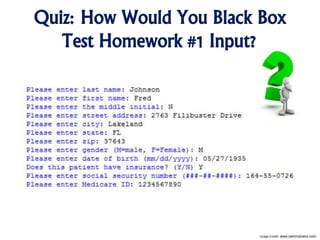
The document outlines the importance of testing in software development, emphasizing different perspectives of users, testers, and developers. It explains black-box, gray-box, and white-box testing methodologies, along with the need for automated testing and regression checks to maintain code quality. Additionally, it highlights the importance of differentiating test types, such as unit, system, and user testing, to ensure effective software functionality.