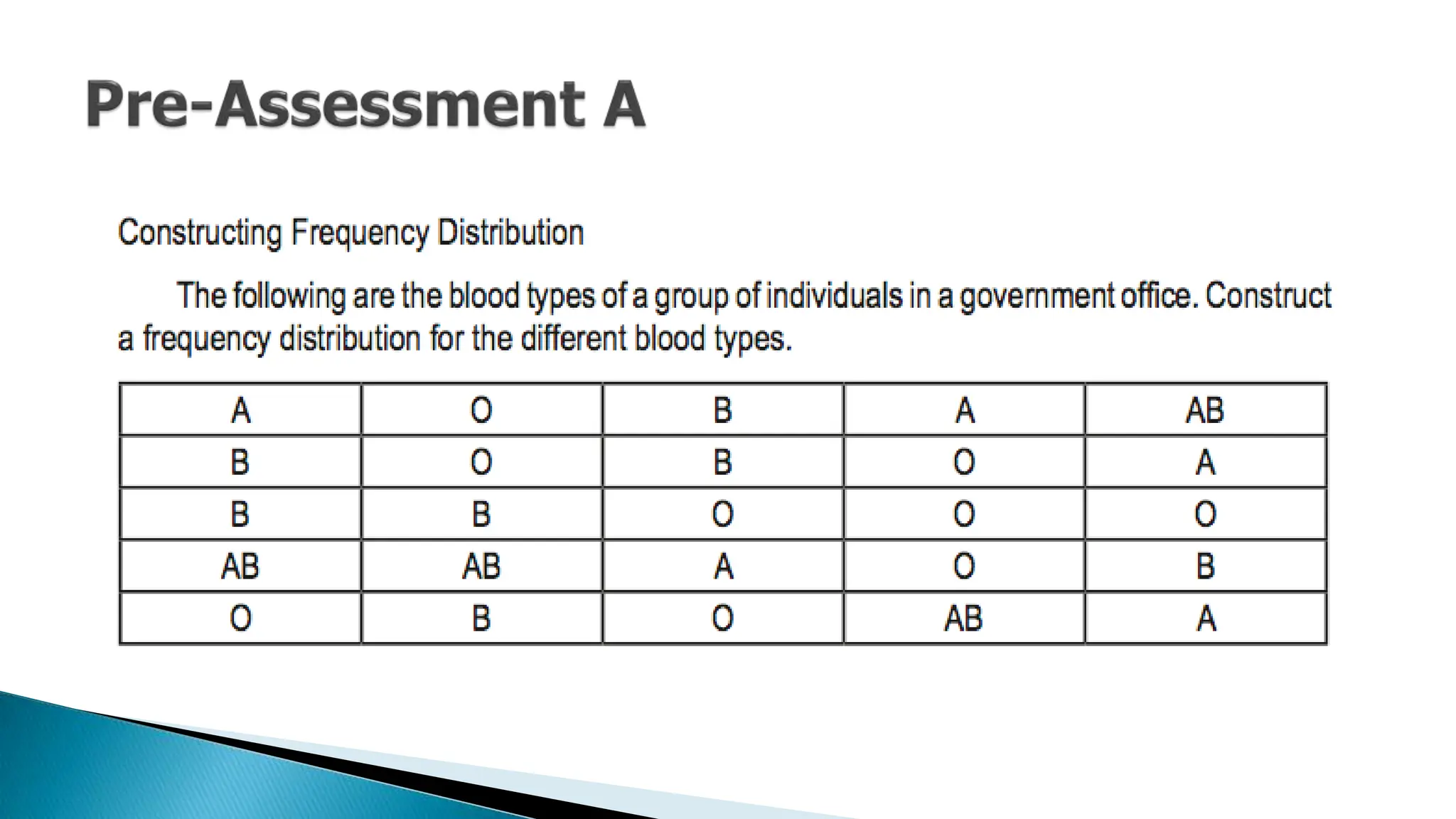
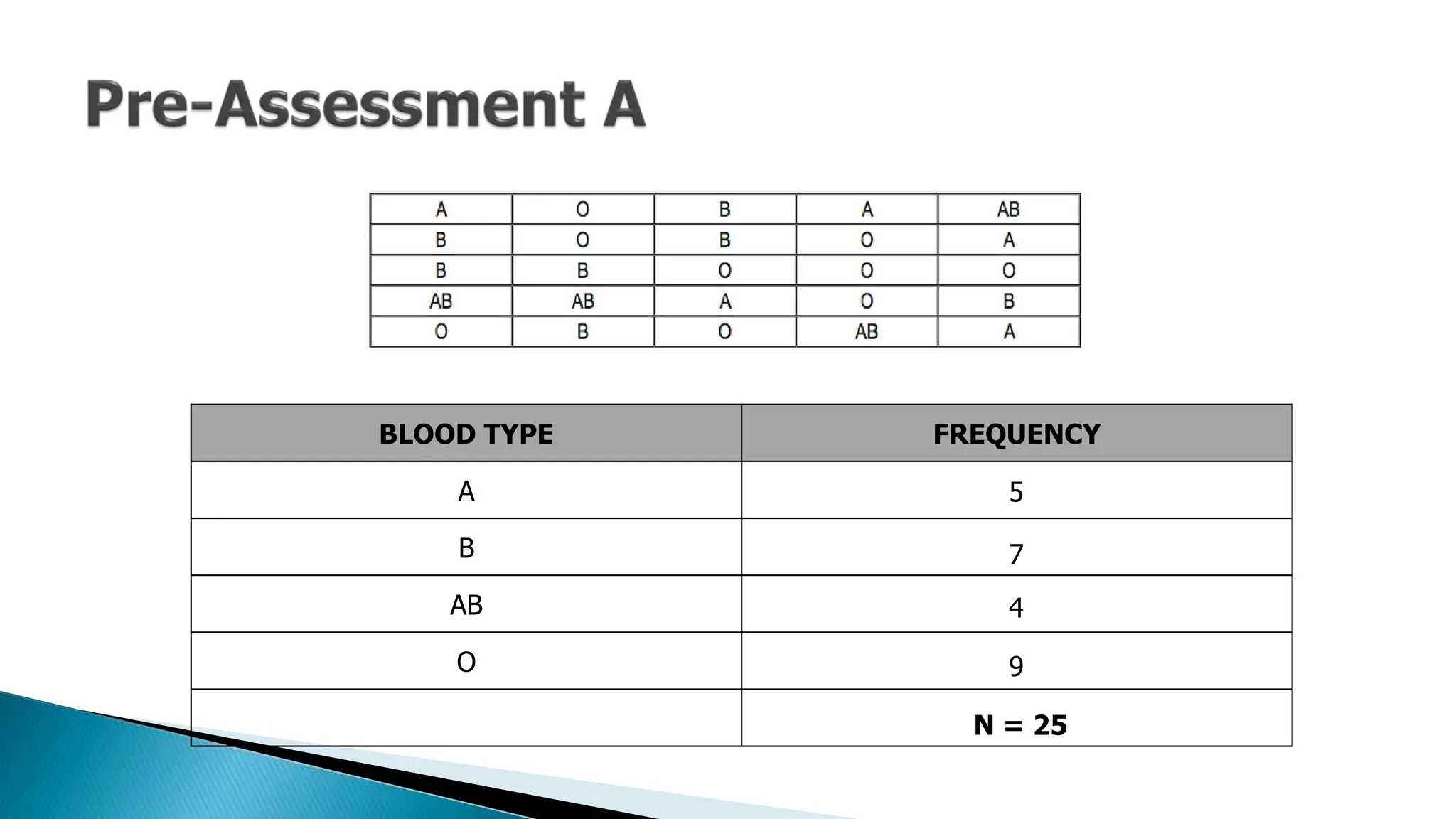
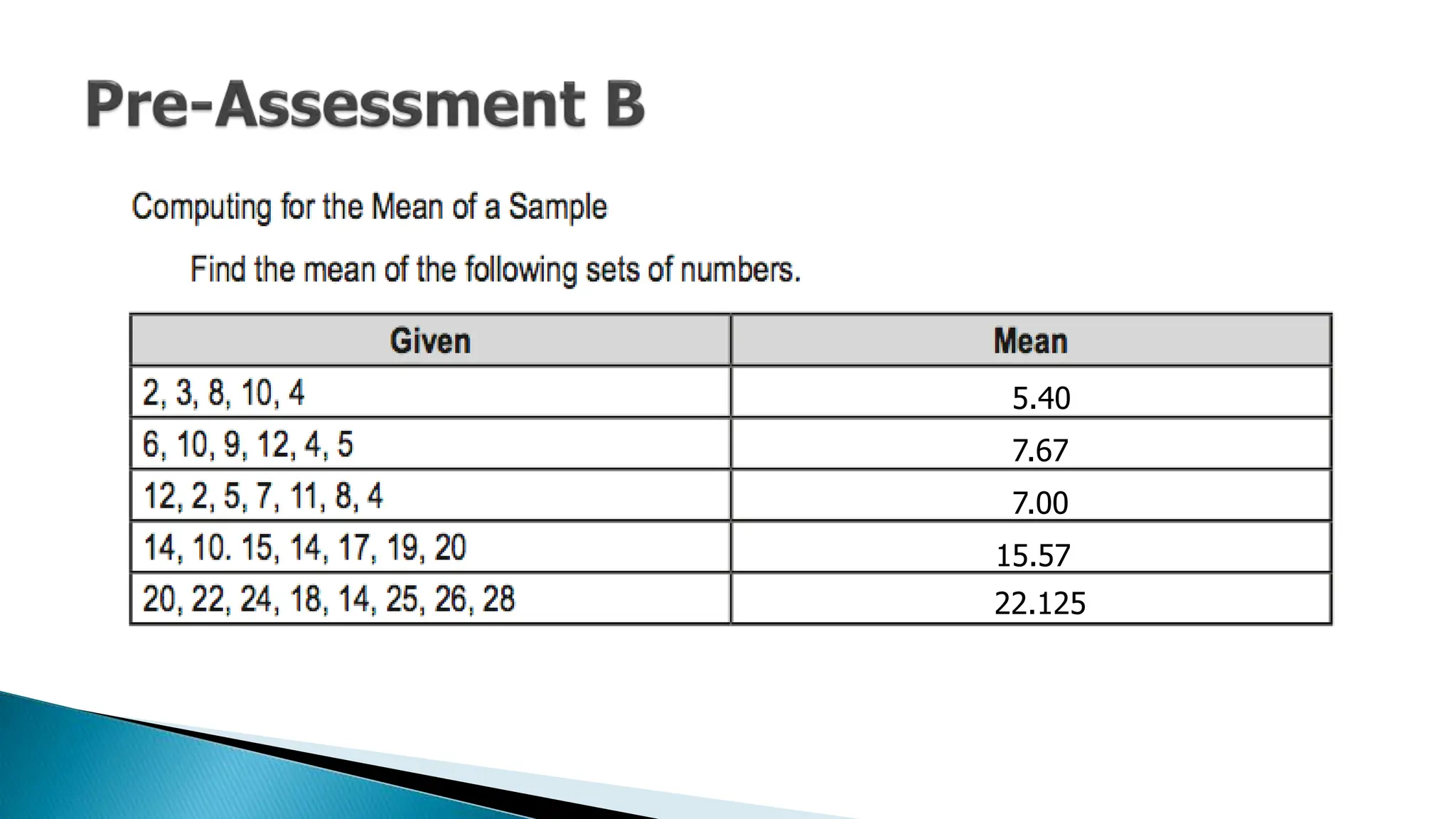
