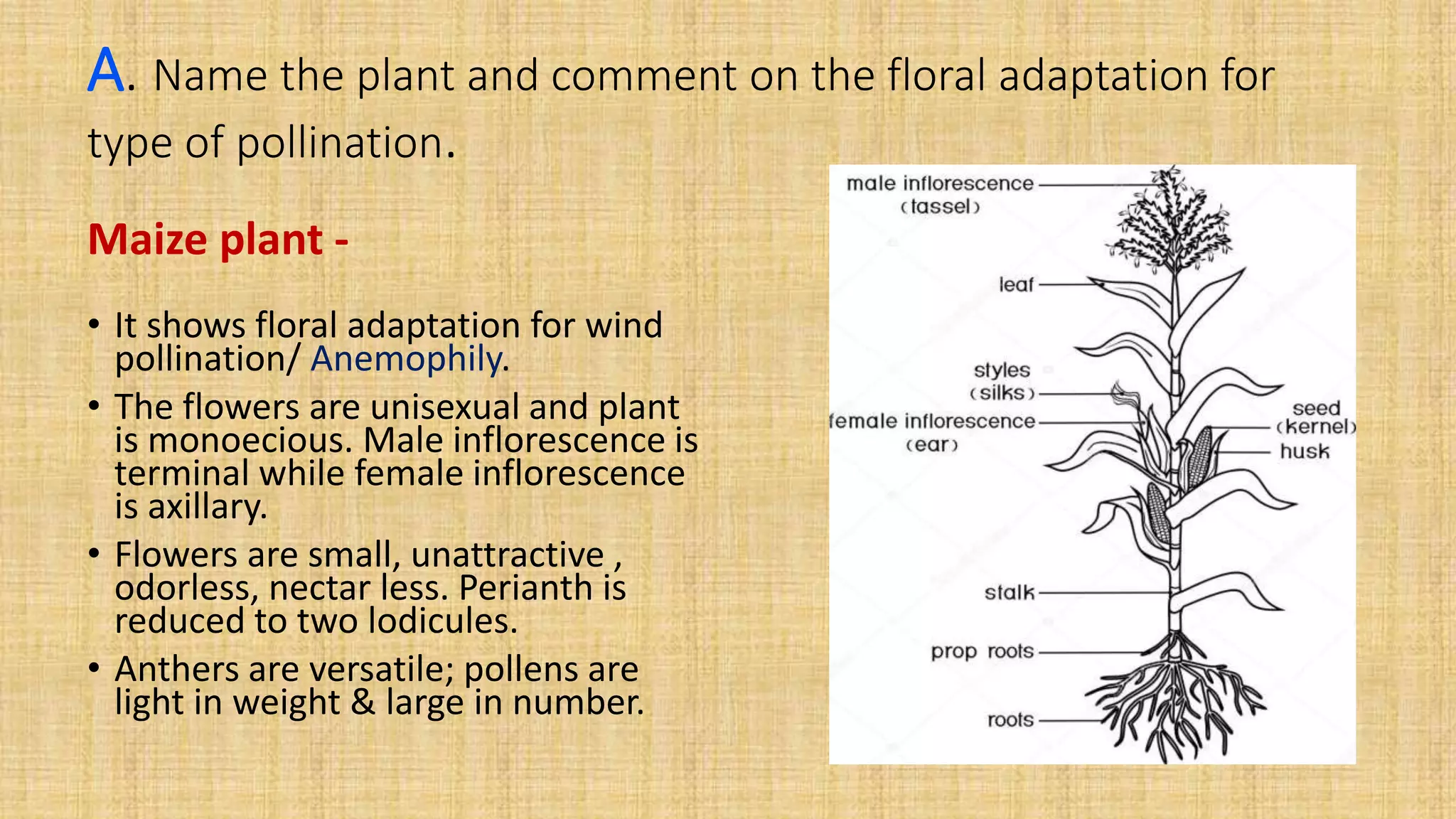
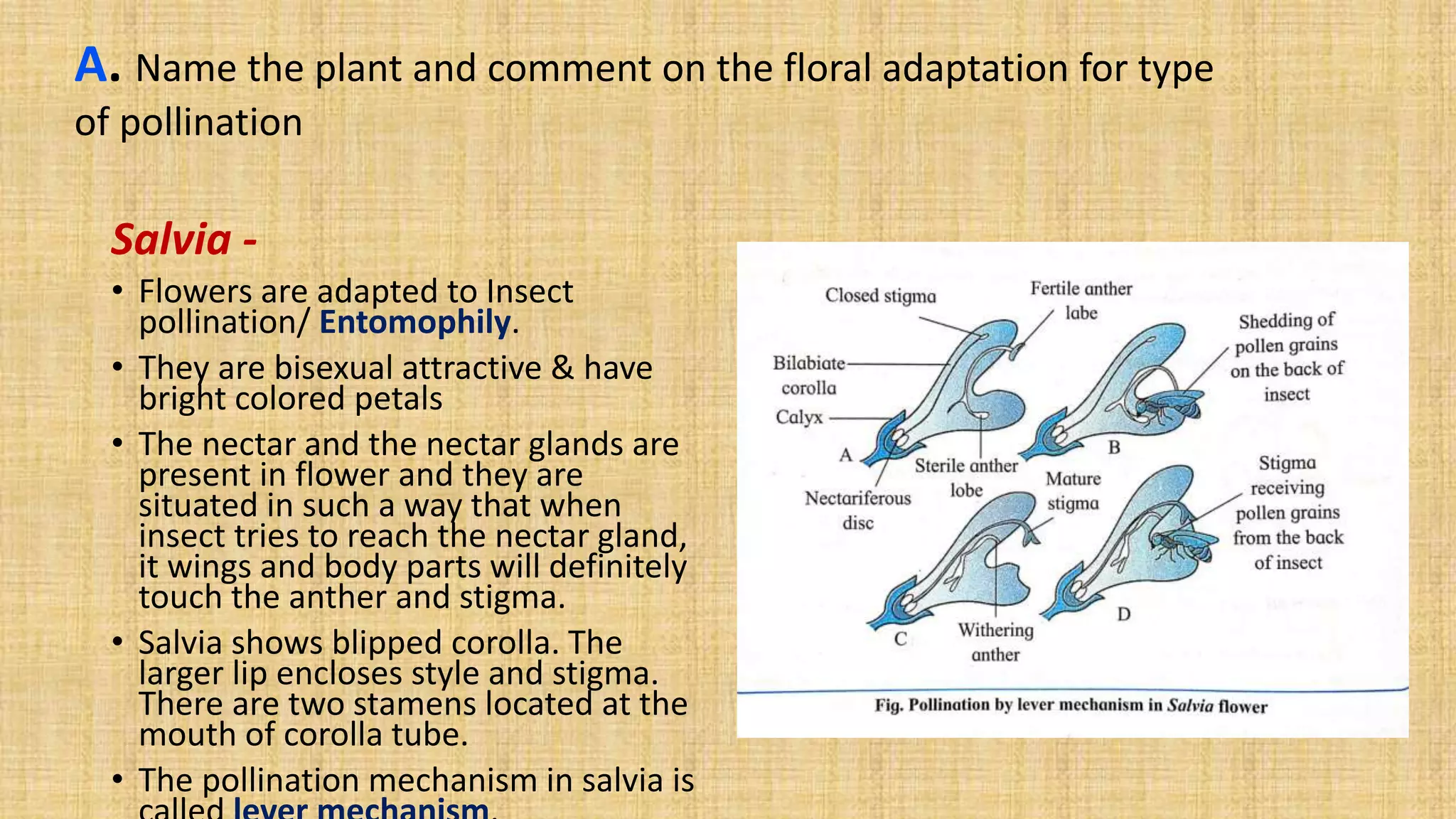
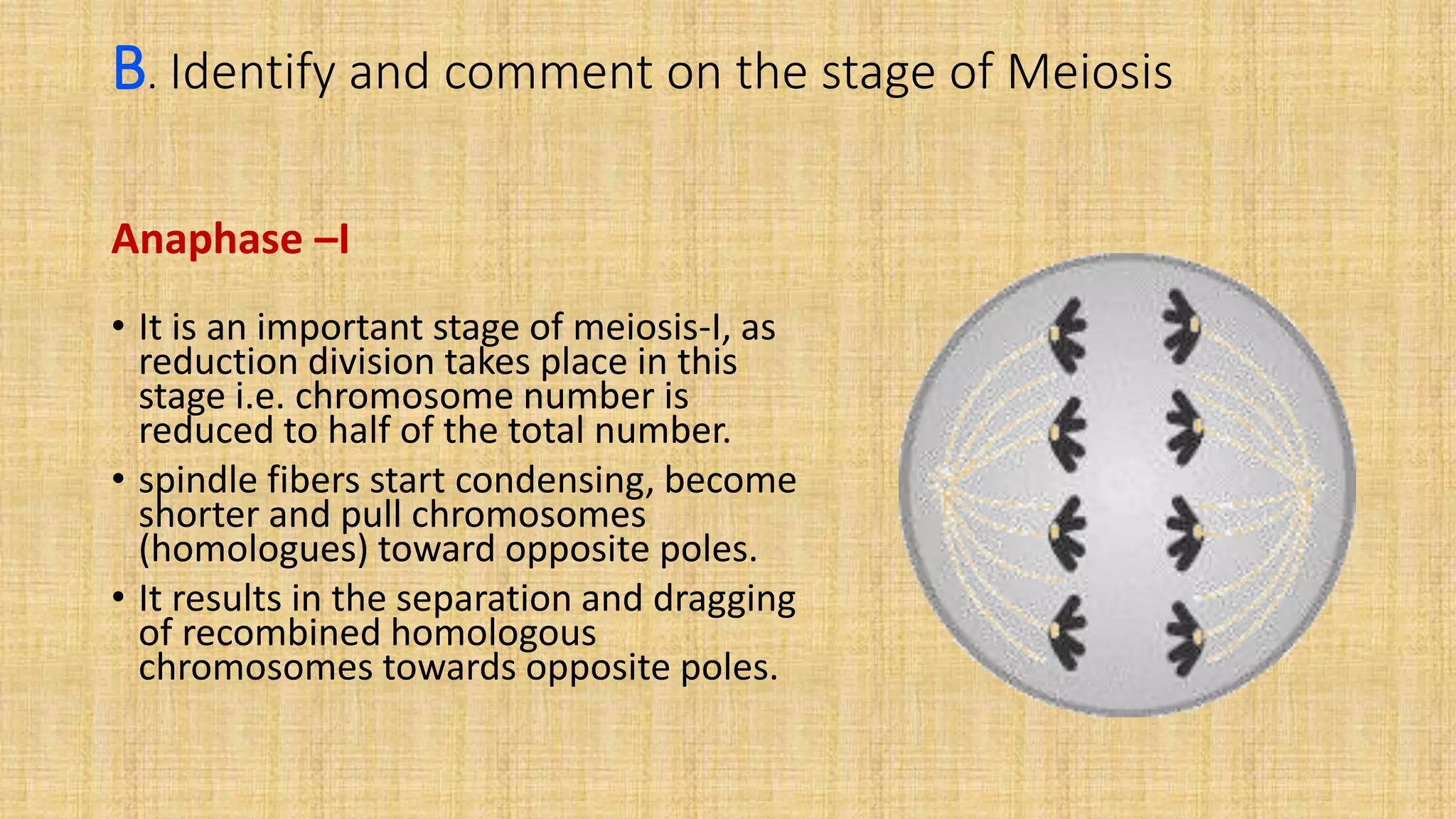
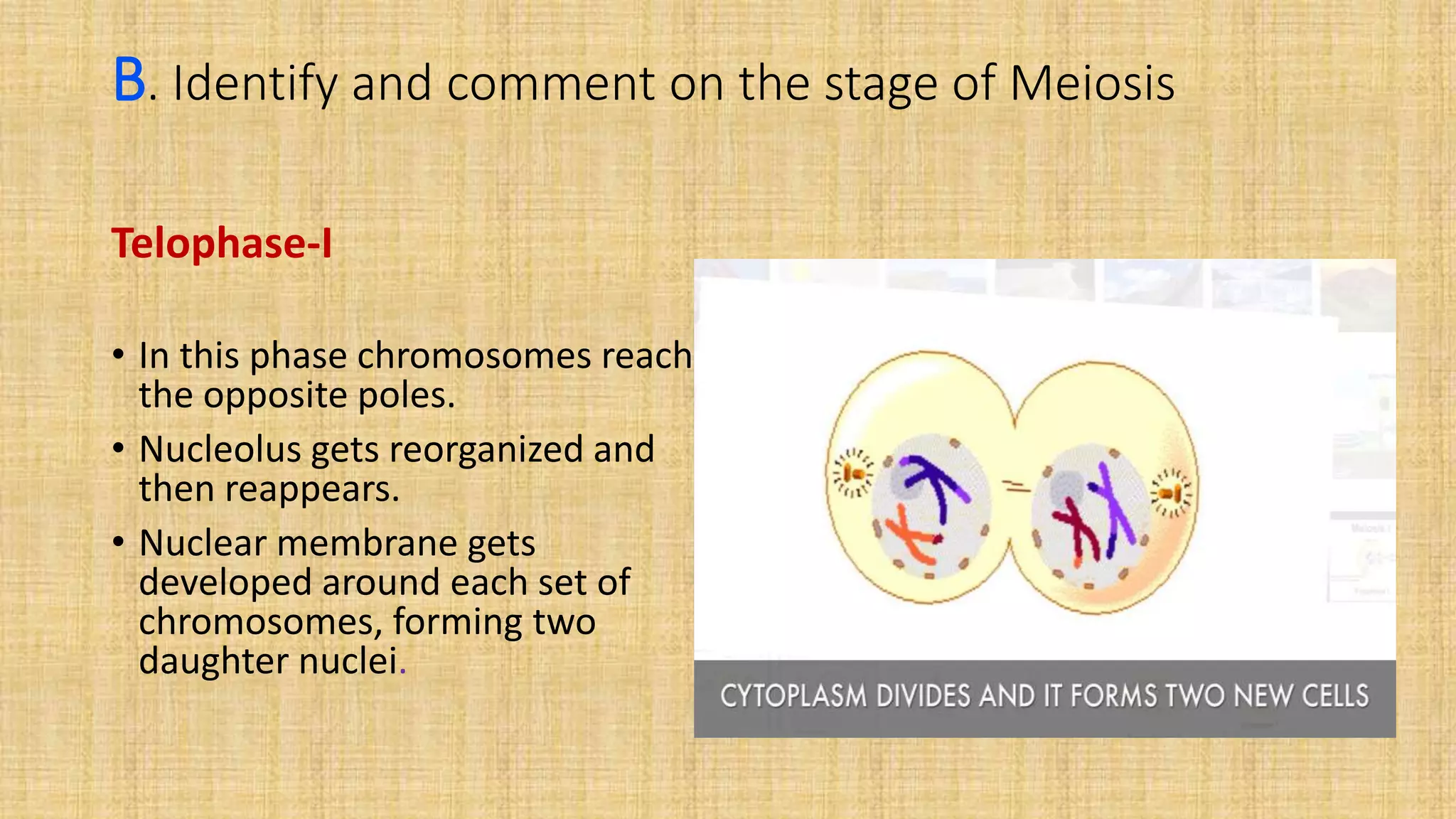
