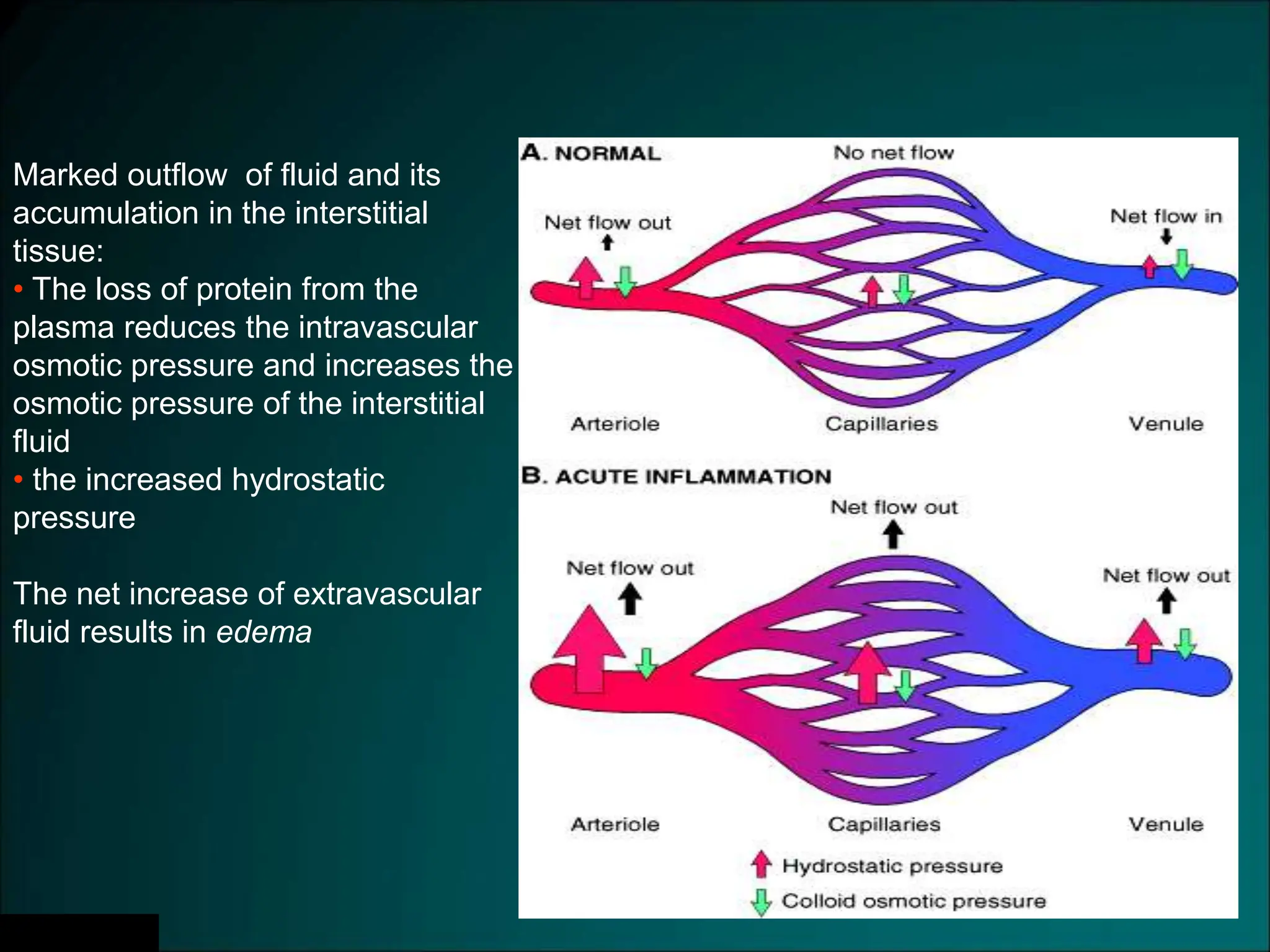
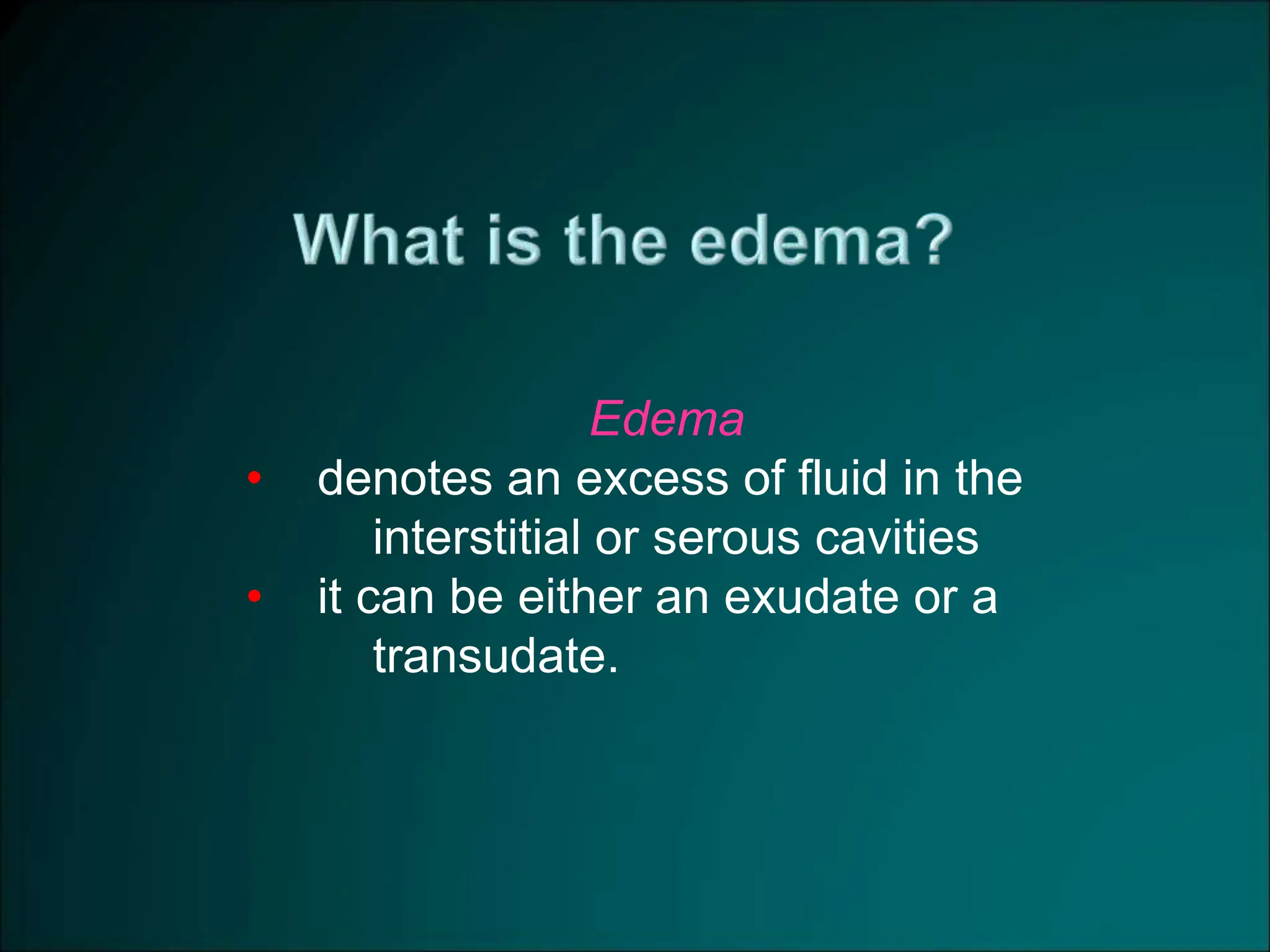
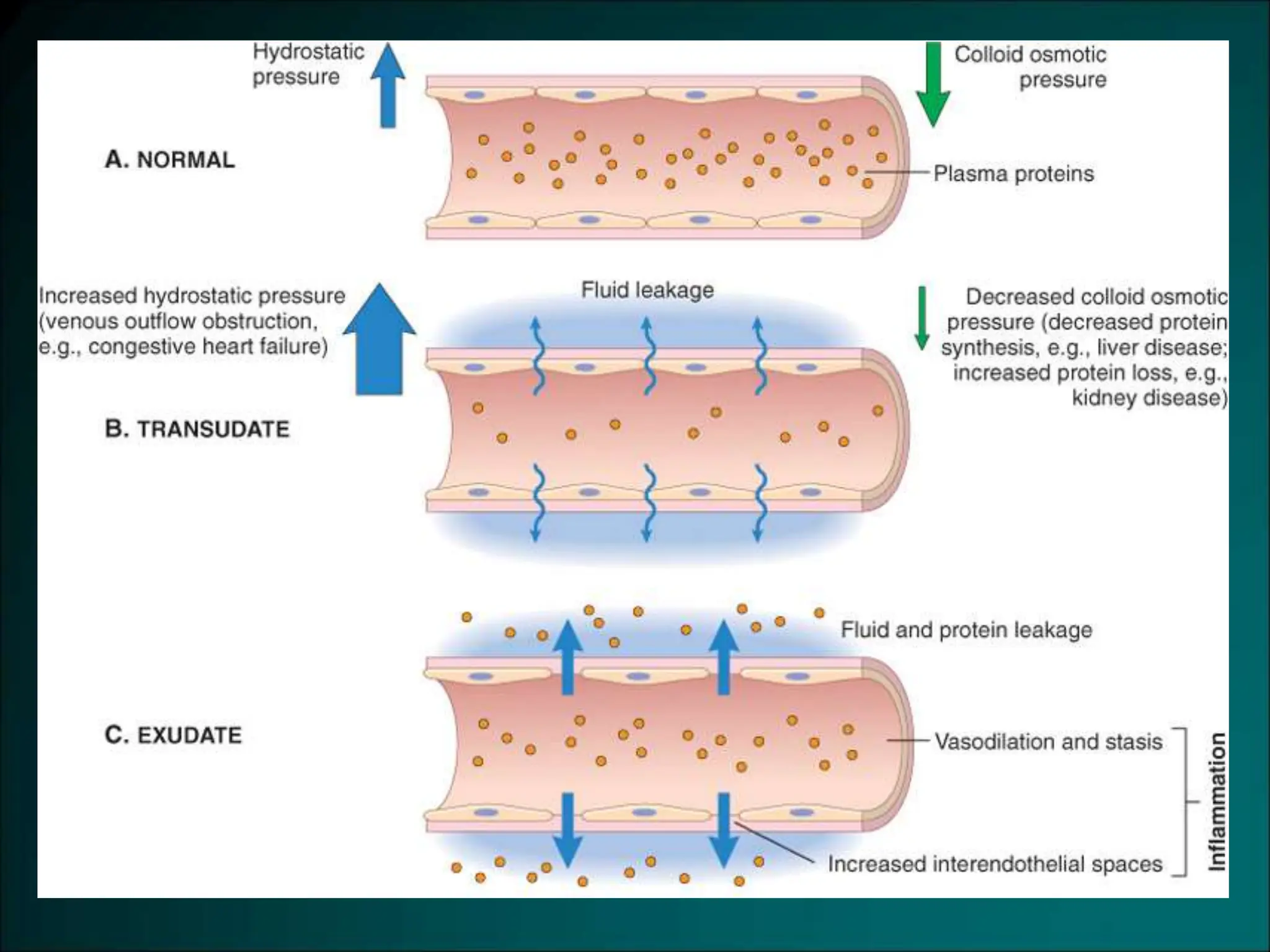
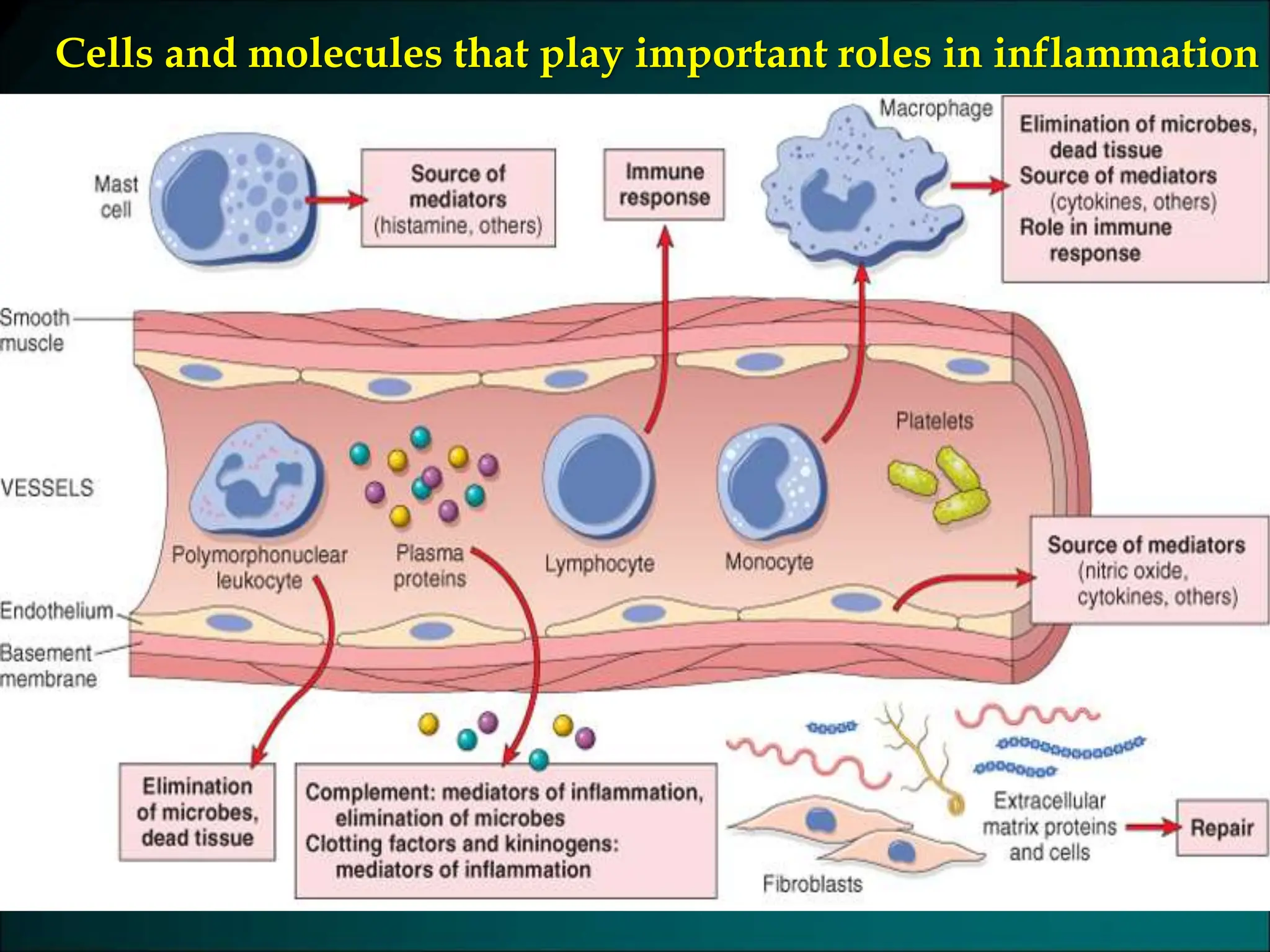
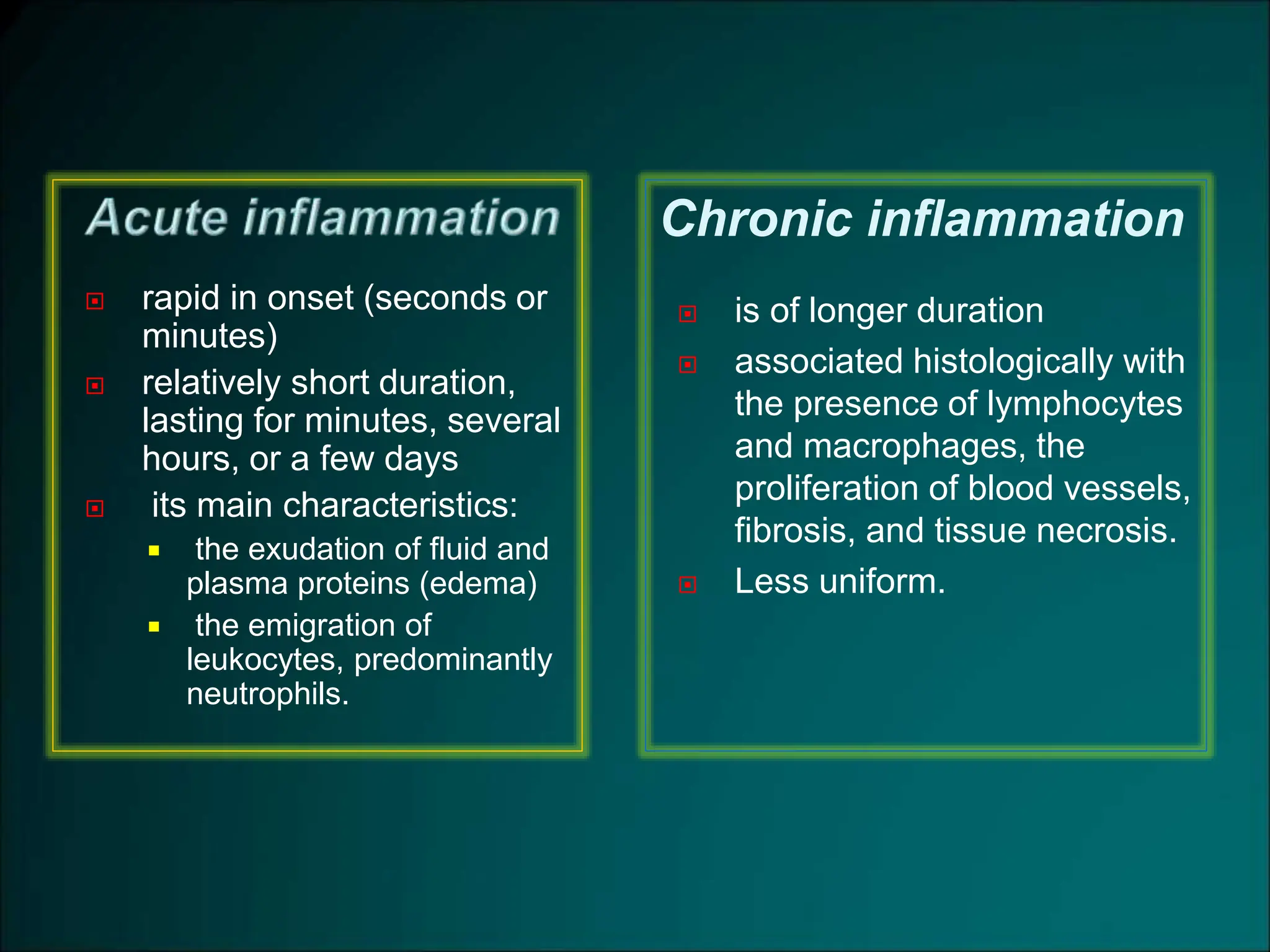
