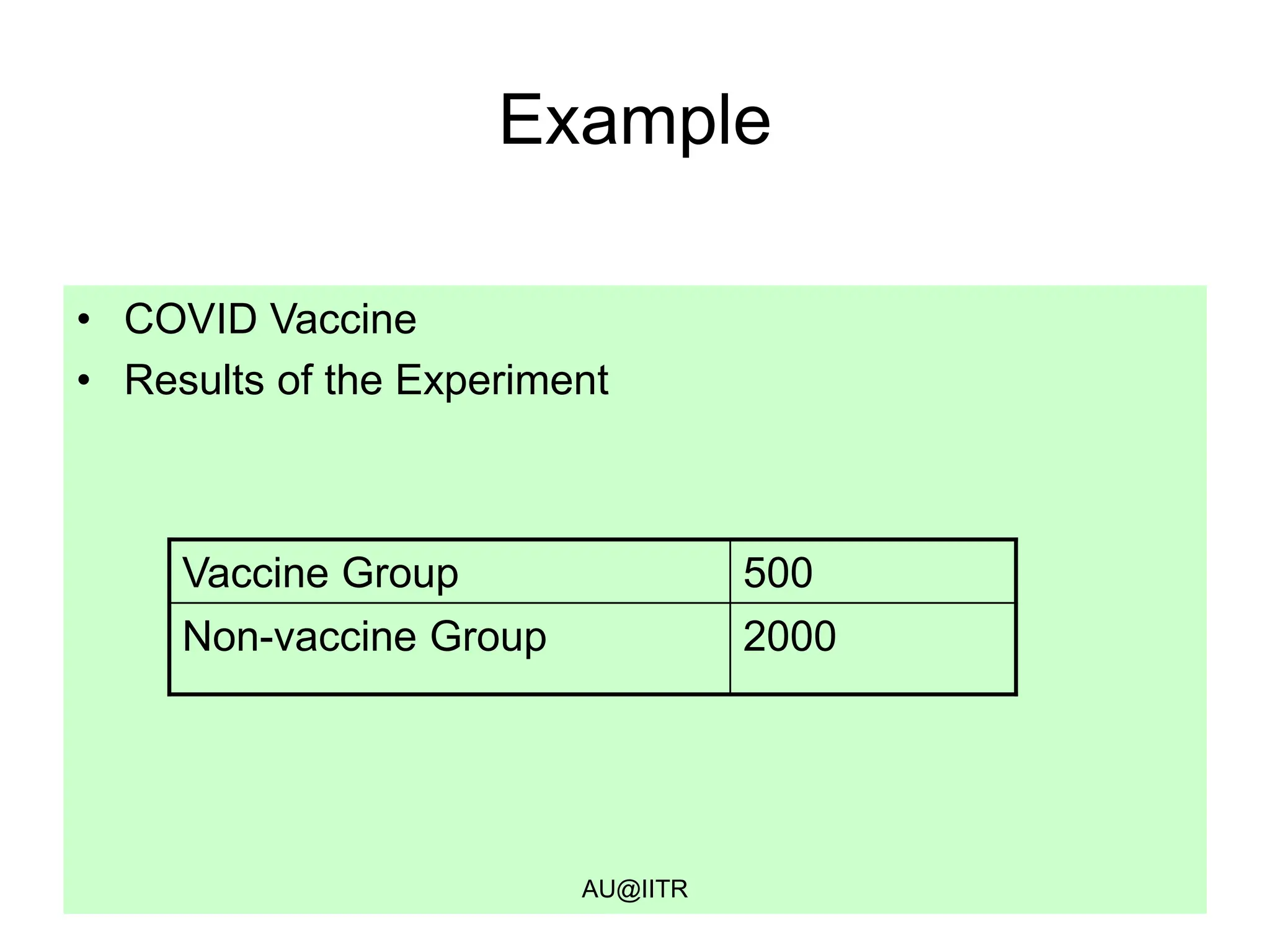
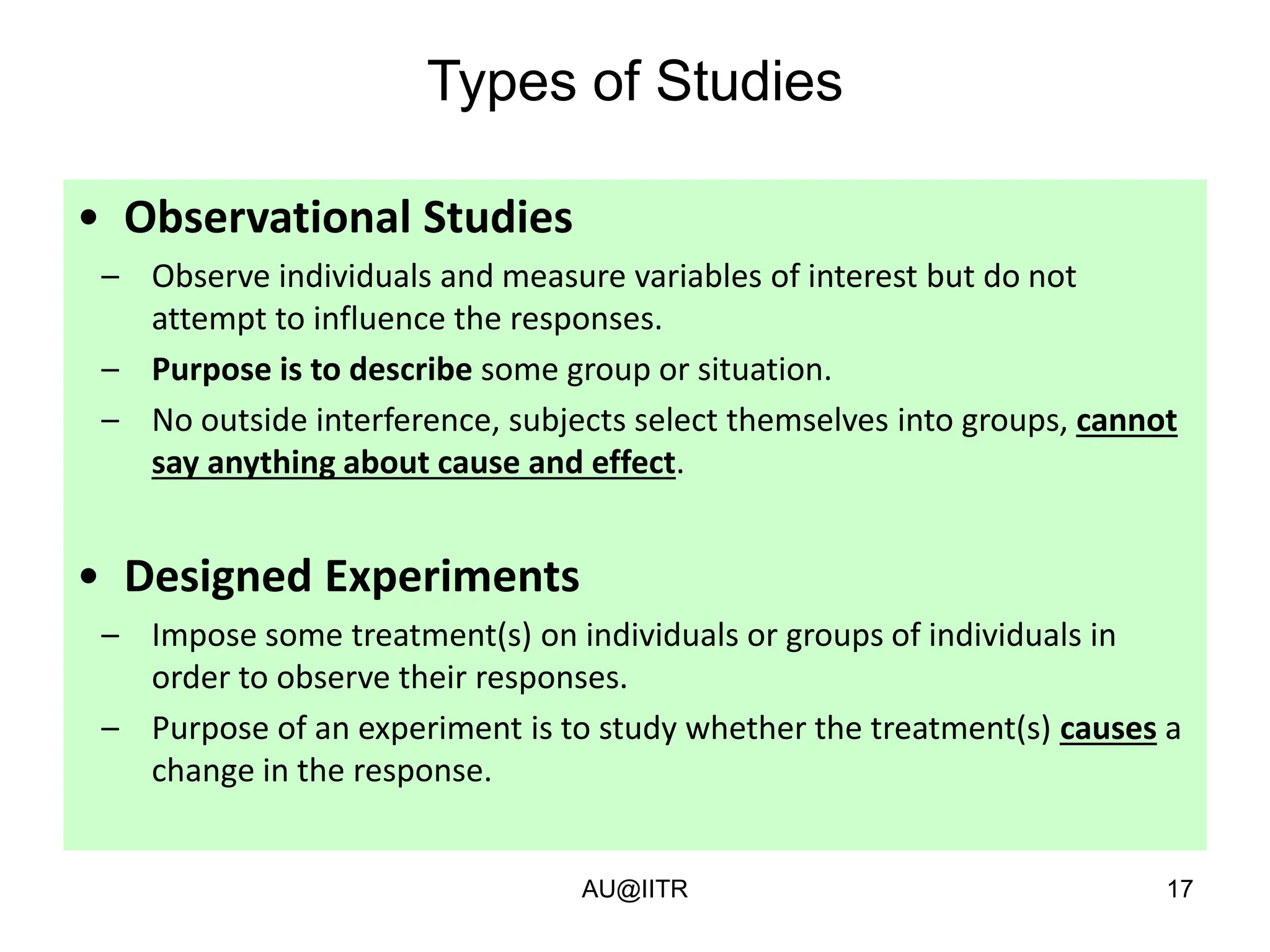
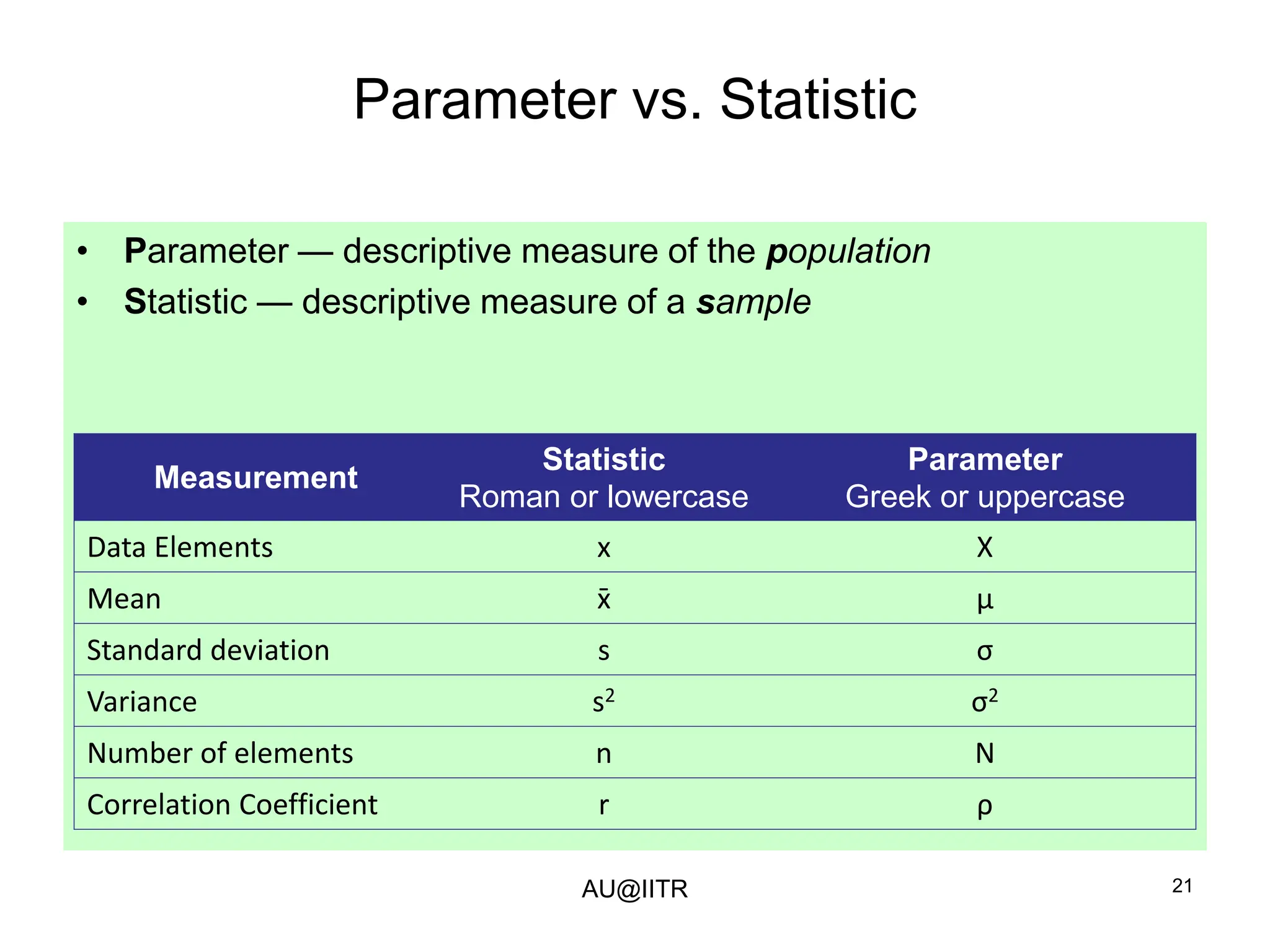
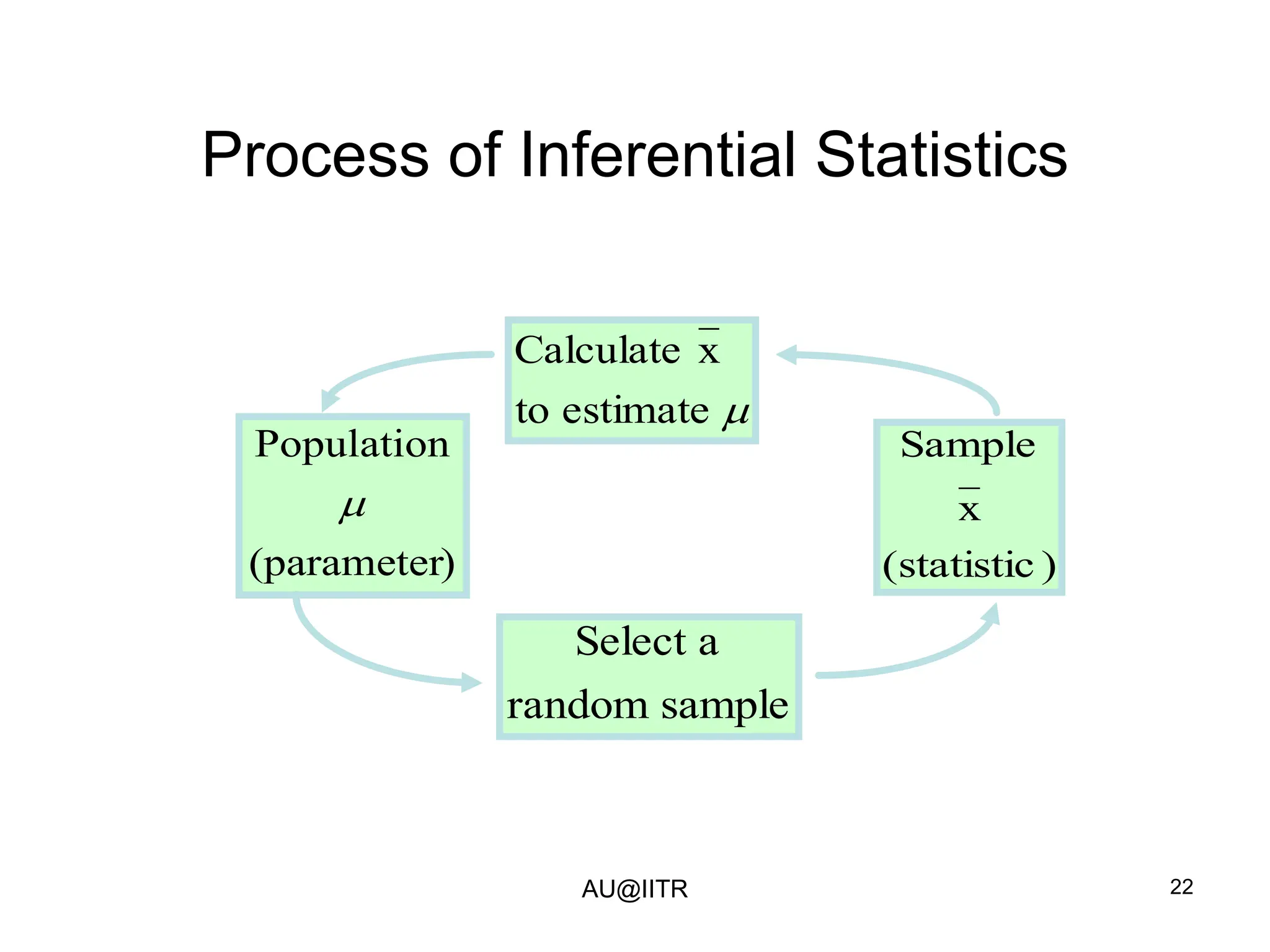
