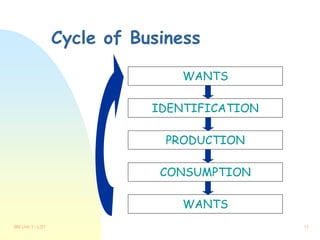
This document provides an overview of key concepts for Unit 1, Learning Outcome 1 of a Business Management course. It defines important business terms like goods, services, and the factors of production. It also describes the role of businesses in society, different business organizations and objectives, and the entrepreneur. Finally, it outlines the sectors of industrial activity and the cycle of business.