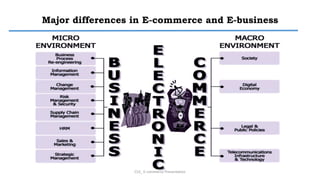
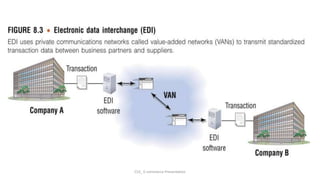
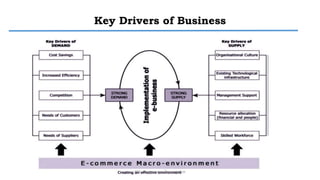
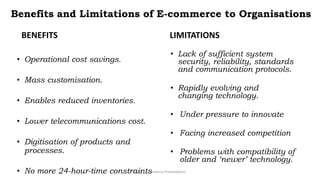
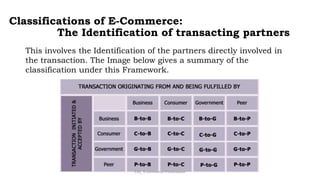
E-commerce refers to conducting business transactions electronically. It allows companies to buy and sell products online and transfer funds electronically. E-business is broader and includes transforming internal business processes through technology. Some key benefits of e-commerce include increased access and choice for consumers, as well as operational cost savings and mass customization opportunities for businesses. However, both consumers and businesses face limitations like a reliance on technology infrastructure and security concerns. E-commerce can be classified based on the environment, transacting partners, or degree of digitization. Barriers to the growth of e-commerce include issues with internet infrastructure, security, and a lack of qualified personnel.