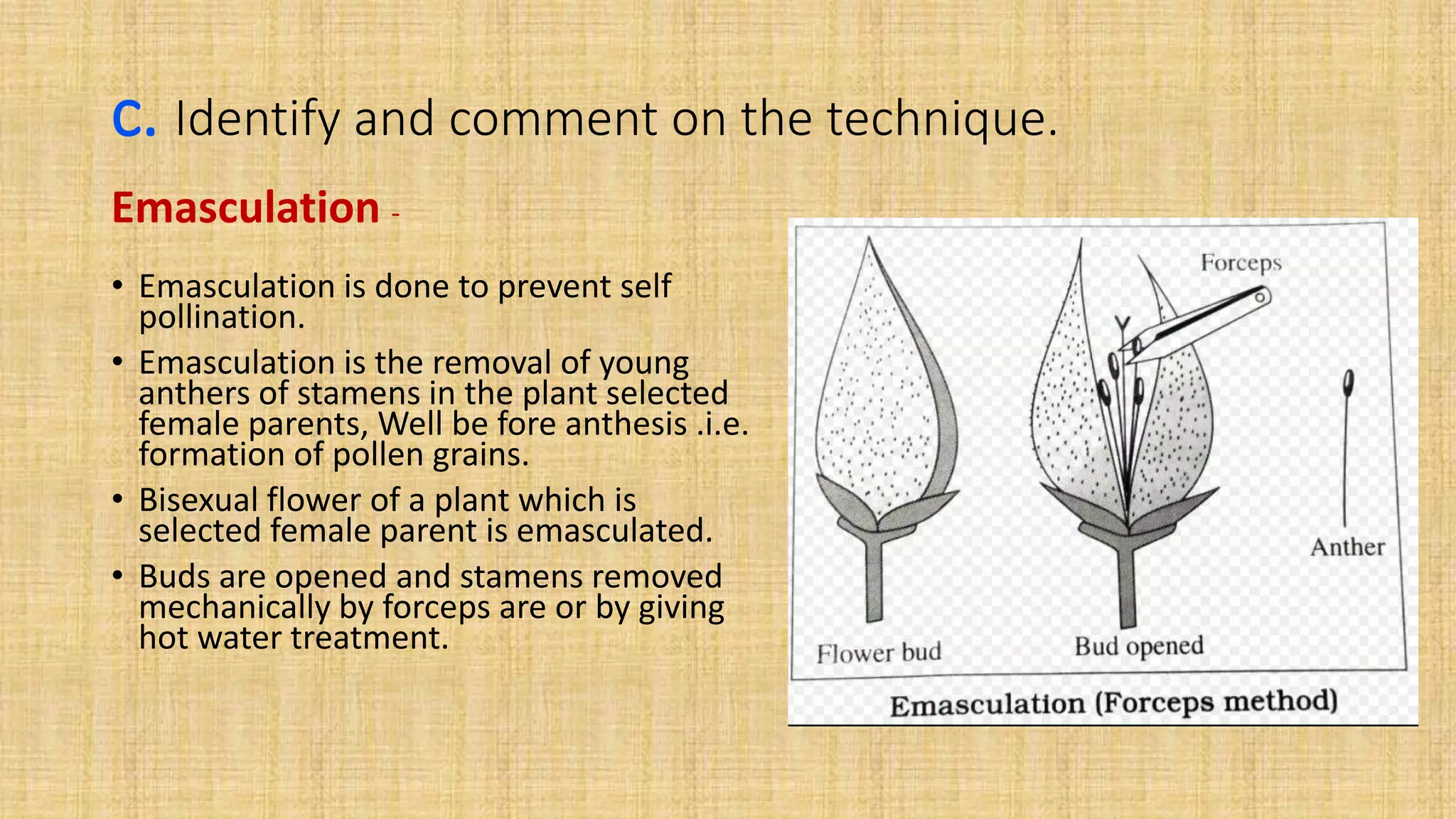
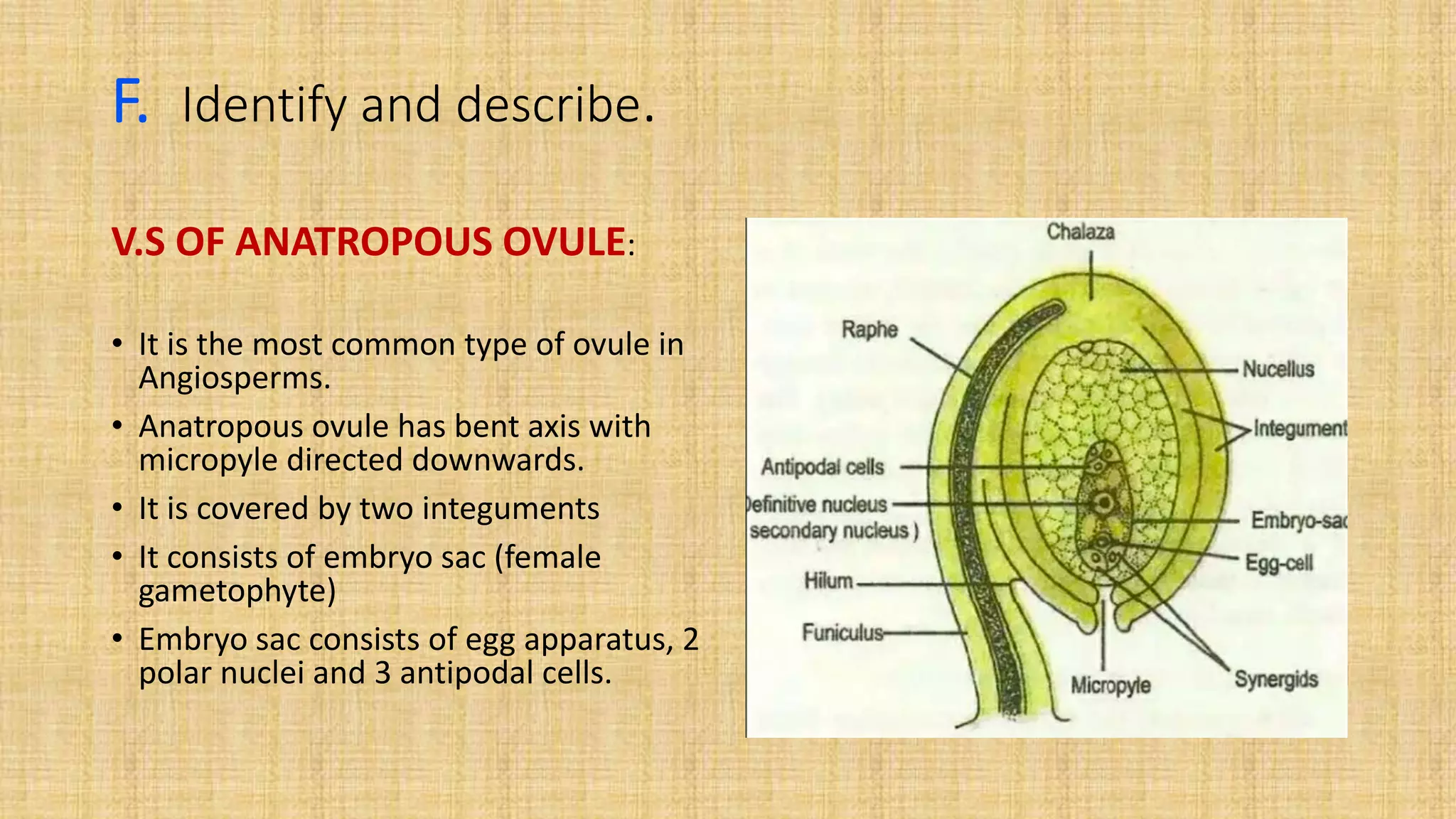
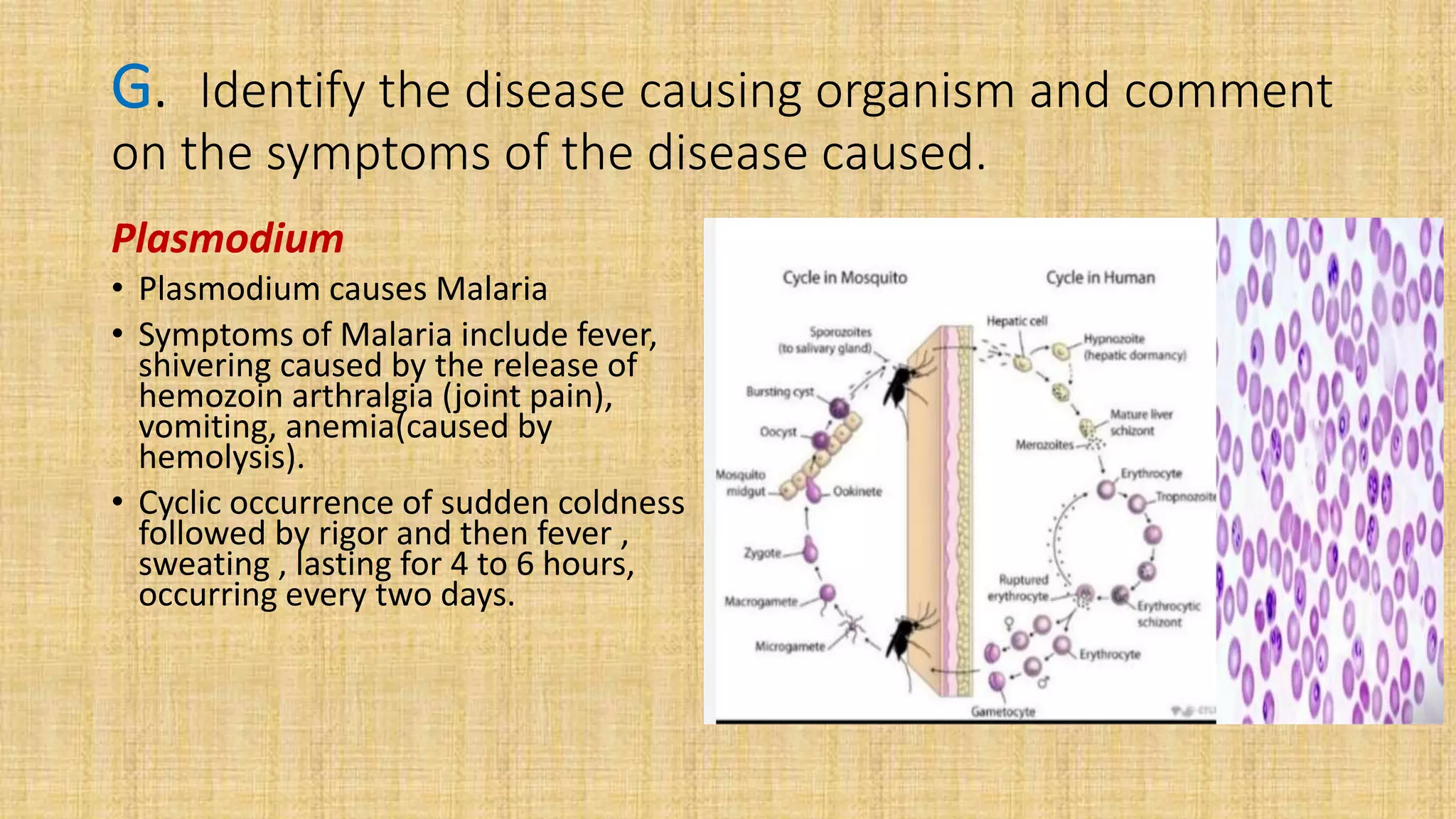
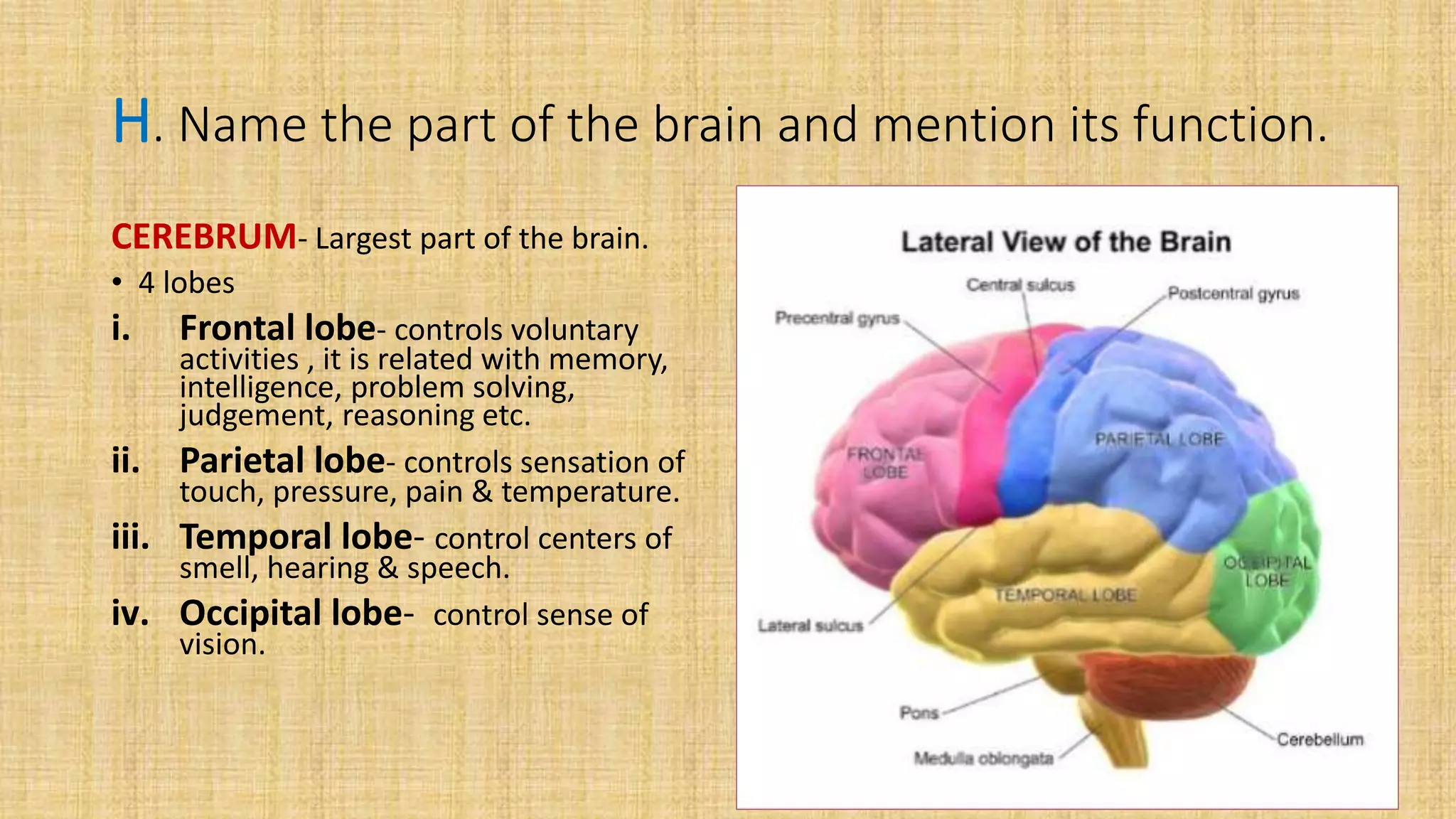