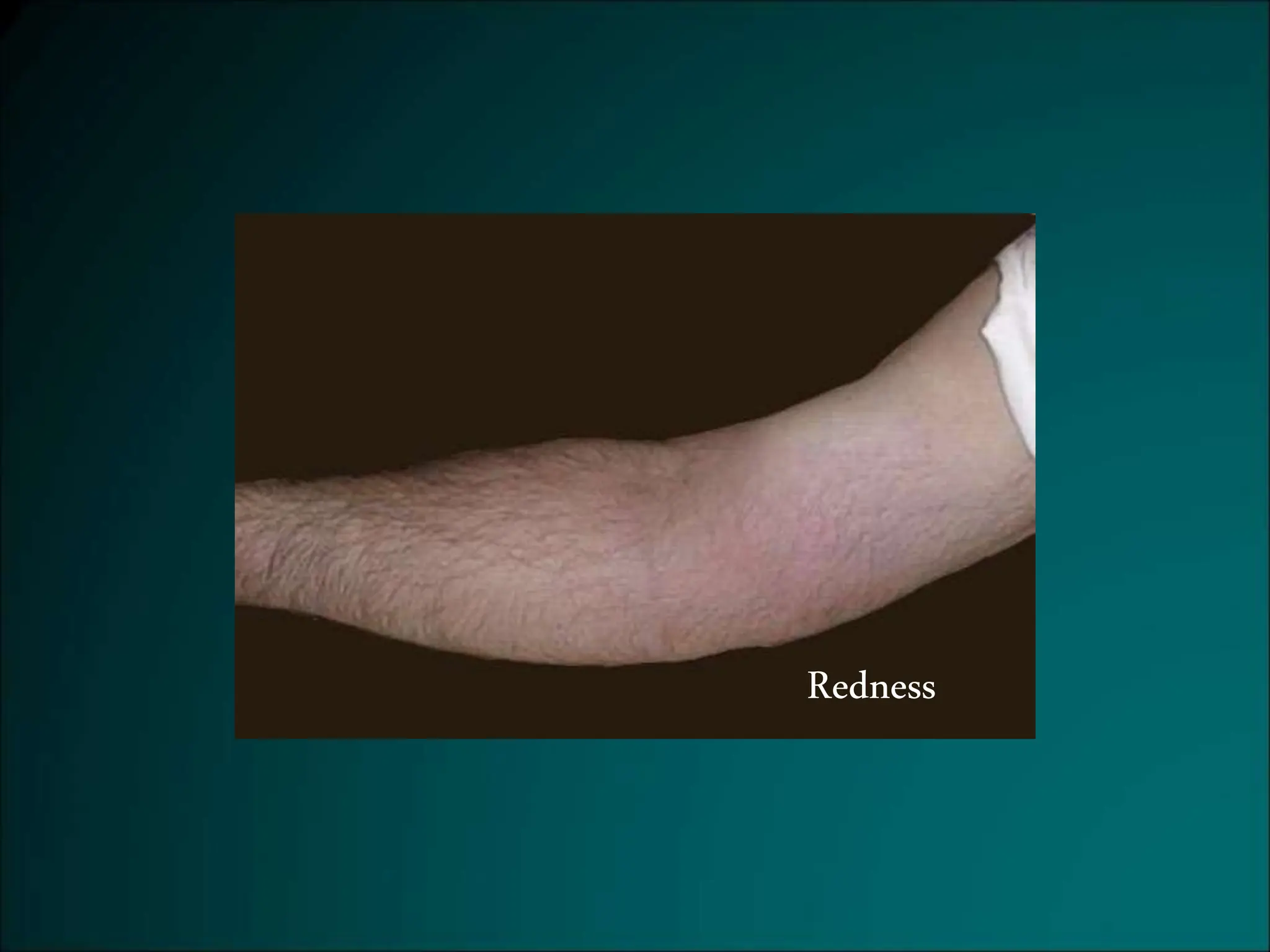
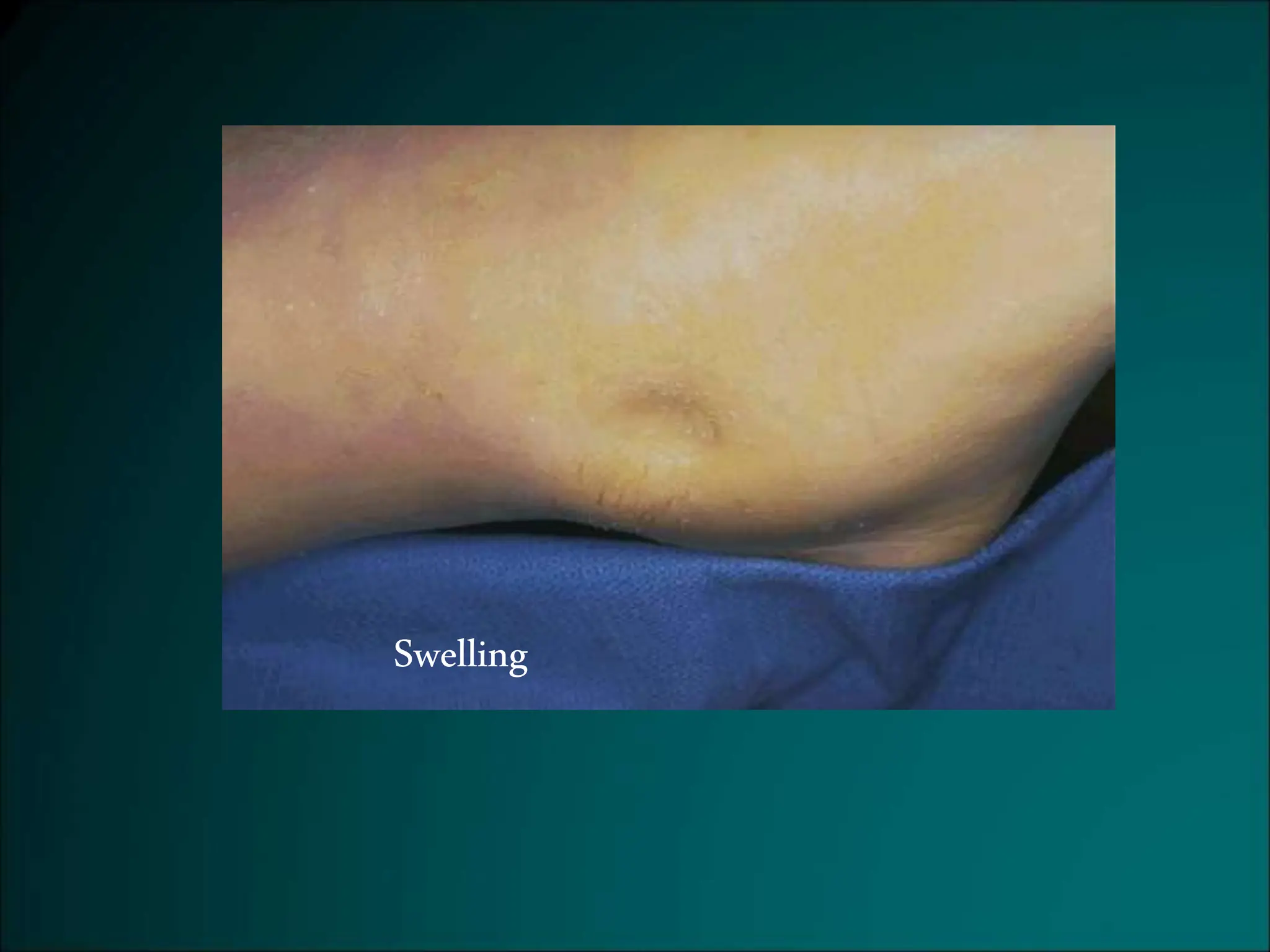
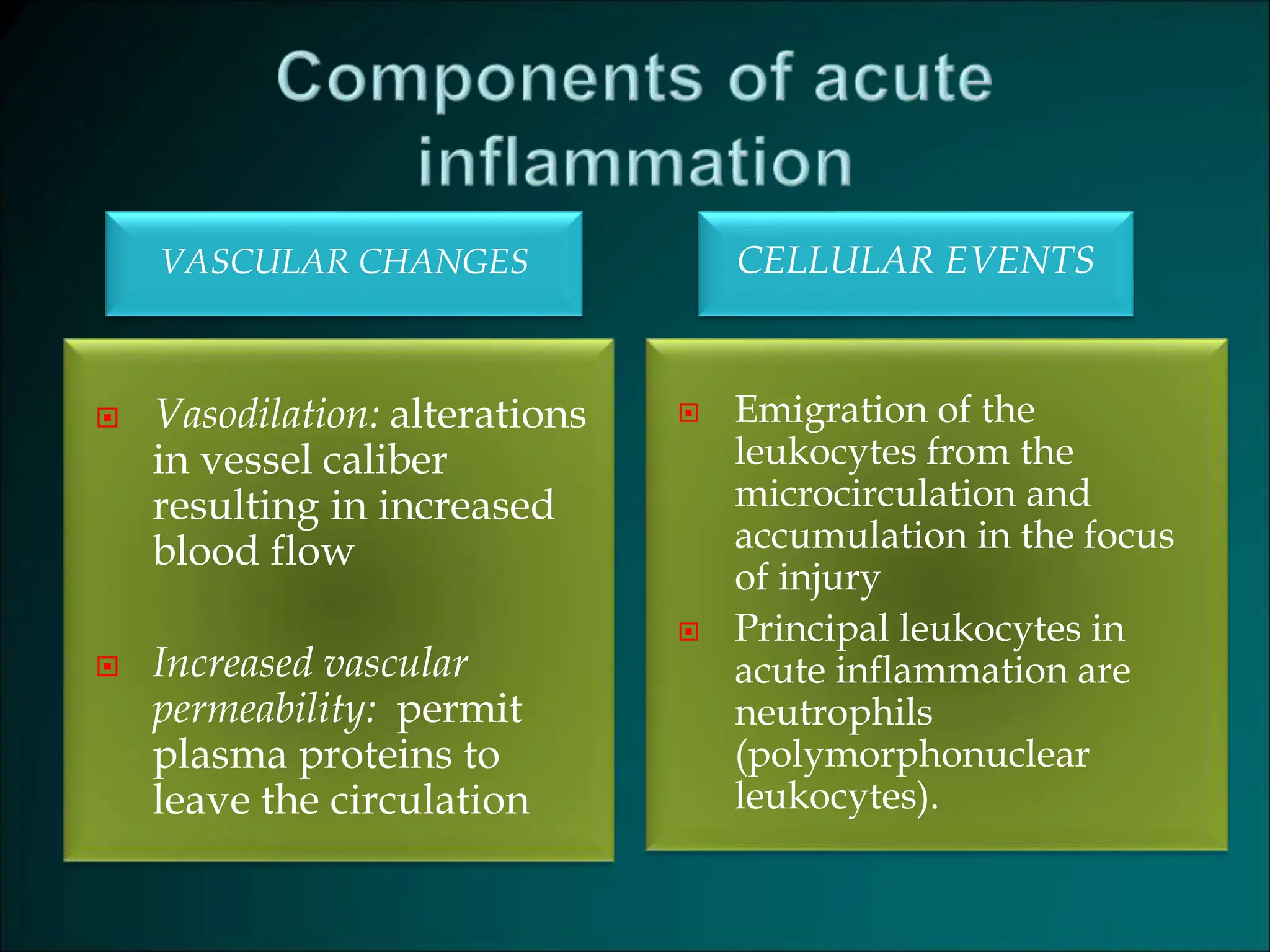
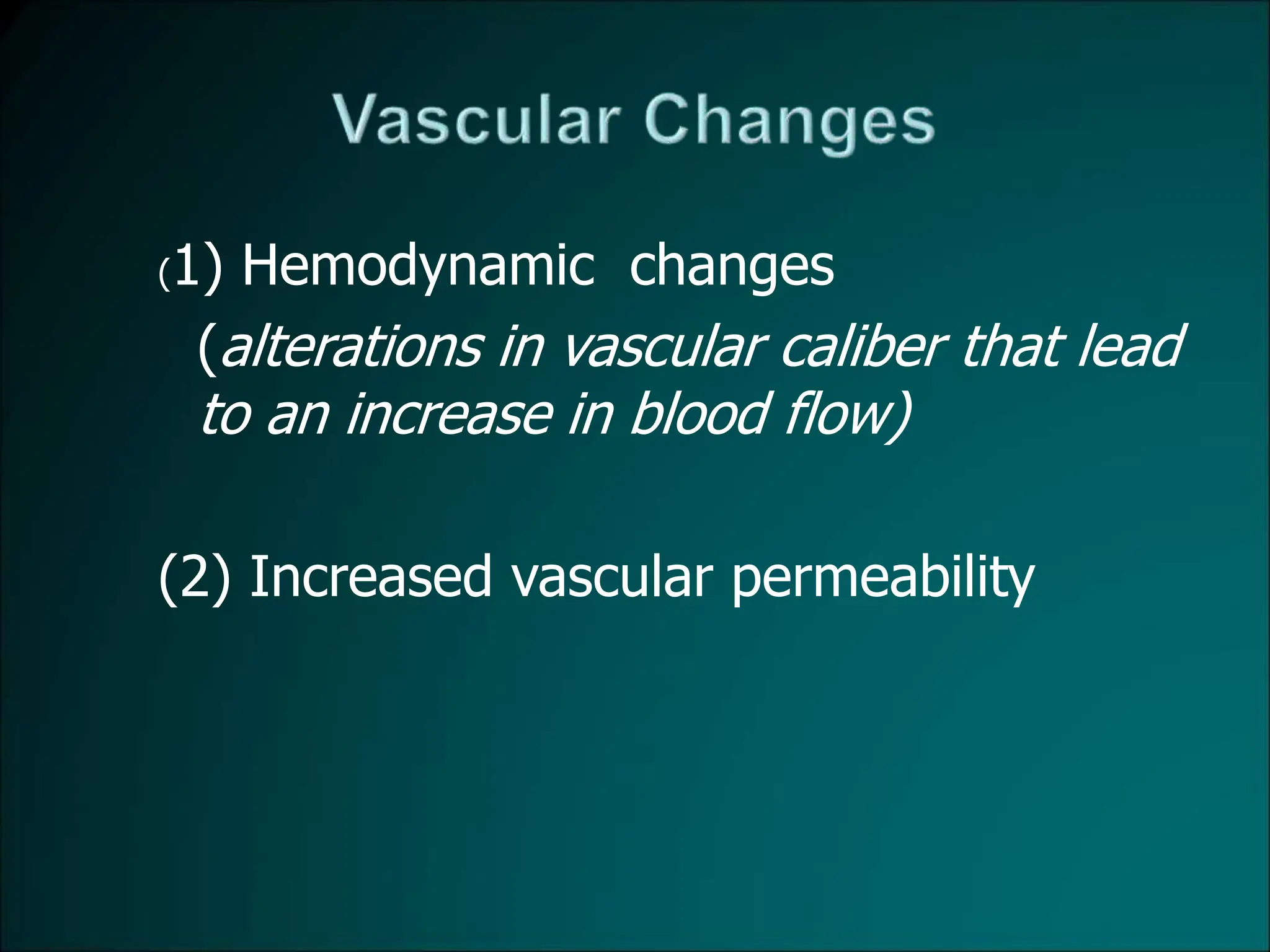
