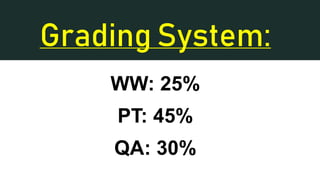
The document provides an overview of key concepts in applied economics for a class including rules, grading system, learning objectives, and definitions of terms like scarcity, needs vs wants, trade-offs, opportunity costs, supply, demand, and the branches of economics. Scarcity exists because resources are limited while wants are unlimited, and economics studies how people deal with scarcity. Trade-offs are options given up when making a choice, and the most desirable alternative given up is the opportunity cost. Supply refers to the total goods available for sale, while demand is the total needs and wants of customers. Applied economics applies economic principles to real-world problems at the micro or macro level.