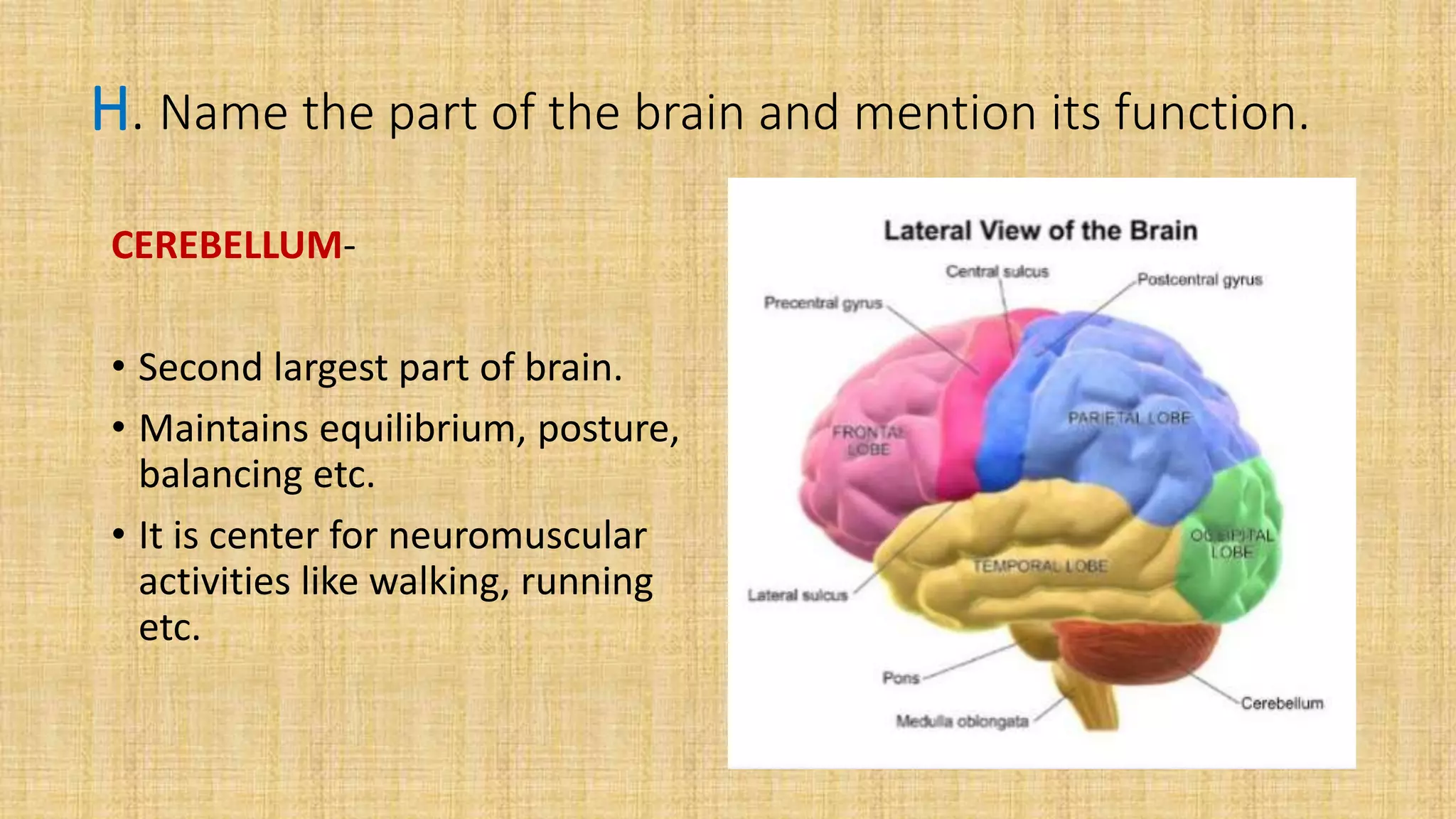
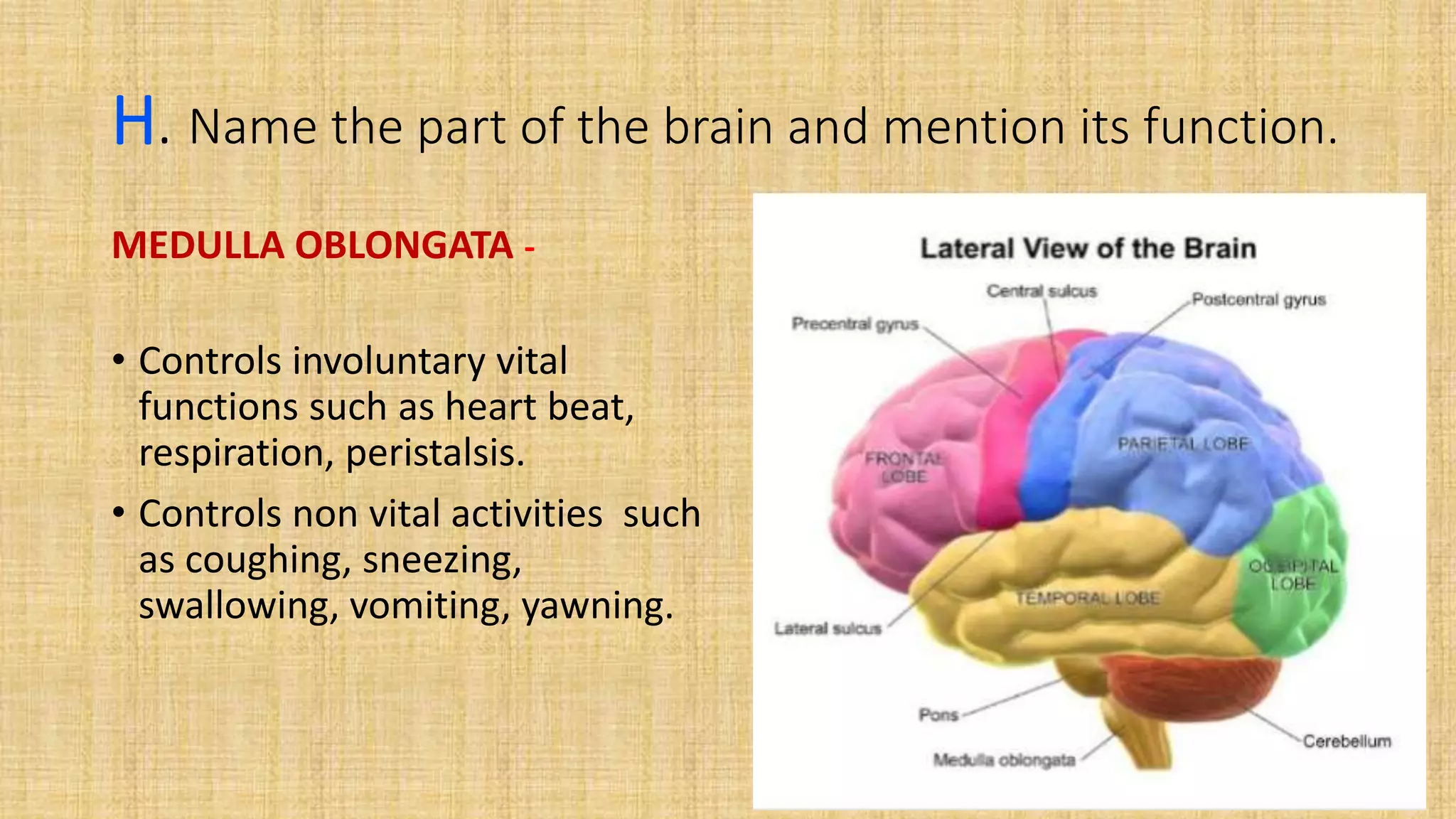
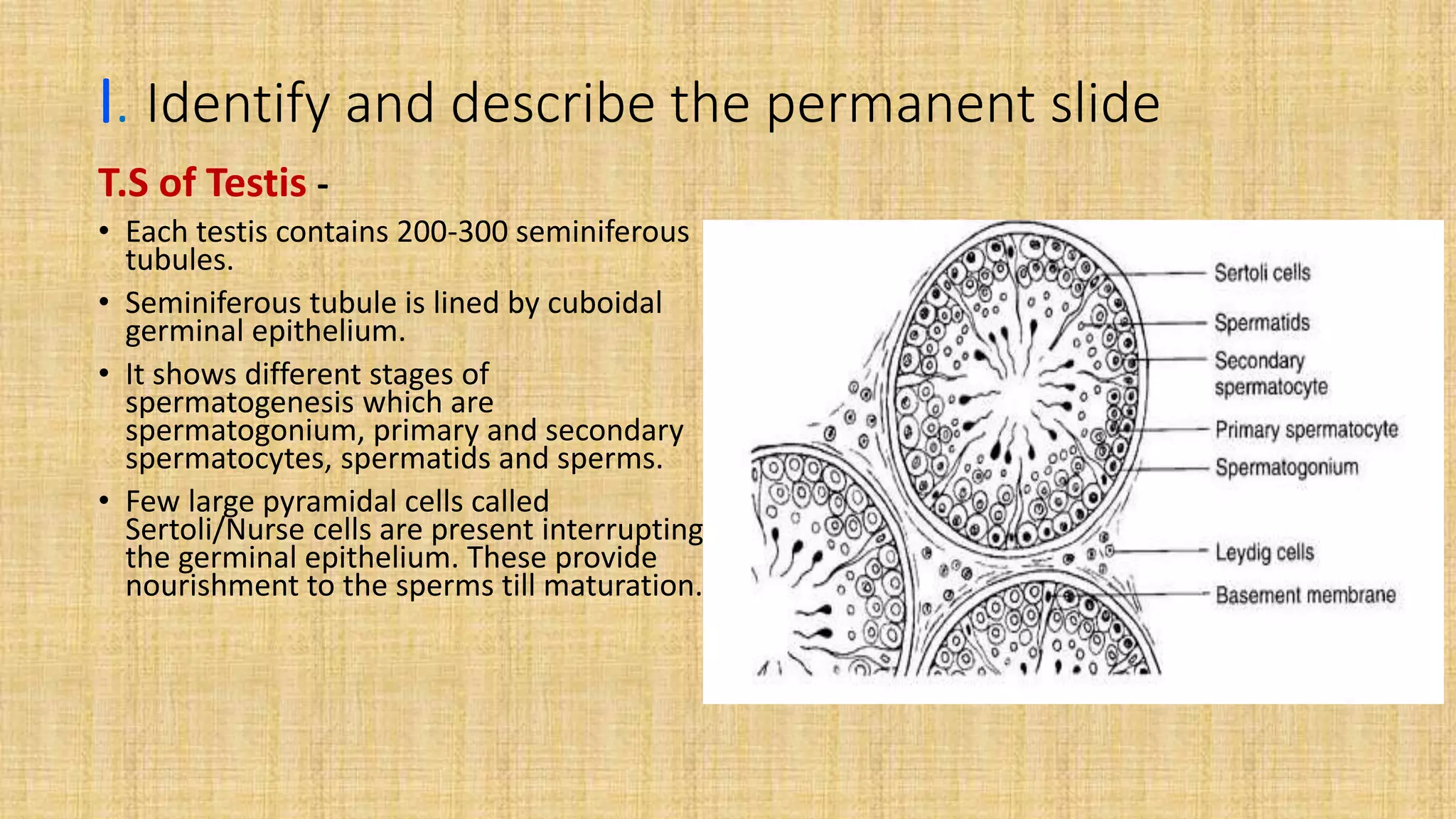
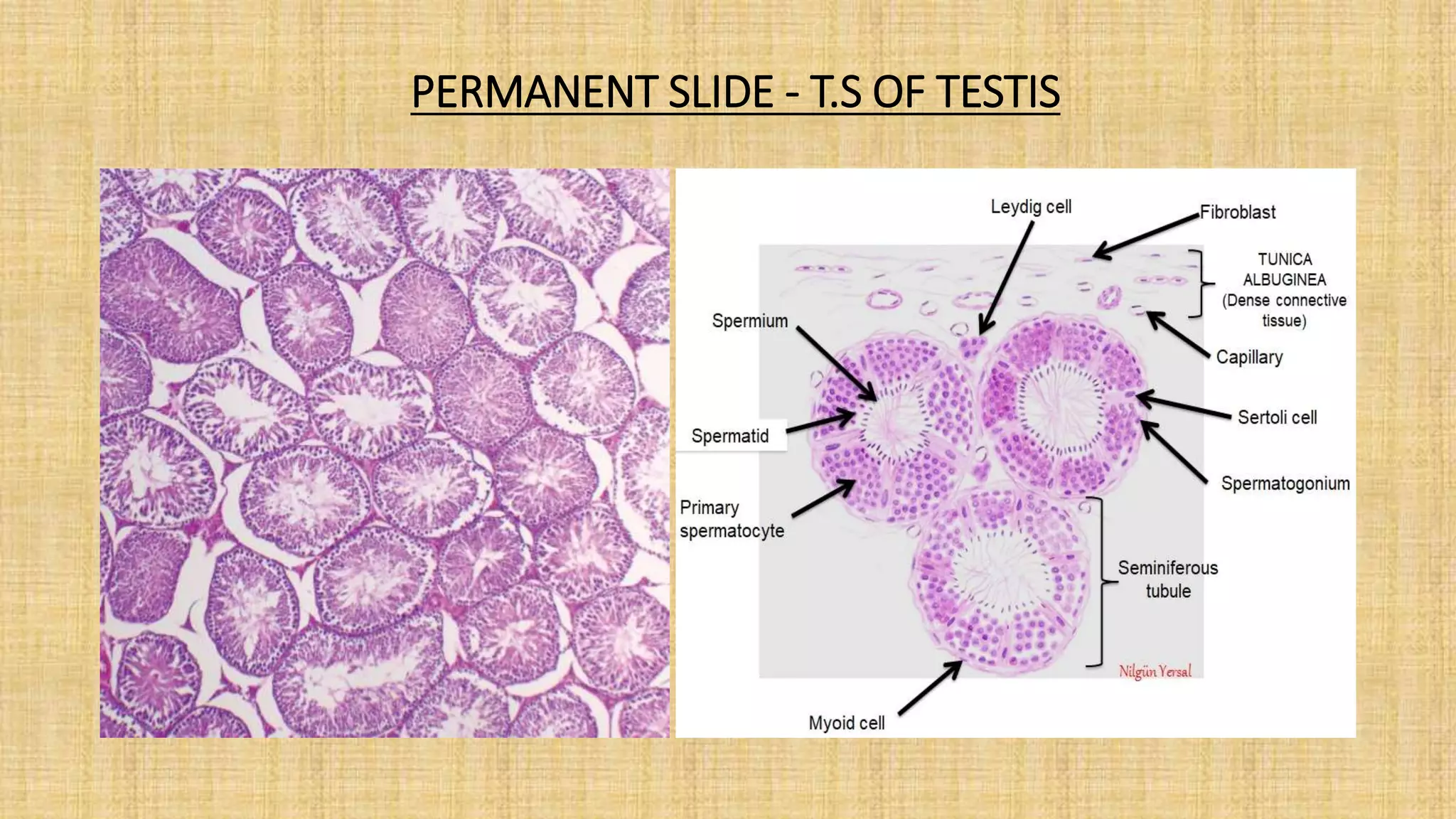