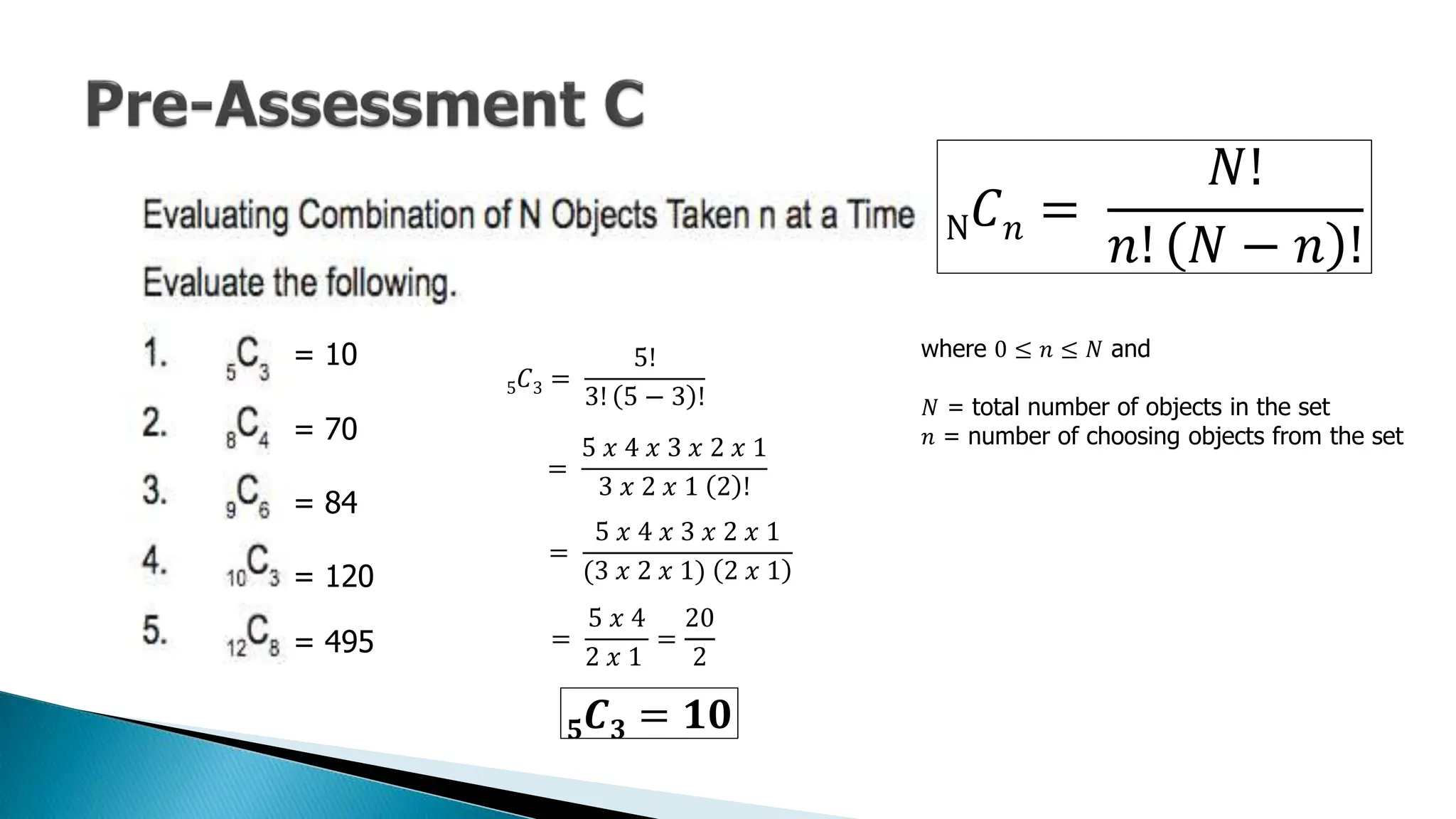
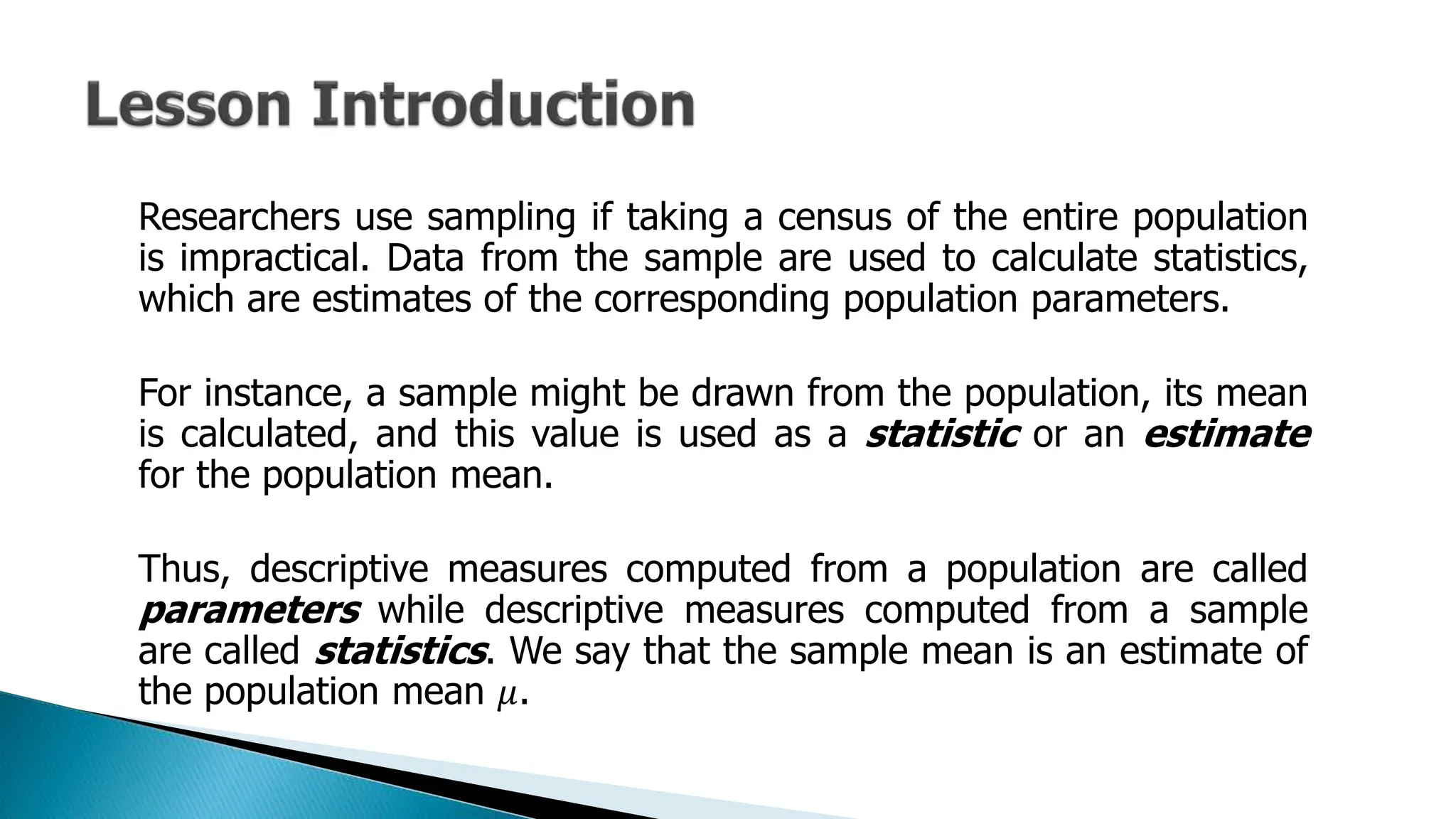
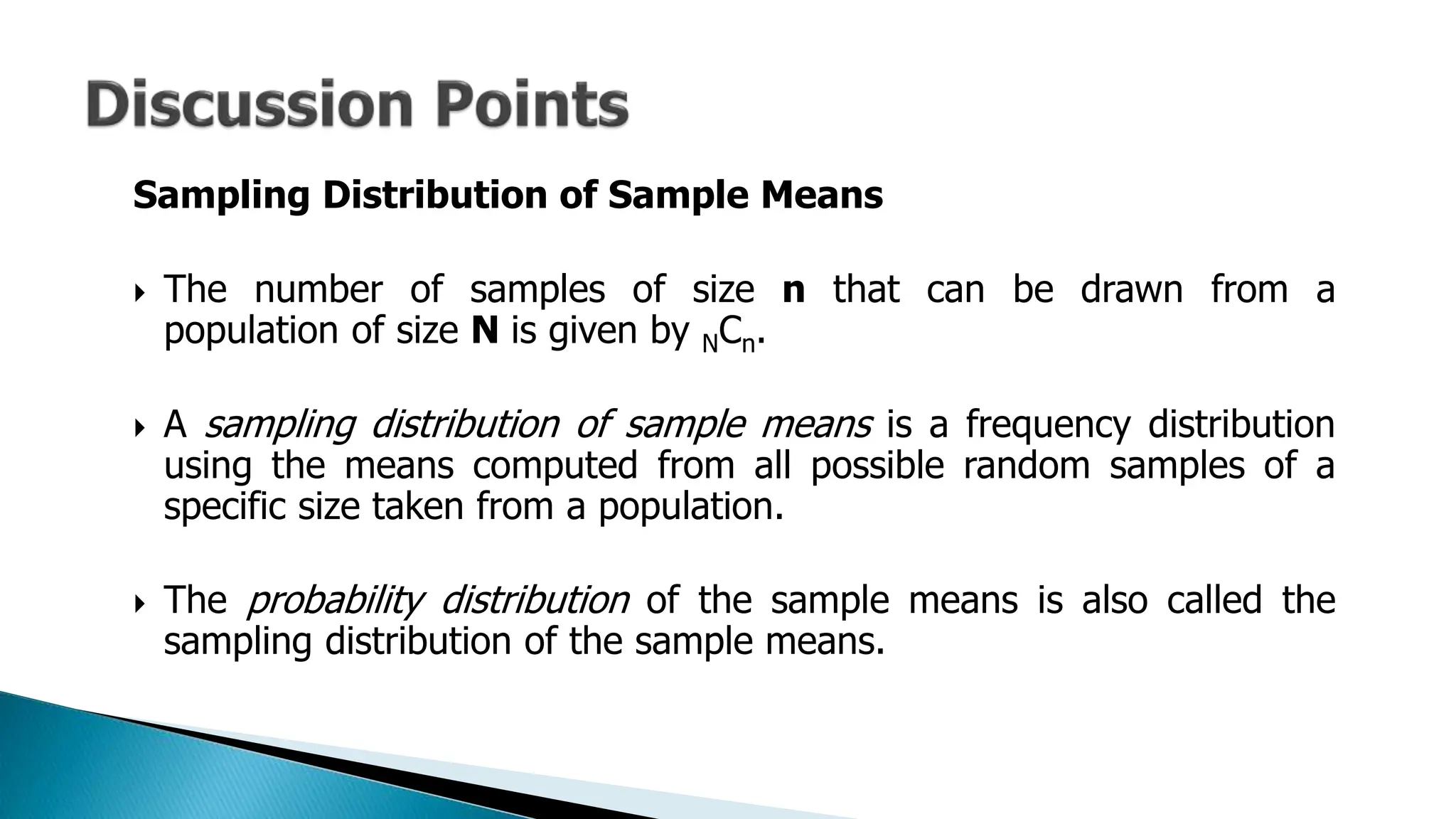
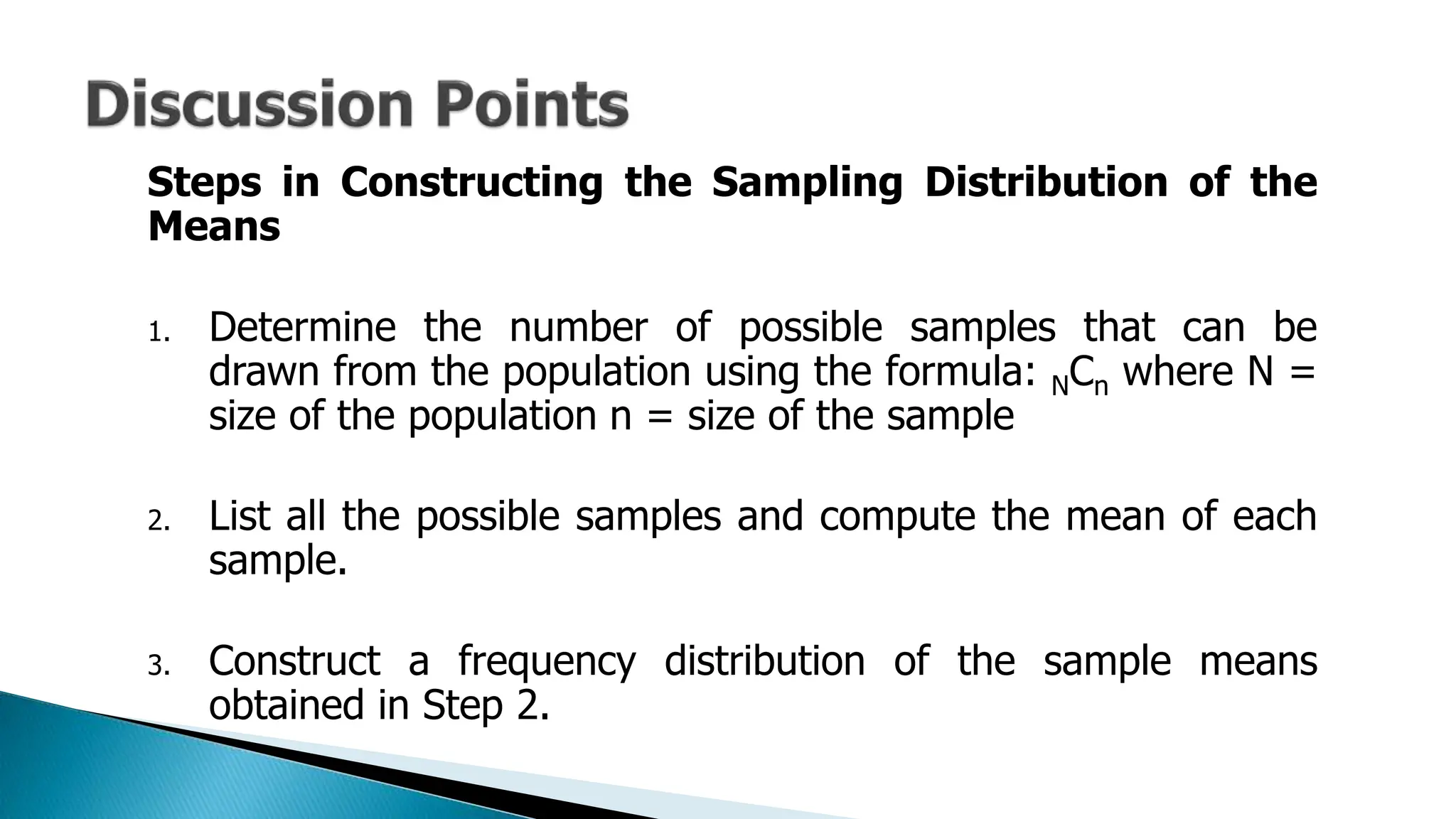
