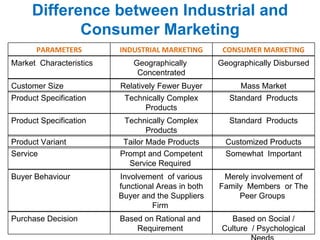
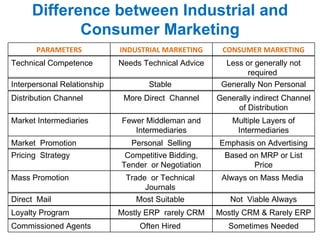
The document provides an overview of the B2B Marketing & CRM course including course content, assessments, and considerations. The course covers topics such as industrial marketing environment, buyer behavior, marketing research, advertising, pricing, distribution, selling, key account management, CRM strategies, and customer relationship management. It also defines B2B marketing, discusses the need for B2B marketing, features, functions, areas of application, characteristics, buying motives, and differences between industrial and consumer marketing.