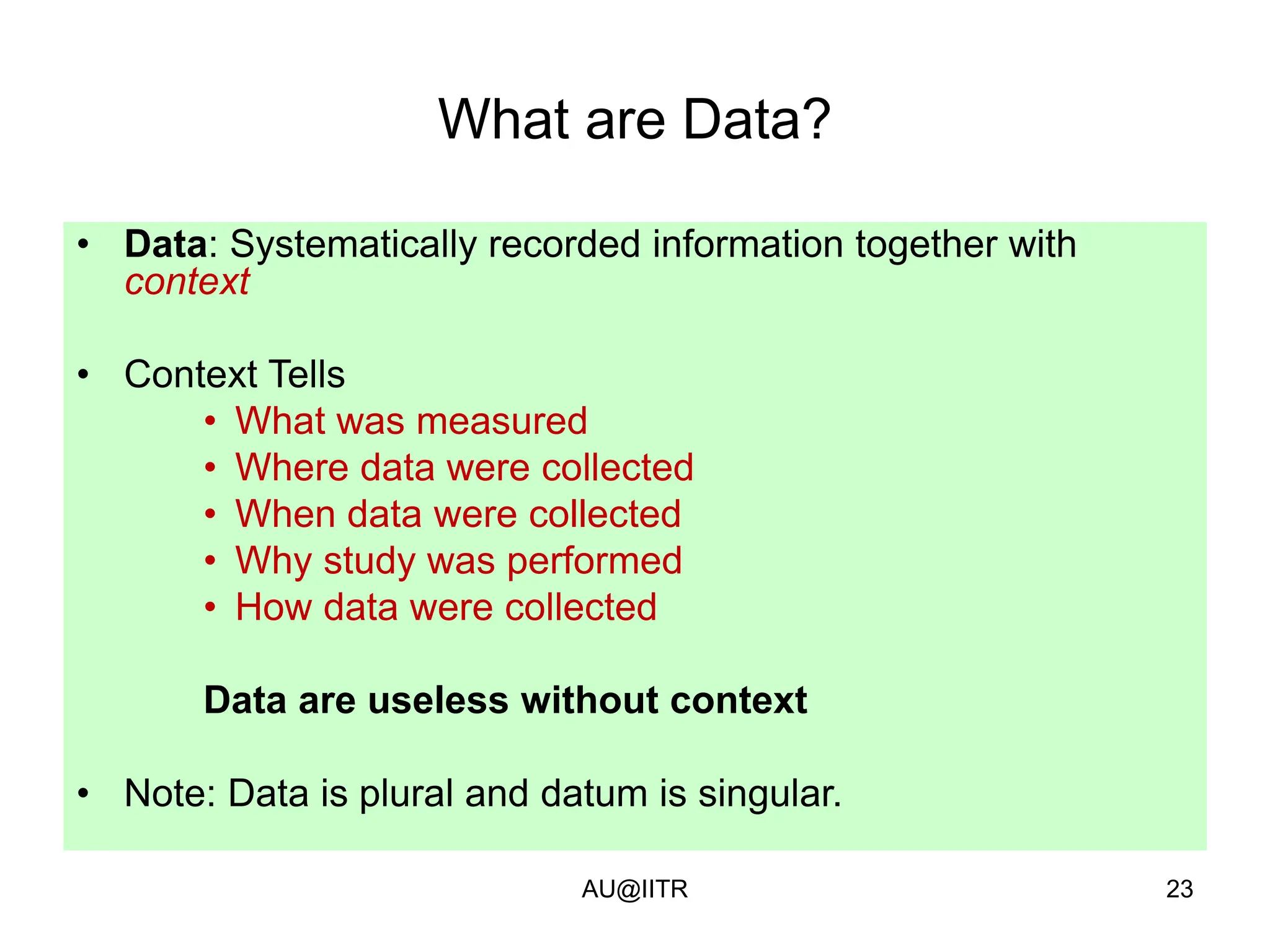
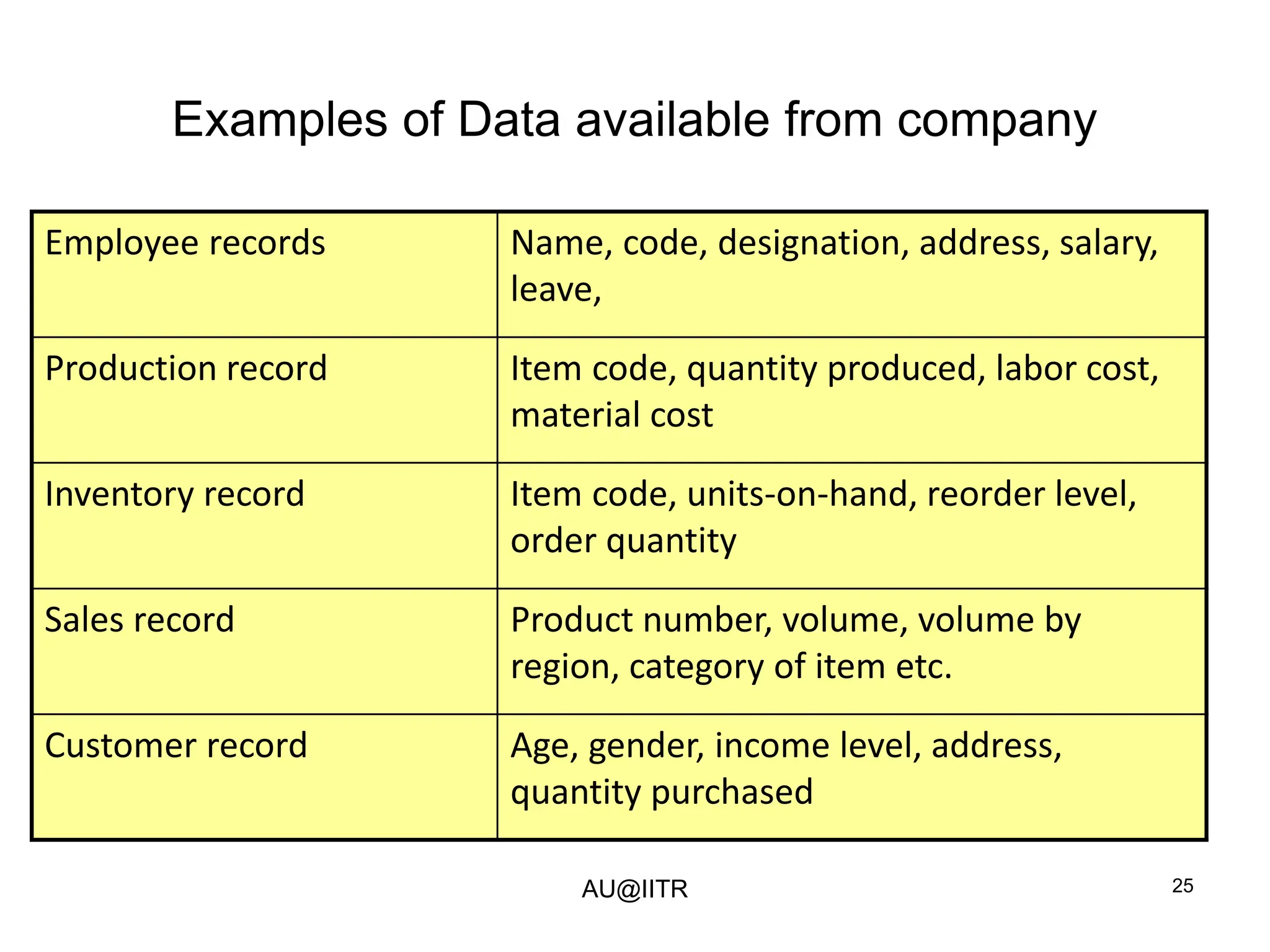
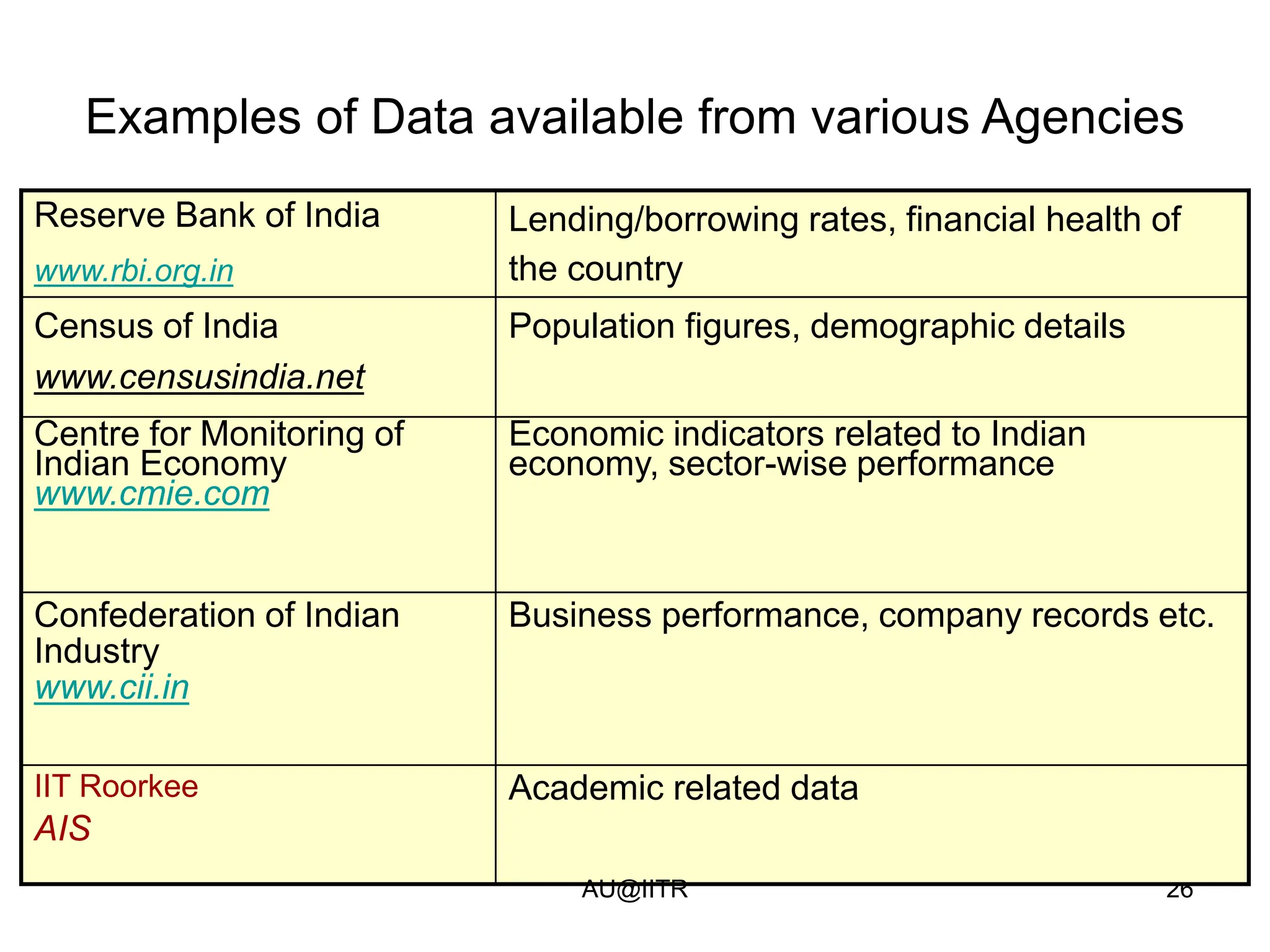
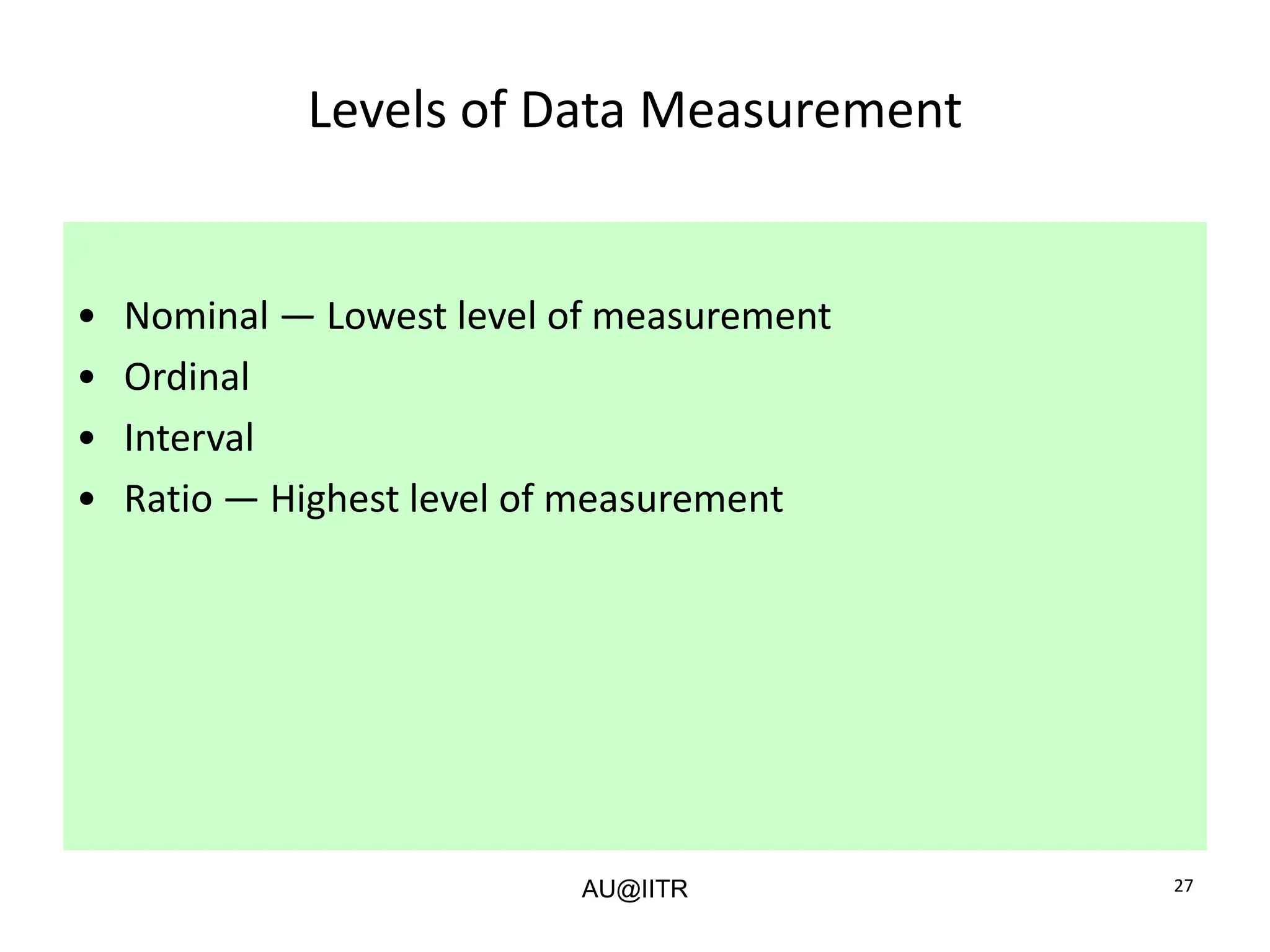
