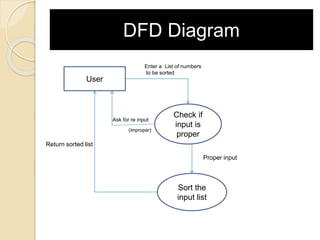
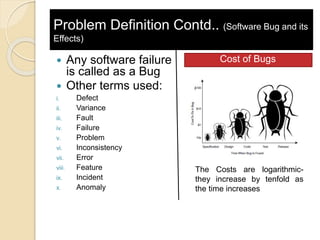
The document discusses various software testing techniques. It describes the need for software testing due to bugs and errors. It covers black-box and white-box testing methods. Black-box testing evaluates software without viewing code, while white-box testing involves examining source code. Static testing analyzes software without running it, and dynamic testing executes software. The document provides examples of specification testing, state testing, code coverage, and formal code reviews. It concludes that rigorous testing is important to discover and fix defects, improving software quality and reputation.




![Literature Survey
Goal of software tester[1]
“The goal if the software tester is to find bugs,
find them early, and make sure they are fixed as
soon as possible”
Software Testing Fundamentals[1]
Testing the Specification.
Testing the Software with Blinders On
Examining the Code.
Testing the Software with X-Ray Glasses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-6-320.jpg)
![BLACK-BOX TESTING[5]
Here tester knows only
what the software is
supposed to do(he
can’t look in the box to
see how it operates
No access to software
code
He a input, he
gets a certain output
but doesn’t how or
why it happens, just
that it does.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-7-320.jpg)
![WHITE-BOX TESTING[5]
Also called as clear
box testing
Tester can see
inside the box ie.,
has access to
program’s code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-8-320.jpg)
![STATIC & DYNAMIC TESTING[1]
• Refers testing to
something which is not
running-examining and
reviewing it.
STATIC
TESTING:-
• testing the software by
running it(normally what
we think of as testing).
DYNAMIC
TESTING:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-9-320.jpg)
![TESTING THE
SPECIFICATION[1]
Also called Static Black-Box Testing.
How is it Done??
Stati
c
BlackBo
x
• Pretend to be the Customer.
• Research Existing Standards & Guidelines.
• Review & Test Similar Software.
High level
Review
• Specification Attribute Checklist.
• Specification Terminology Checklist
Low level
Review
Attribute CheckList
1. Complete 2. Accurate 3. Precise, Unambigous, Clear
4. Consistent 5. Relevant 6. Feasible
Terminology CheckList
1. Always, Every, All, None, Never
2. Certainly, Therefore, Clearly
3. Some, Sometimes, Often, Usually,Etc., And So Forth, And So On,
Such As
4. 5.If…Then…(missing Else)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-10-320.jpg)
![TESTING THE SOFTWARE
WITH BLINDERS ON[1]
Also called as Dynamic Black-Box
Testing.
How is it Done??
Dynami
c
BlackBo
x
Data Testing:
1) Boundary Conditions:
2) Sub-Boundary Conditions:- (refers to internal boundaries)
3) Default, Empty, Blank, Zero or None.
4) Invalid, Incorrect, Wrong, Garbage.
State Testing:
Testing s/w logic flow(by creating state transition map).
int data[]=new int[5];
for(int i=1;i<5;i++)
data[i]=-1;
data[1]=-1
data[2]=-1
data[3]=-1 what about
data[0]???
data[4]=-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-11-320.jpg)
![EXAMINING THE CODE[1]
Also called Static White Box testing
How is it Done??
What is to be done??
1. Formal
Reviews.
2. Peer Reviews.
3. WalkThroughs
4. Inspections.Coding Standards and Guidelines
Generic Code Review Checklist
Stati
c
Whitebox](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-12-320.jpg)
![TESTING THE SOFTWARE
WITH XRAY GLASSES[1]
Also called as Dynamic White-Box
Testing
How is it Done??
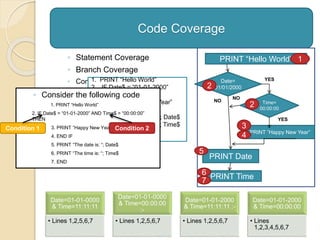
Code Coverage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaretesting-141117015910-conversion-gate02/85/Software-testing-13-320.jpg)