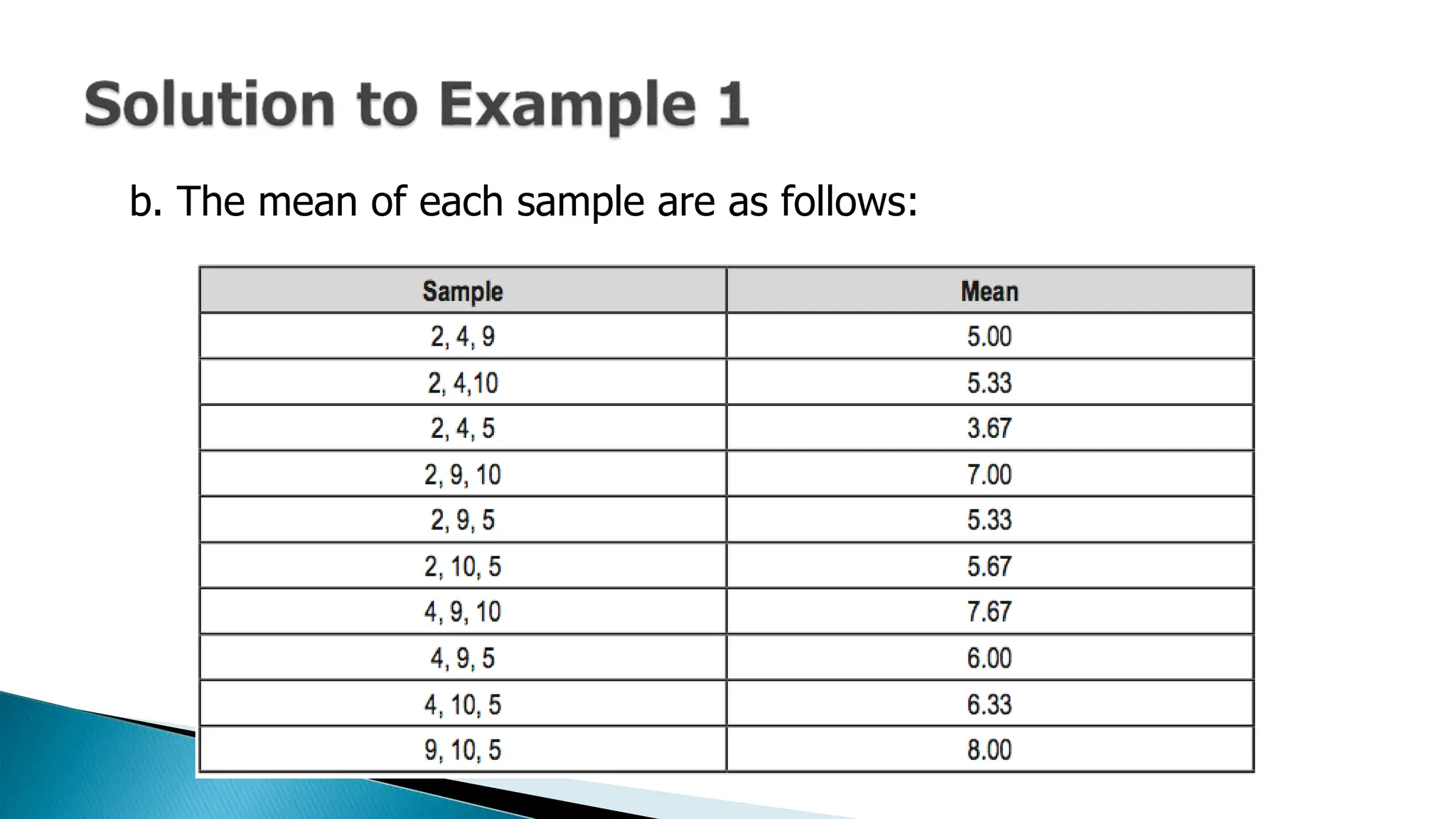
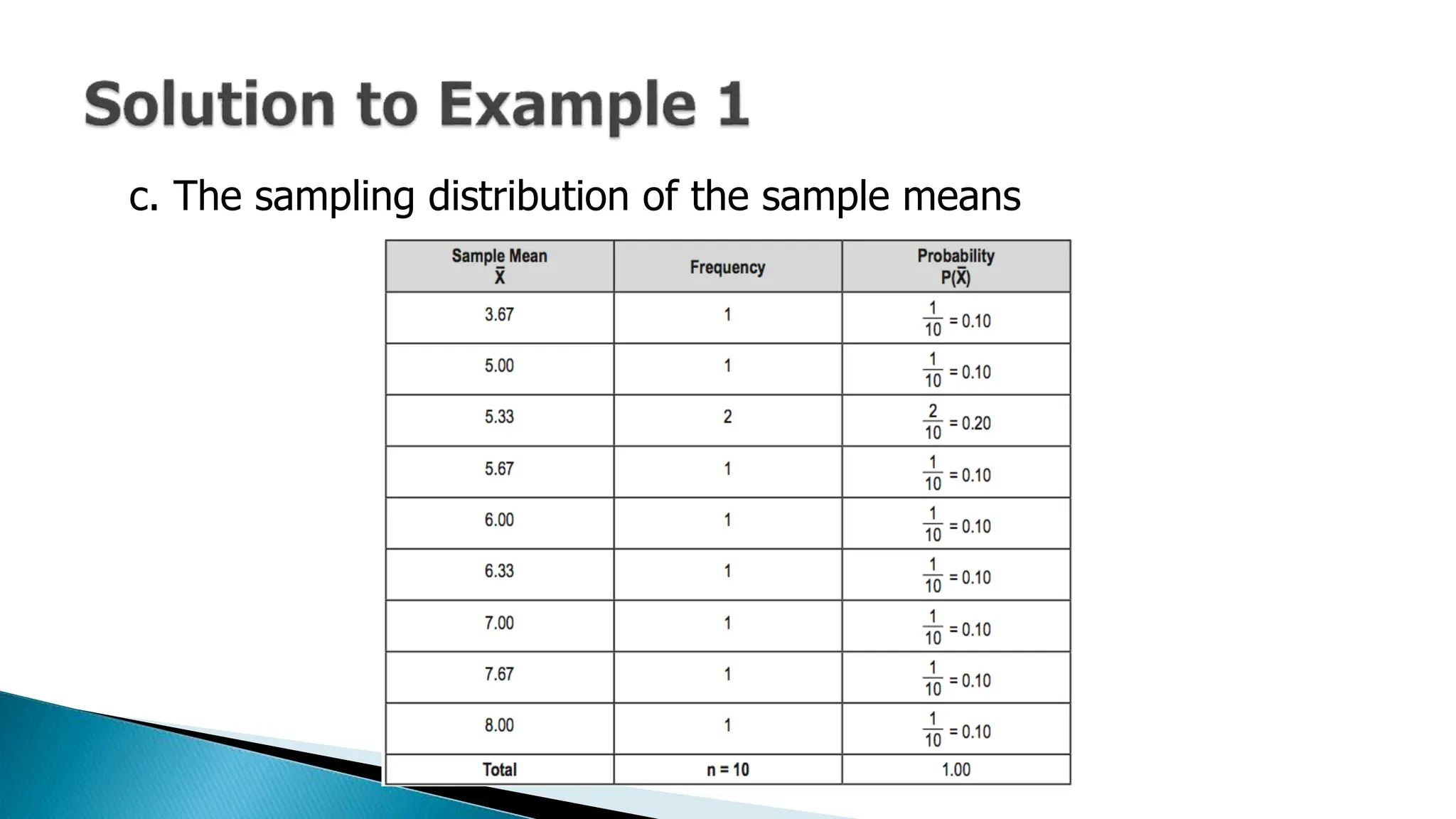
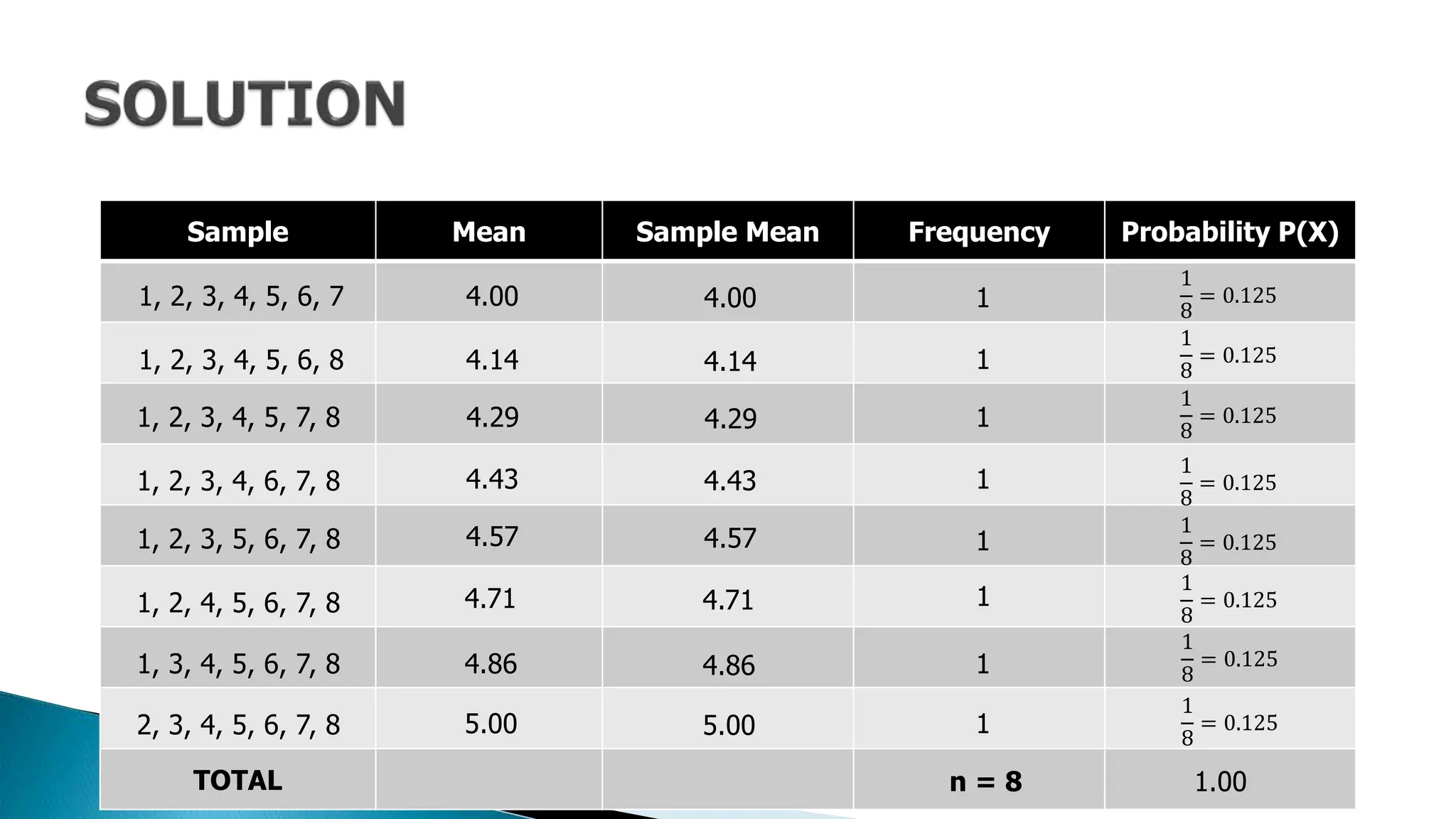