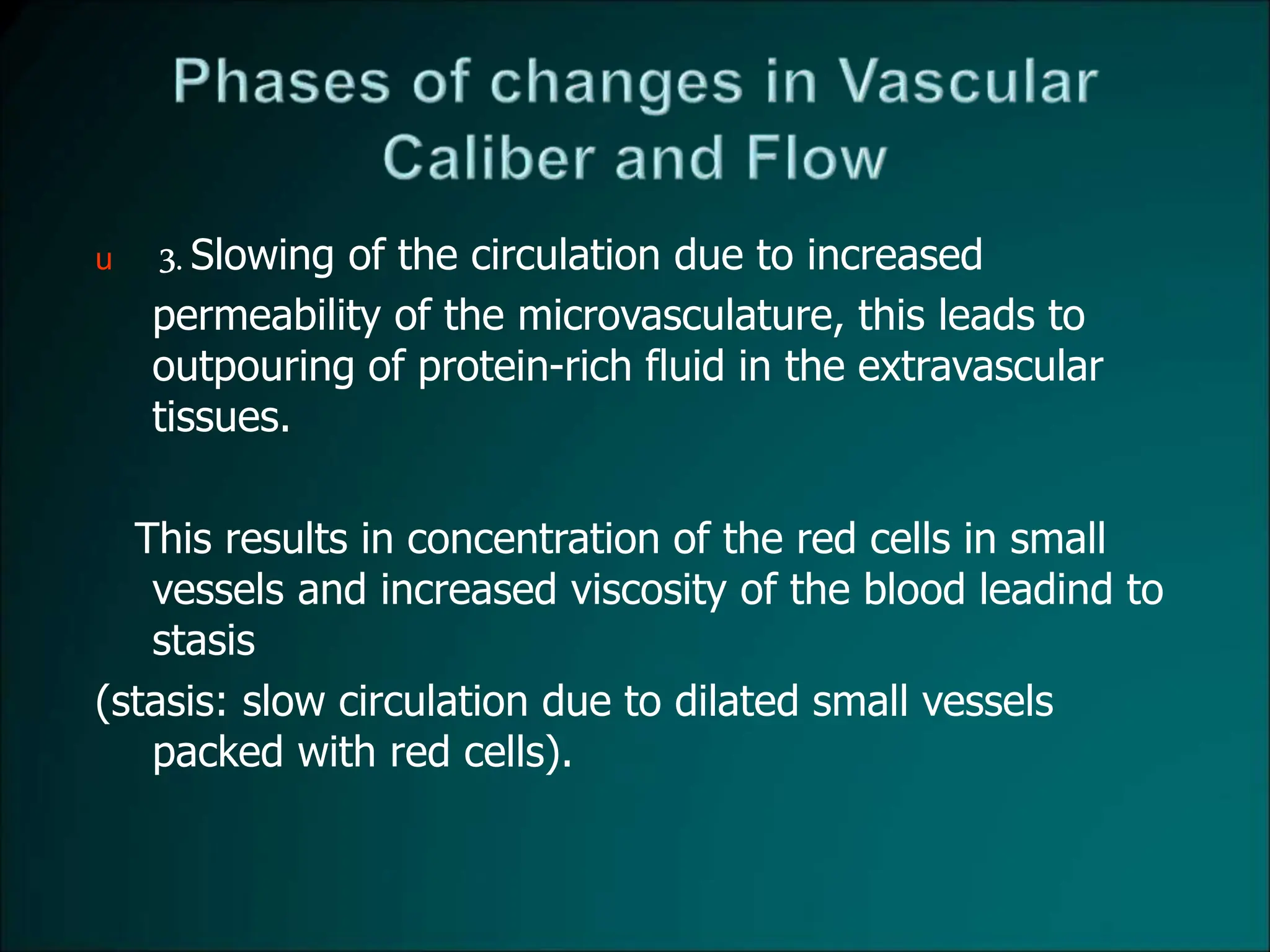
Inflammation is a protective response that aims to eliminate harmful agents and facilitate tissue healing, characterized by processes such as vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and recruitment of leukocytes. It is classified into acute and chronic inflammation, with acute inflammation having a rapid onset and predominantly involving neutrophils, while chronic inflammation involves lymphocytes and macrophages. Key terms include edema, which denotes excess fluid, exudate representing high-protein inflammatory fluid, and transudate, a low-protein fluid resulting from imbalances rather than injury.












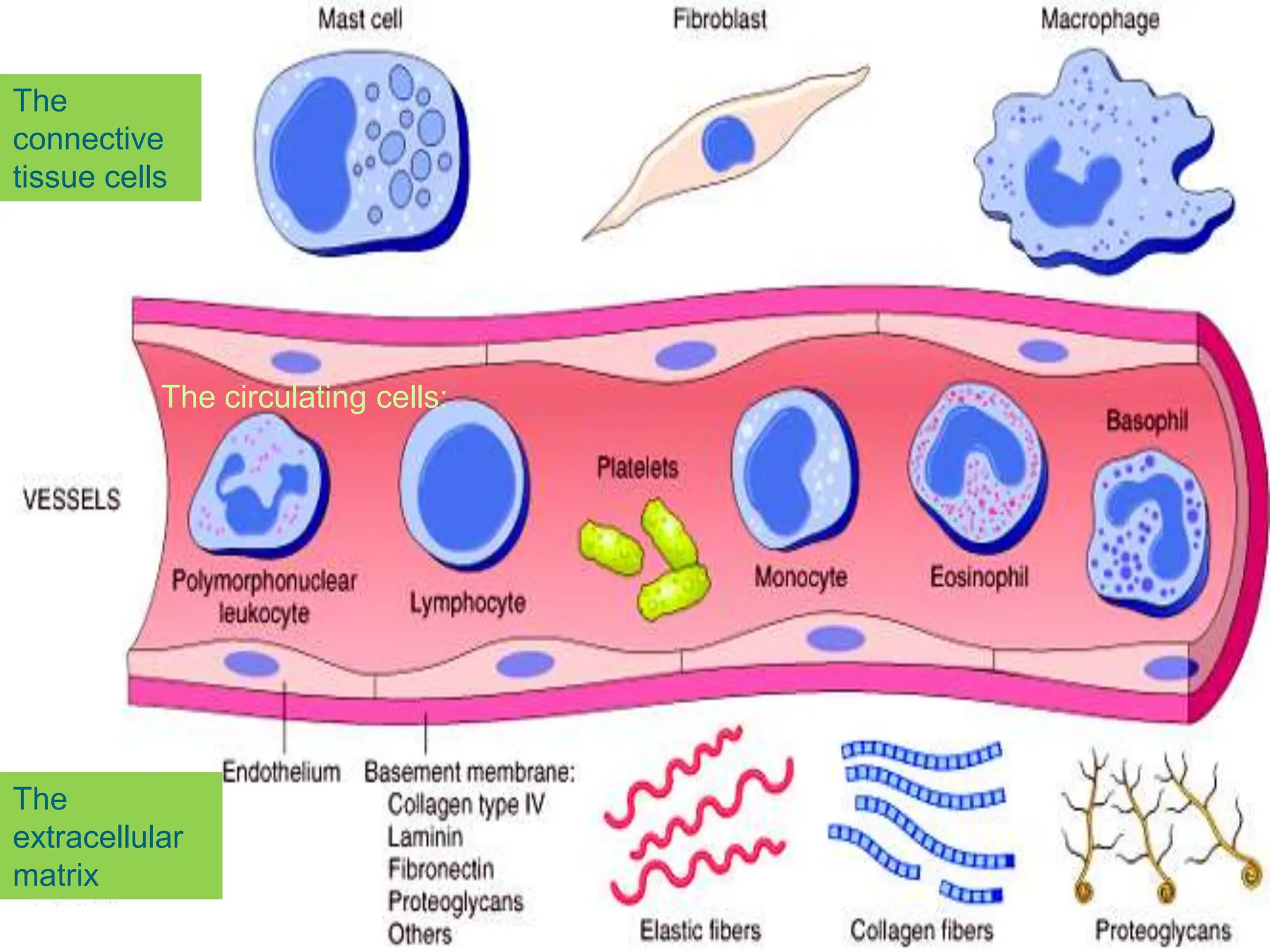


















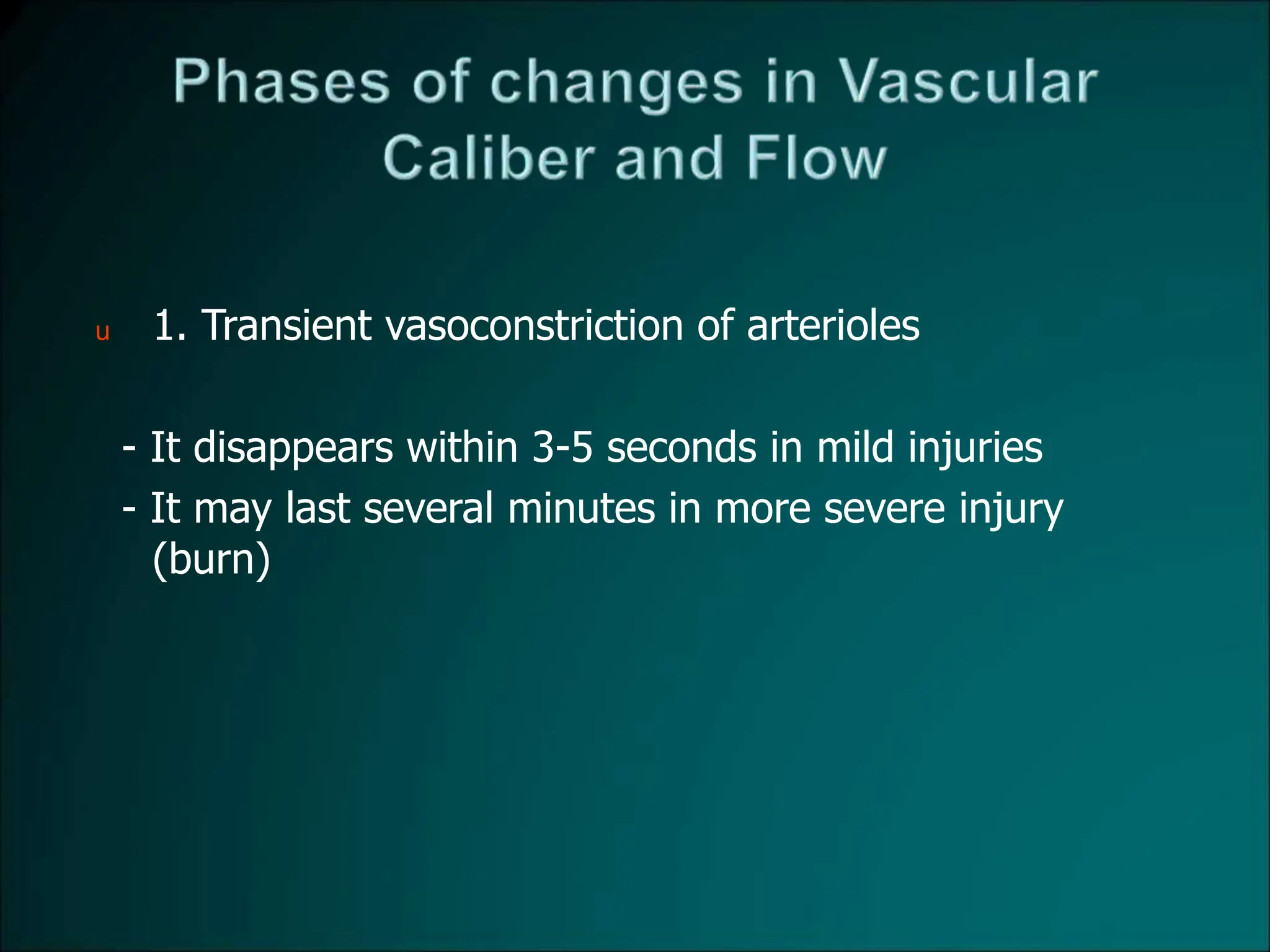

![u 4.persistence of stasis
leads to peripheral orientation of leukocytes (mainly
neutrophils) along the vascular endothelium [leukocytic
margination], then they migrate through the vascular
wall into the interstitial tissue [emigration].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-inflammation-240418151356-ae7e865d/75/07-inflammation-wound-repair-regeneration-ppt-42-2048.jpg)