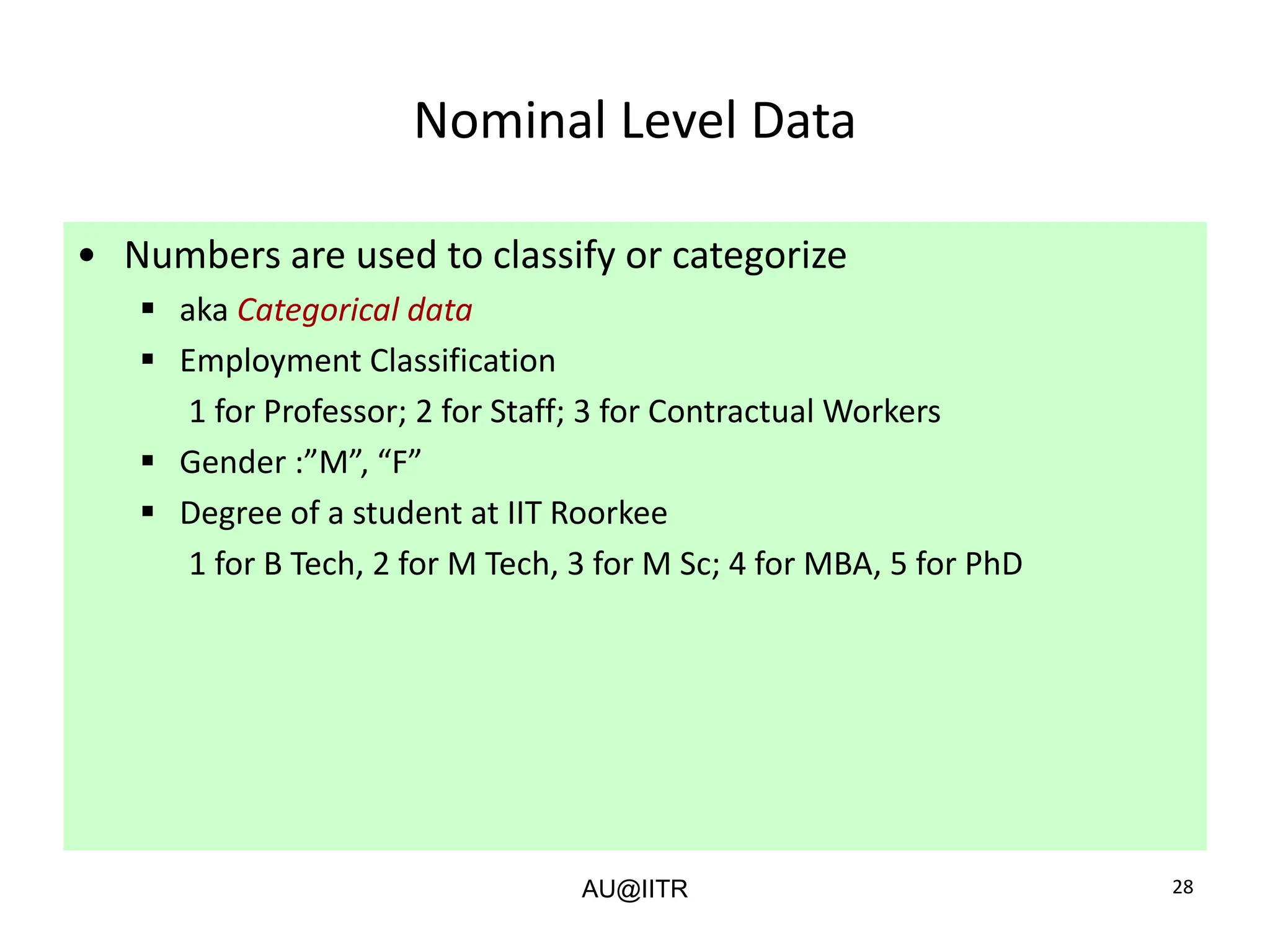
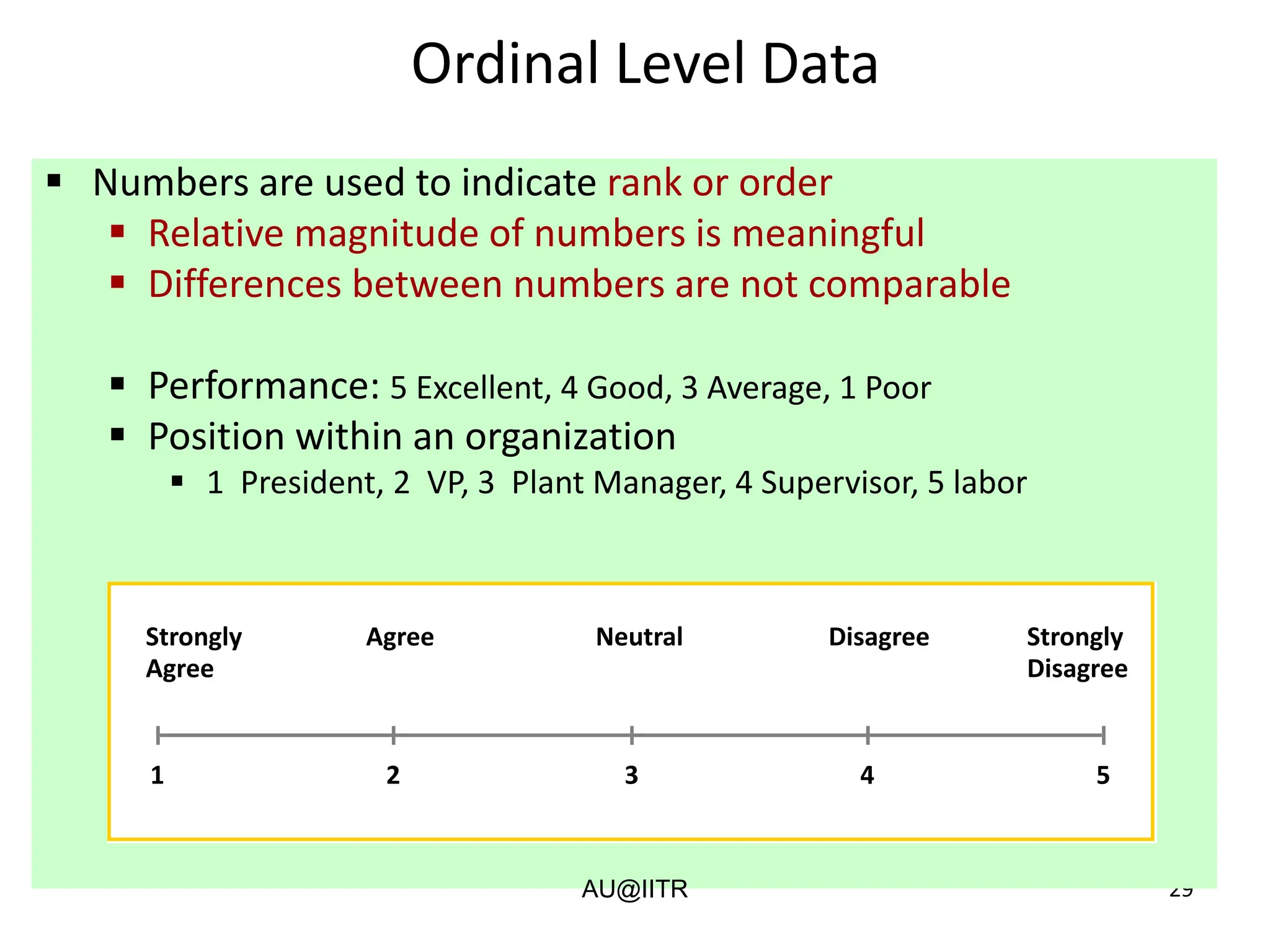
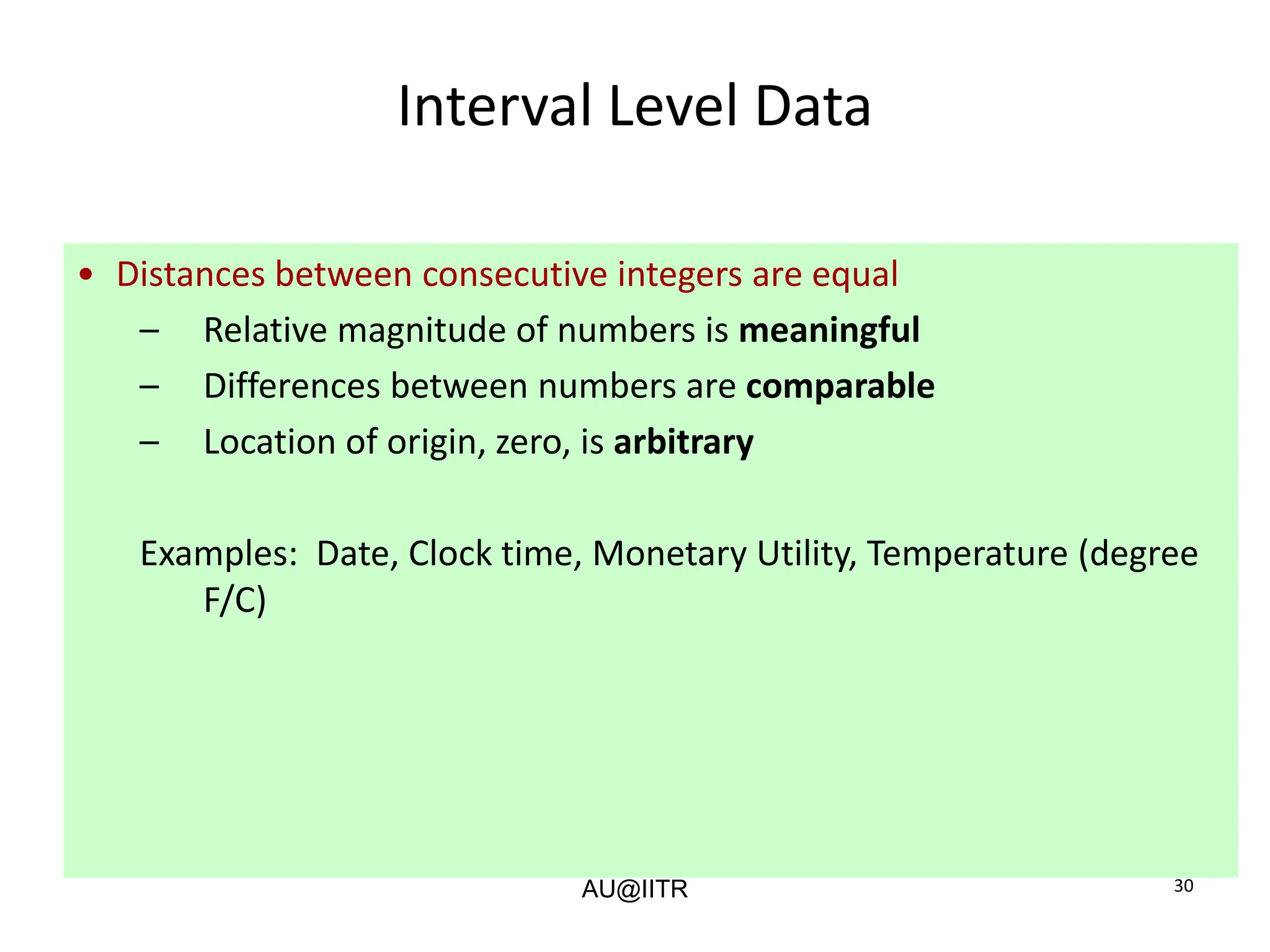
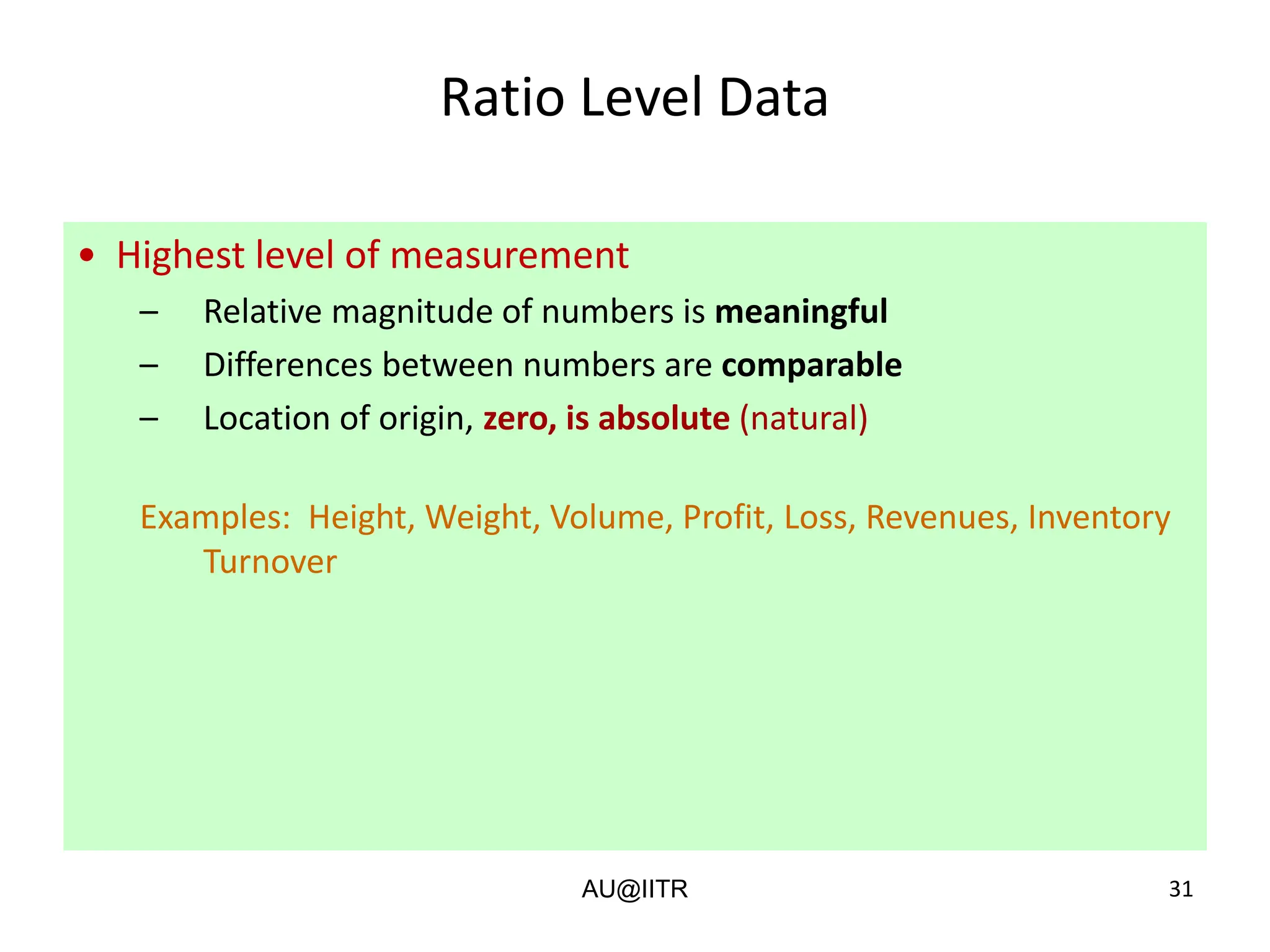