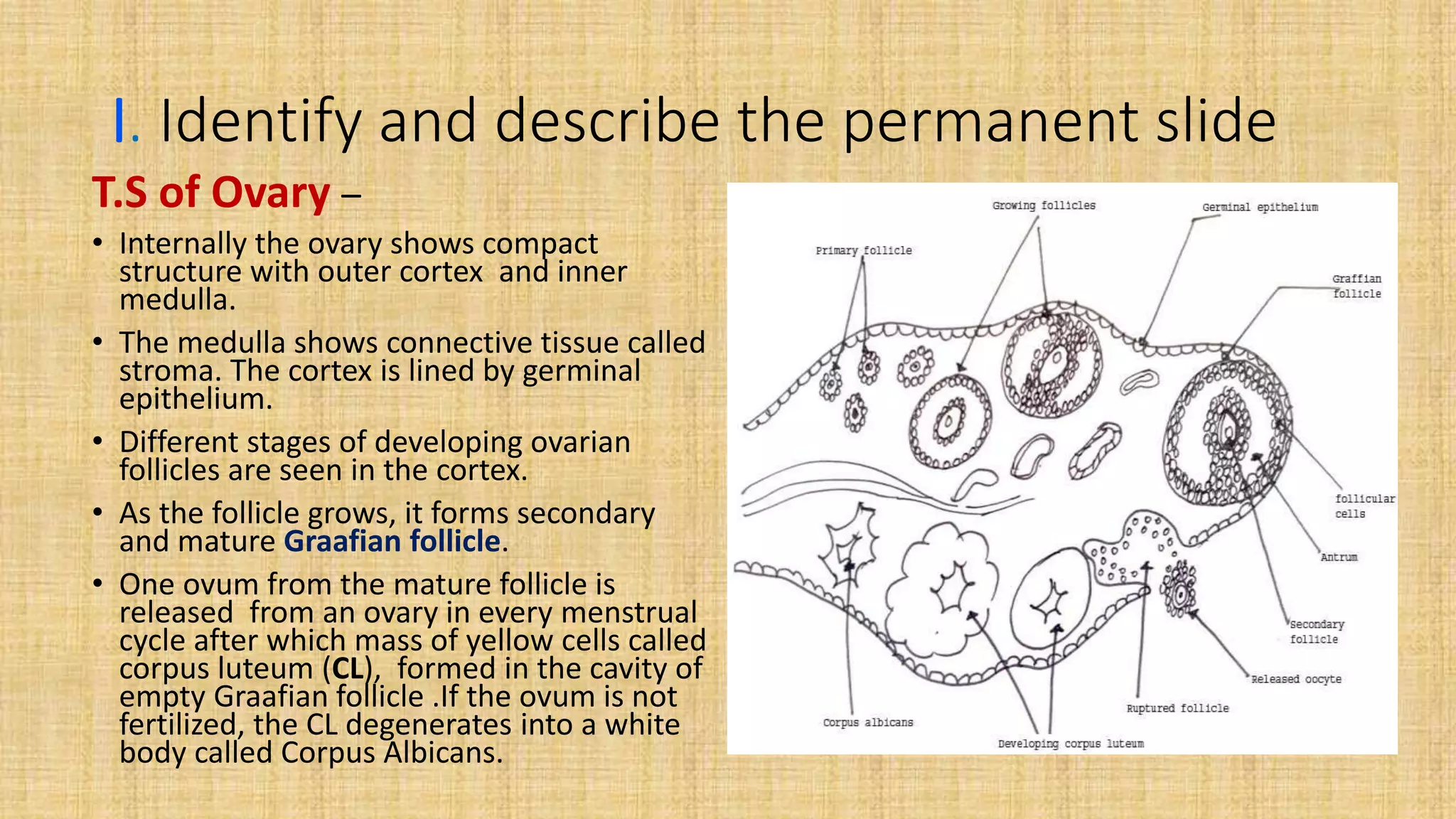
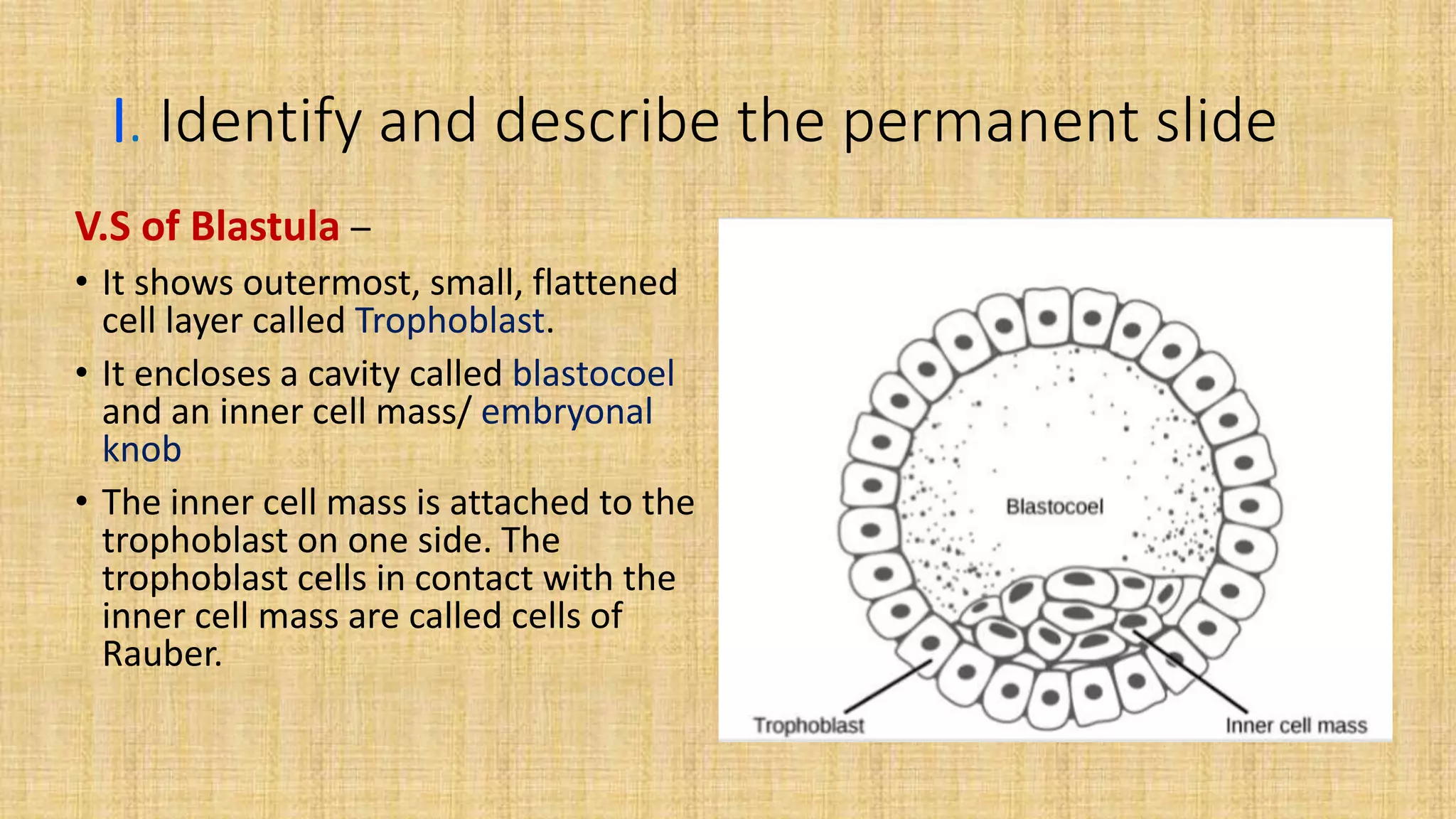
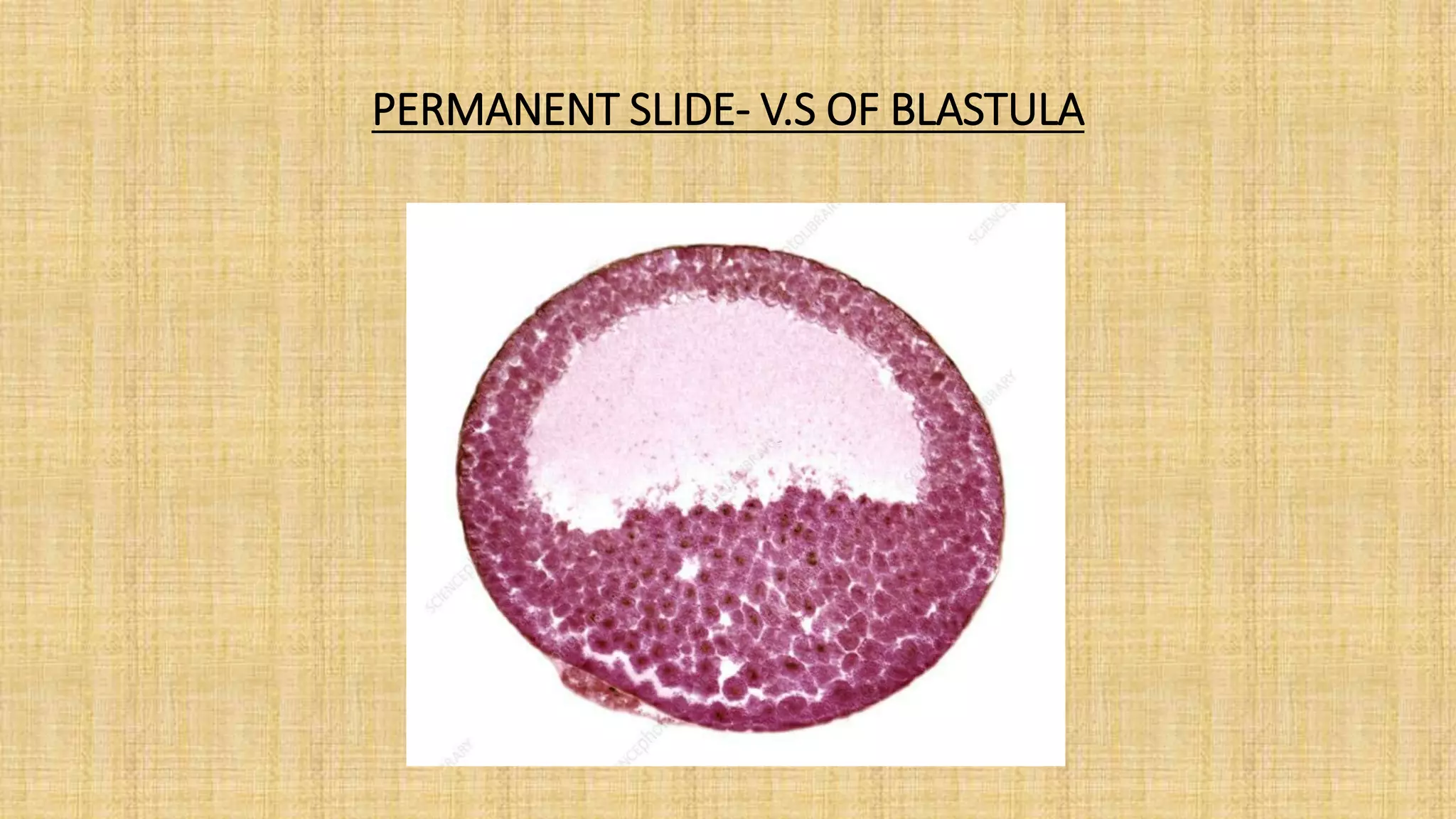
This document provides details for a biology practical exam question on spotting. It includes descriptions of 10 spots (A-I for botany, G-J for zoology) that students must identify and comment on. Spot A involves identifying two plants (maize and salvia) and commenting on their floral adaptations for pollination. Spot B involves identifying and commenting on stages of meiosis. Spot C identifies and comments on techniques like emasculation, bagging, and tagging. Spot D identifies plants and comments on their xeric or aquatic adaptations. Spot E identifies plant pigments separated via paper chromatography. Spot F identifies and describes the vascular system of an anatropous ovule. Spots G-J identify