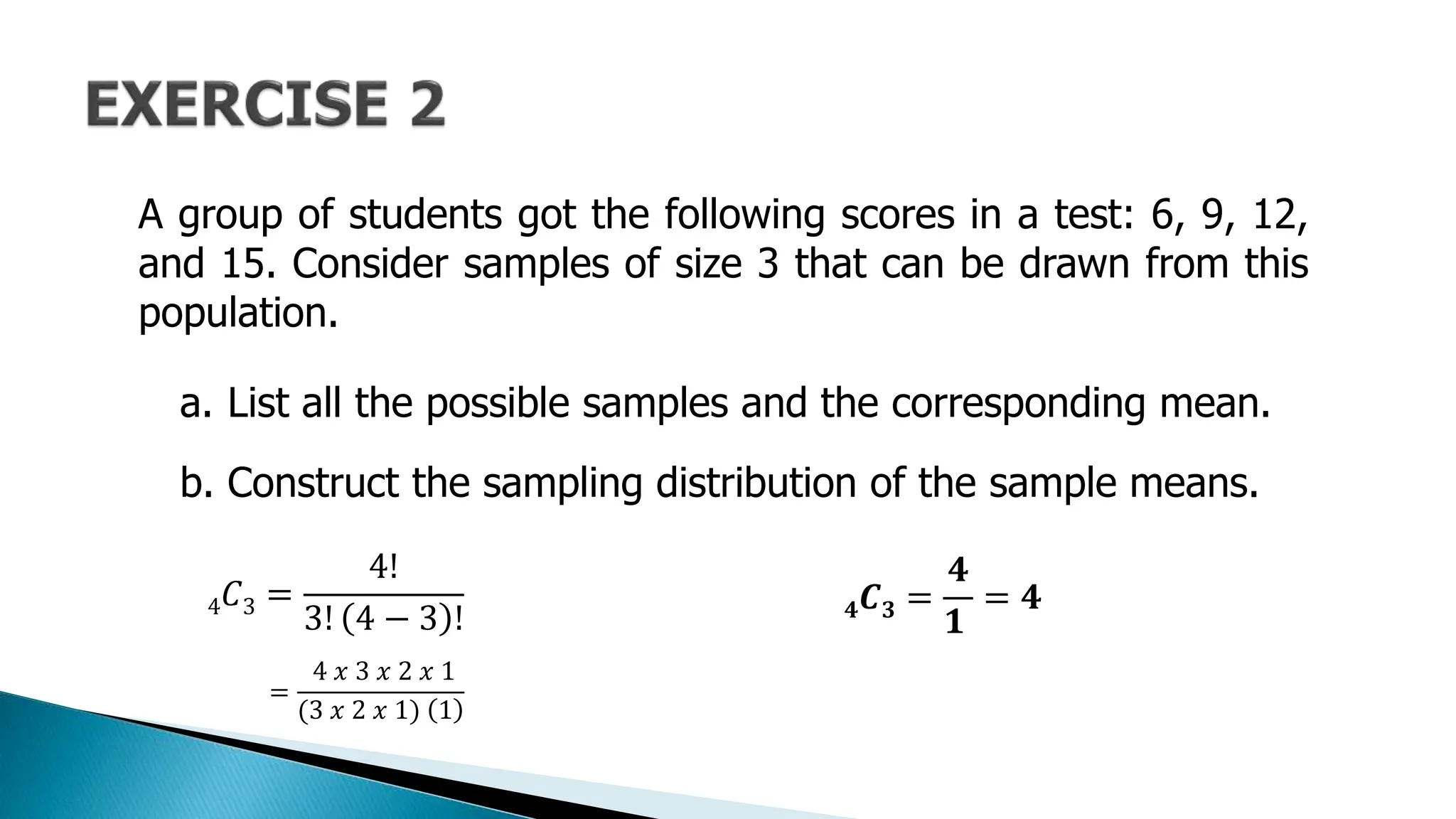
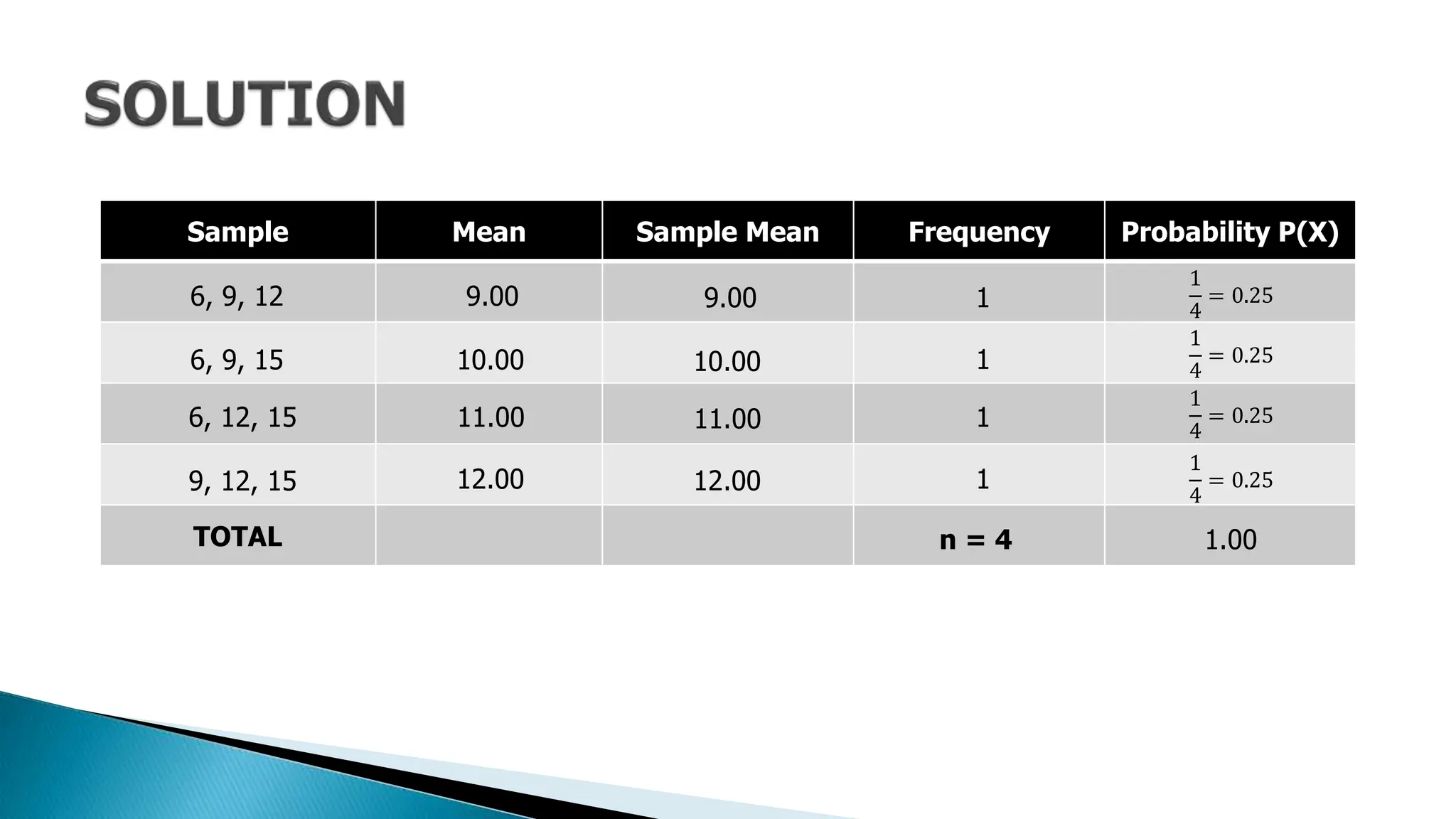
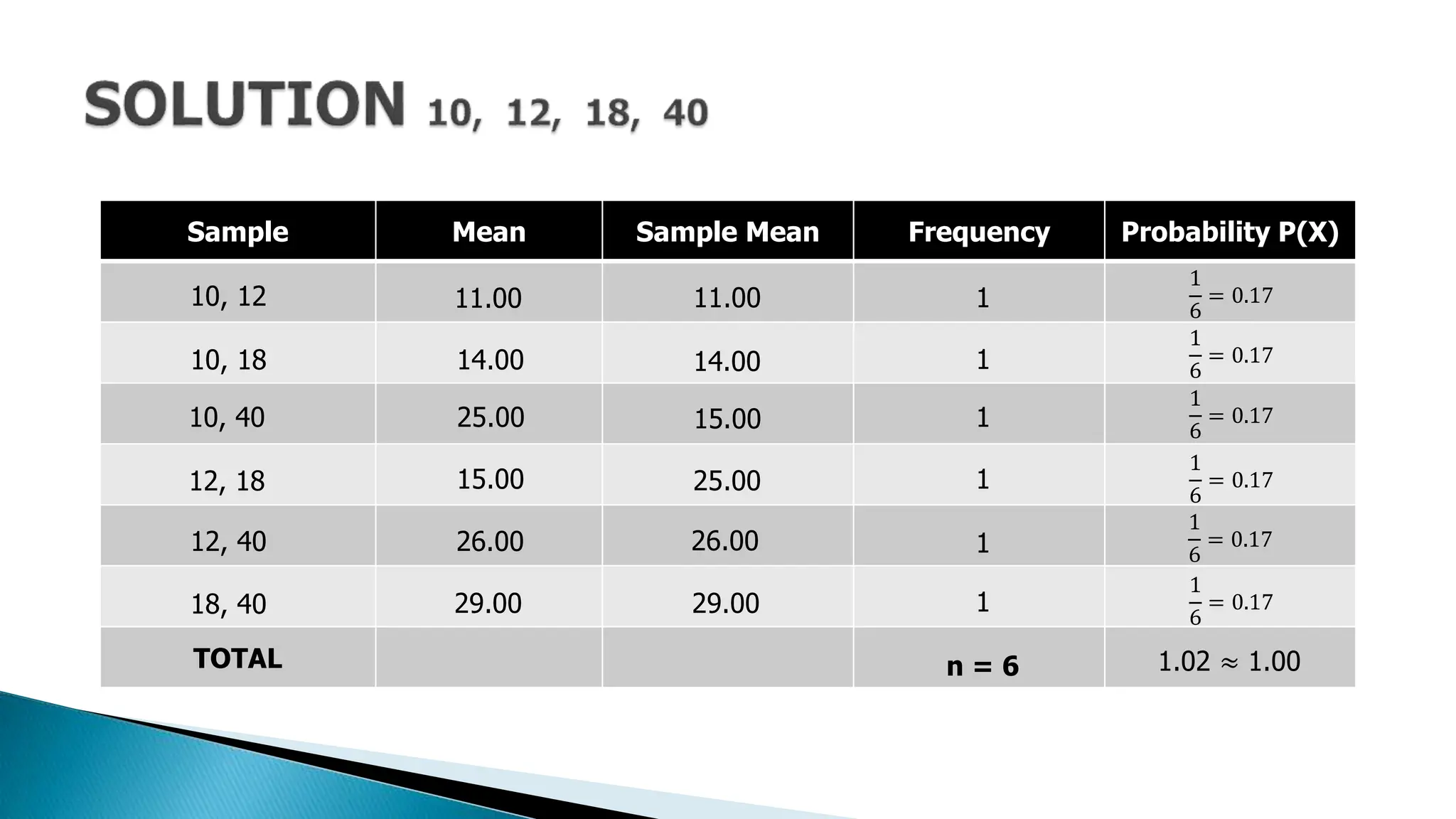