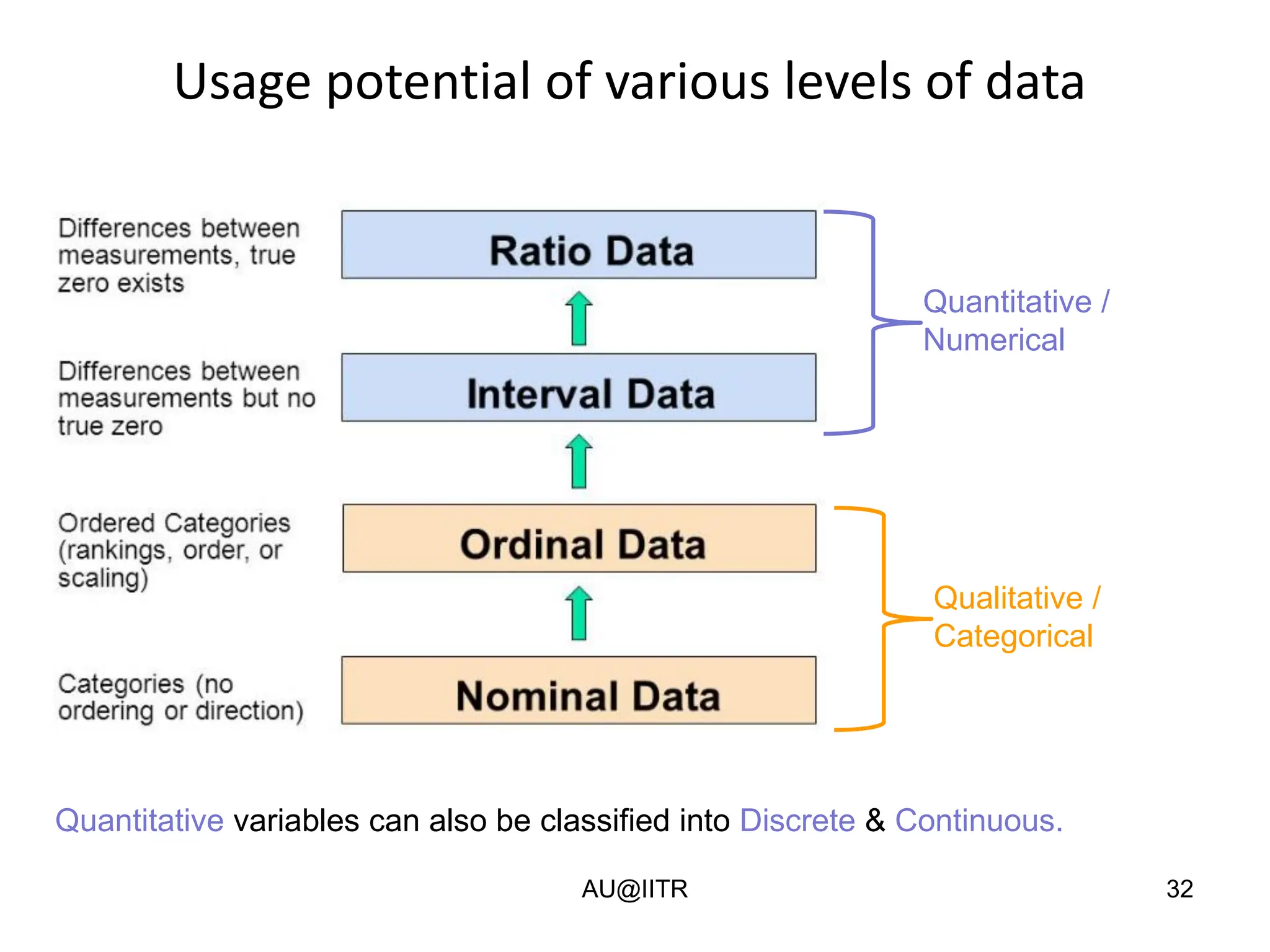
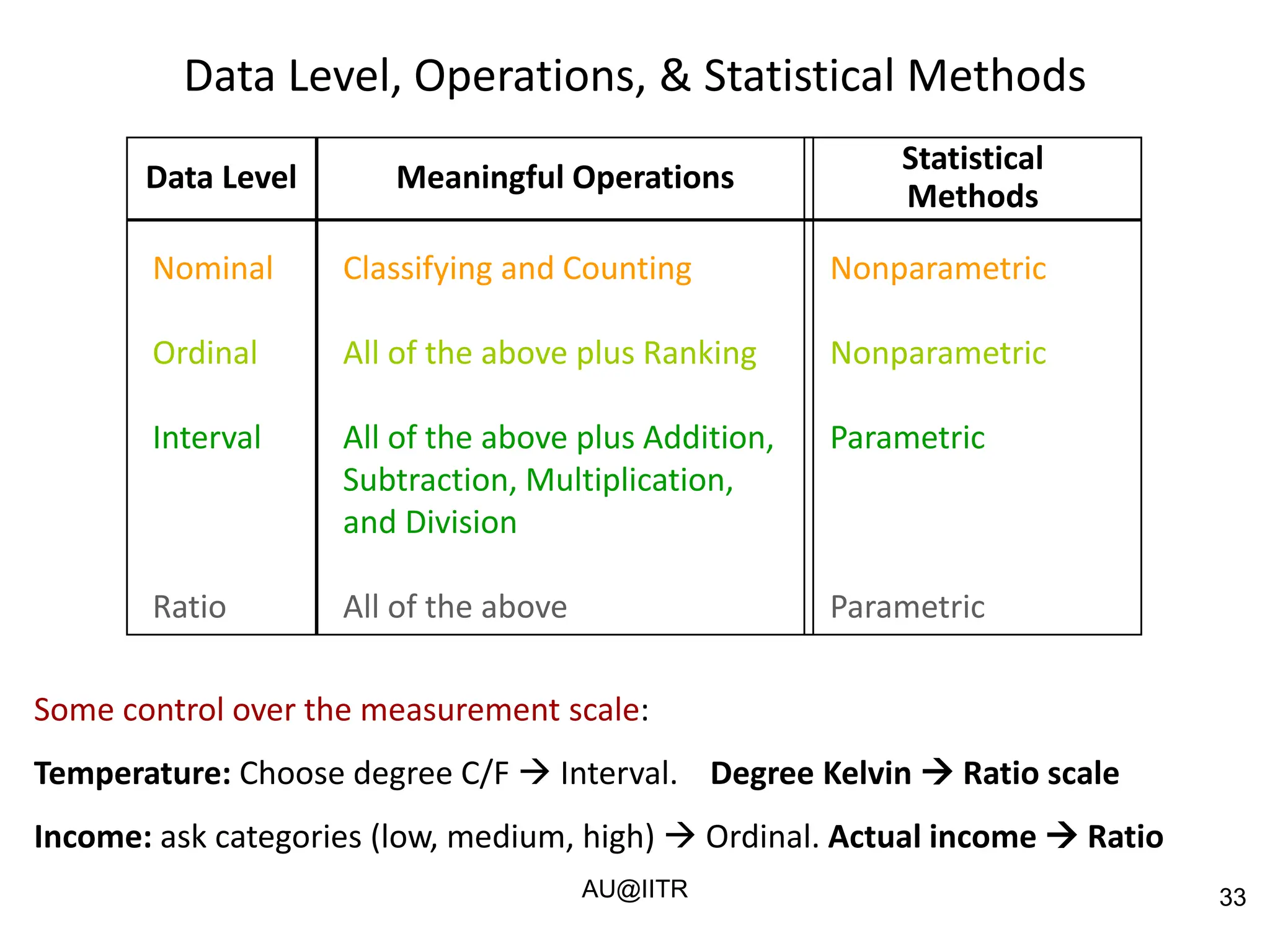
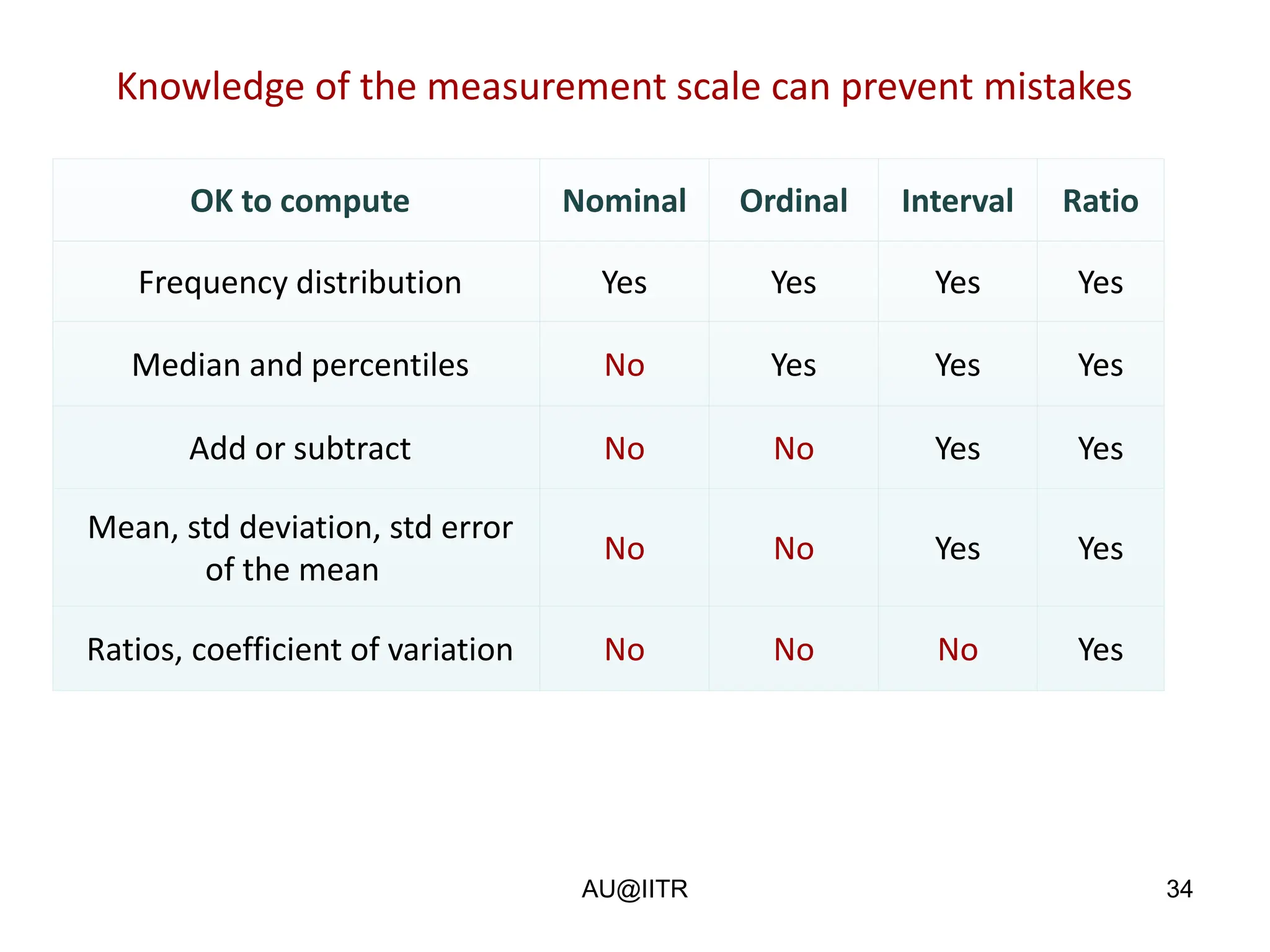
This document provides an introduction to statistics for management. It outlines the course, which will cover descriptive and inferential statistics. Statistics is defined as the science of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data to draw conclusions. It plays an important role in decision making across many fields like business, medicine, government and everyday life. The course will examine how statistics are used in areas like accounting, economics, finance, management, and marketing. It will also explore key statistical concepts like populations, samples, parameters, and statistics. Finally, it discusses the importance of understanding data measurement and levels of data to appropriately apply statistical methods.