passing method where a special packet is passed between nodes for transmission rights. FDDI provides a fiber-optic dual-ring topology for high-speed transmission over greater distances.