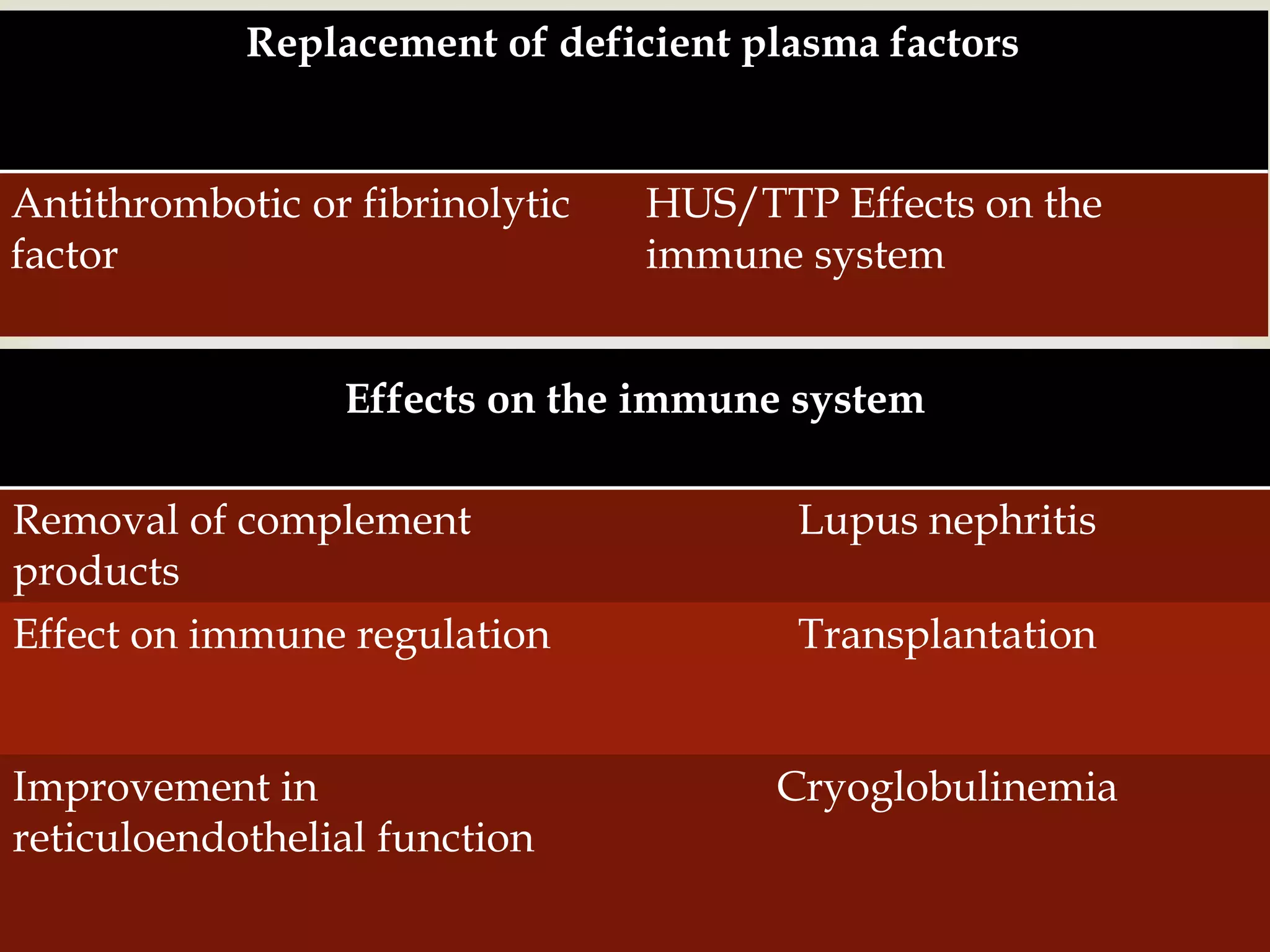
Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) is an extracorporeal treatment that removes plasma and pathogenic substances like antibodies, immune complexes, or large molecules from the plasma. During TPE, whole blood is separated into components by centrifugation and the plasma is removed and discarded while cellular elements are returned to the patient mixed with a replacement fluid. Early studies found that TPE plus standard therapy for multiple myeloma patients with acute kidney injury improved renal recovery rates compared to standard therapy alone, though larger subsequent studies found no difference in outcomes. TPE is effective at removing various pathogenic factors from circulation that cause diseases like Guillain-Barré syndrome, antibody-mediated transplant rejection, systemic lupus erythematosus, and
















![
Kaplan's equation
[0.065 x weight (kg)] x (1- Hct)
A course of plasma exchange consist of 3-5 exchanges of 1-1.5
volumes each, with an interval of 1-2 days between procedures.
Continue..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therapeuticplasmaexchange-180721050218/75/Therapeutic-plasma-exchange-17-2048.jpg)