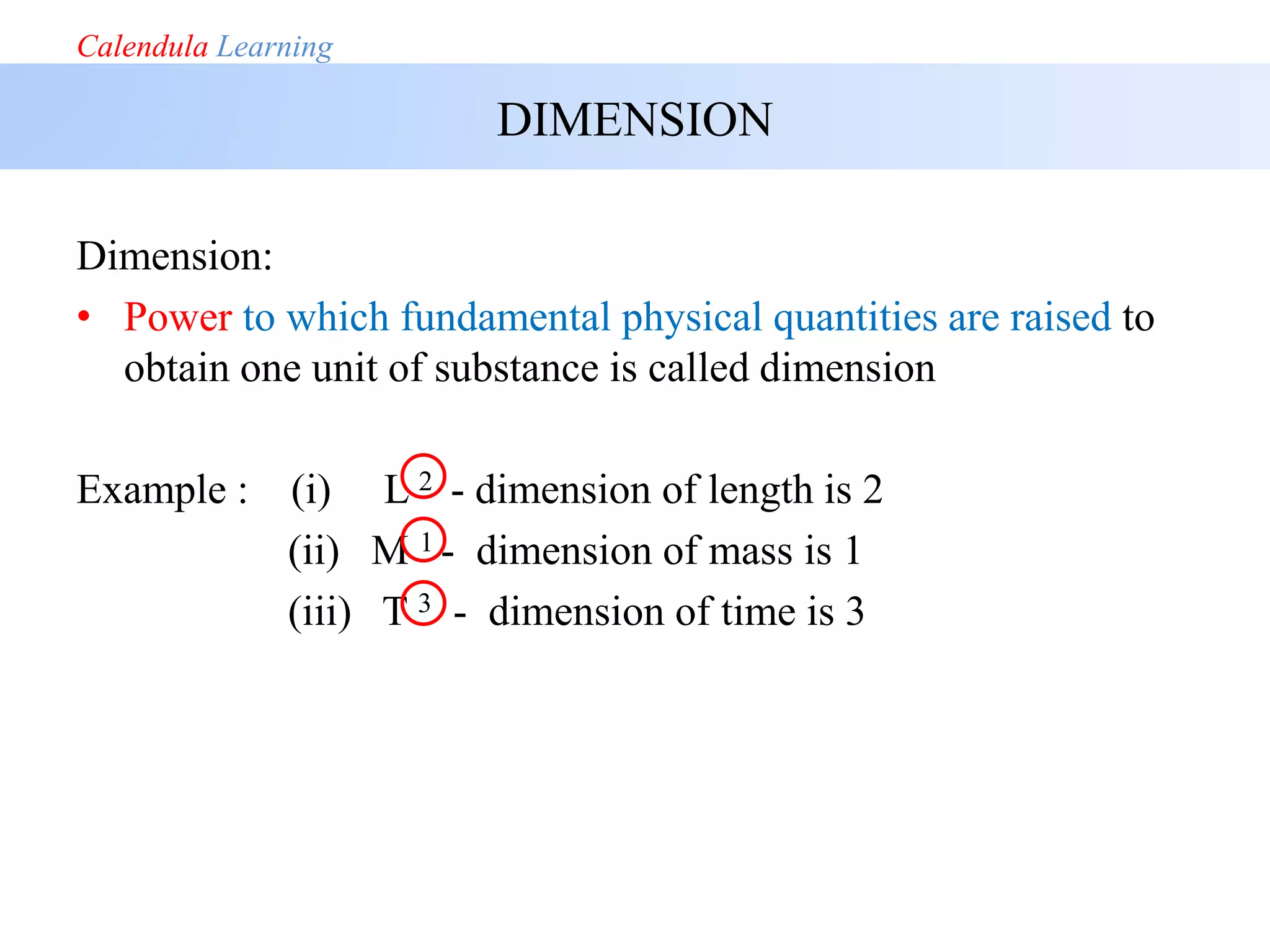
This document discusses physics concepts including physical quantities, fundamental and derived quantities, units of measurement, and dimensions. It defines physics as the study of nature and its laws through observation. Physical quantities that can be measured are classified as either fundamental quantities that are independent of others, or derived quantities that depend on fundamental quantities. The seven fundamental quantities are listed as mass, length, time, temperature, electric current, amount of substance, and luminous intensity. Common unit systems like SI, CGS, MKS, and FPS are also outlined.