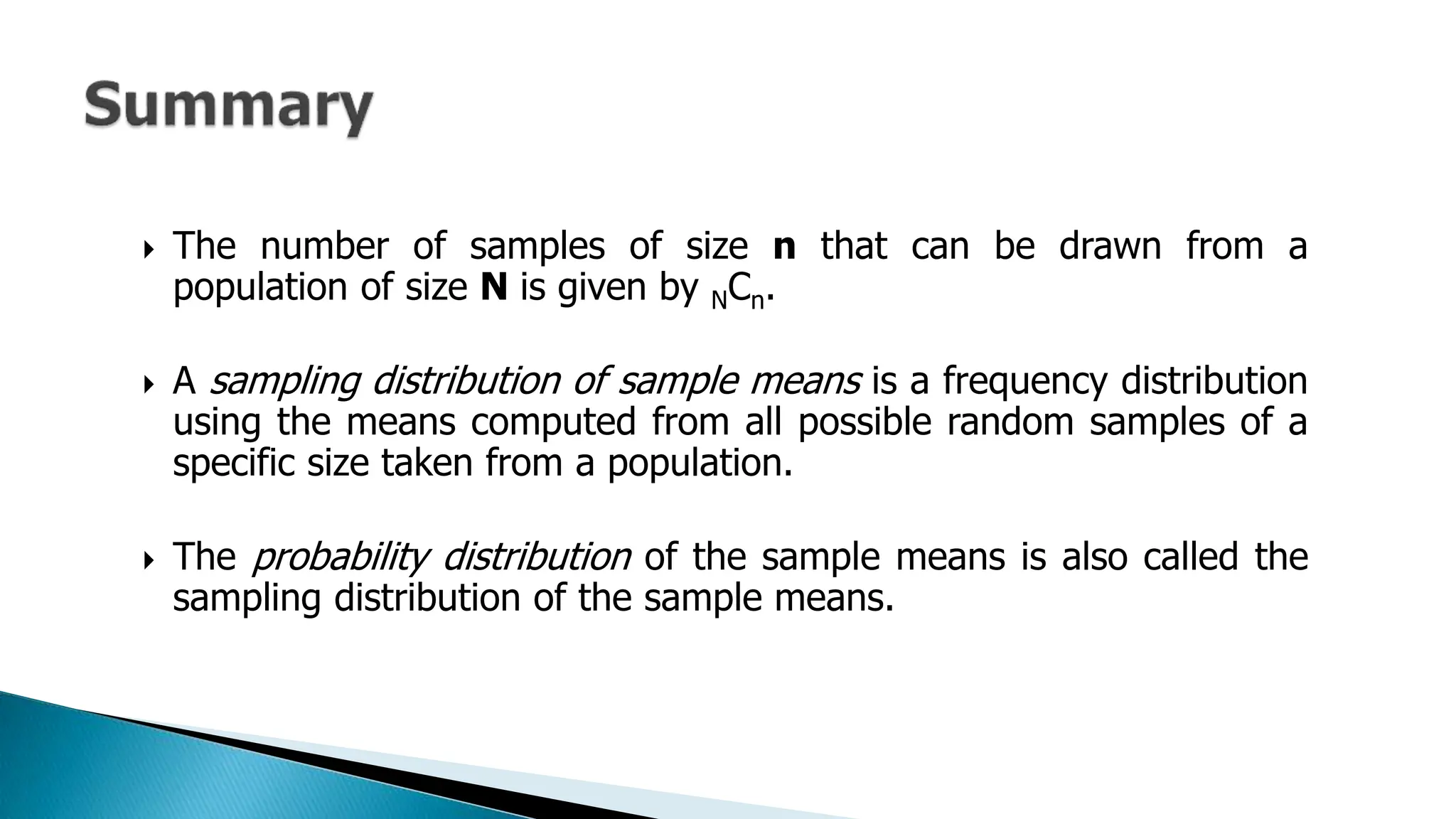
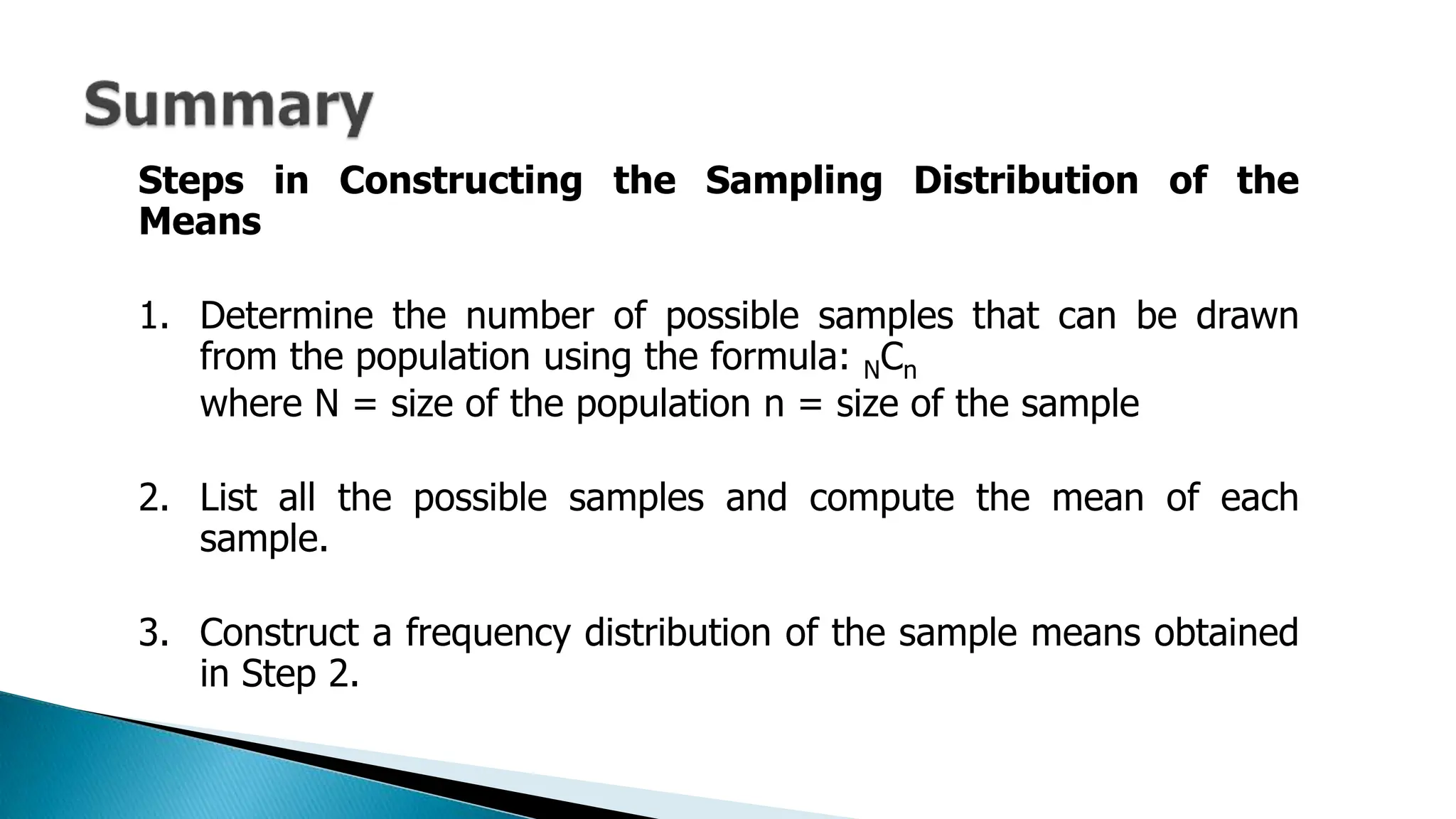
The document outlines key concepts in statistics and probability for Grade 11, focusing on random sampling, the distinction between parameters and statistics, and constructing sampling distributions of sample means. It includes formulas for calculating combinations and provides detailed examples and steps for deriving sampling distributions from various populations. Additionally, it describes the significance of sample means as estimates of population parameters.