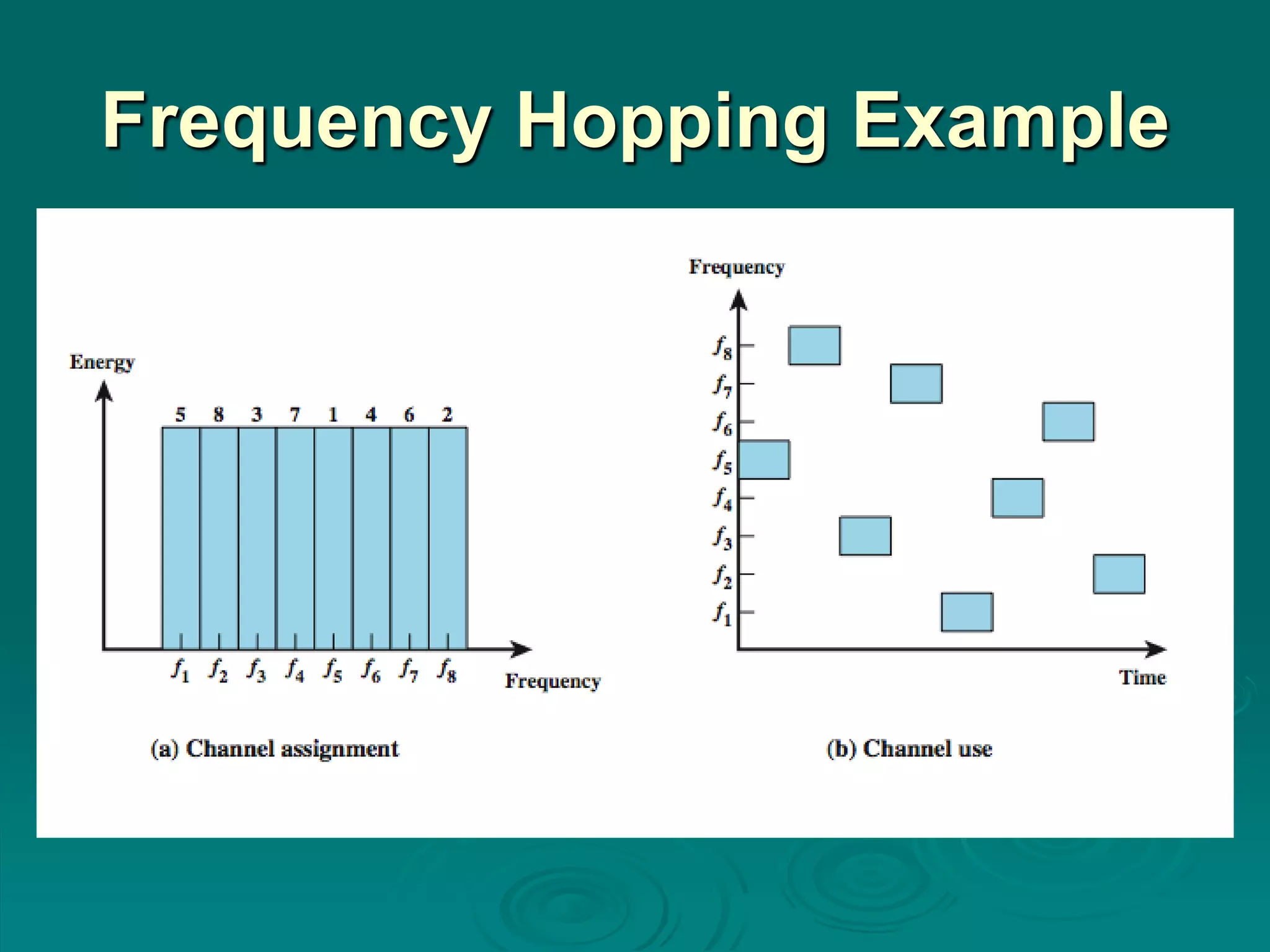
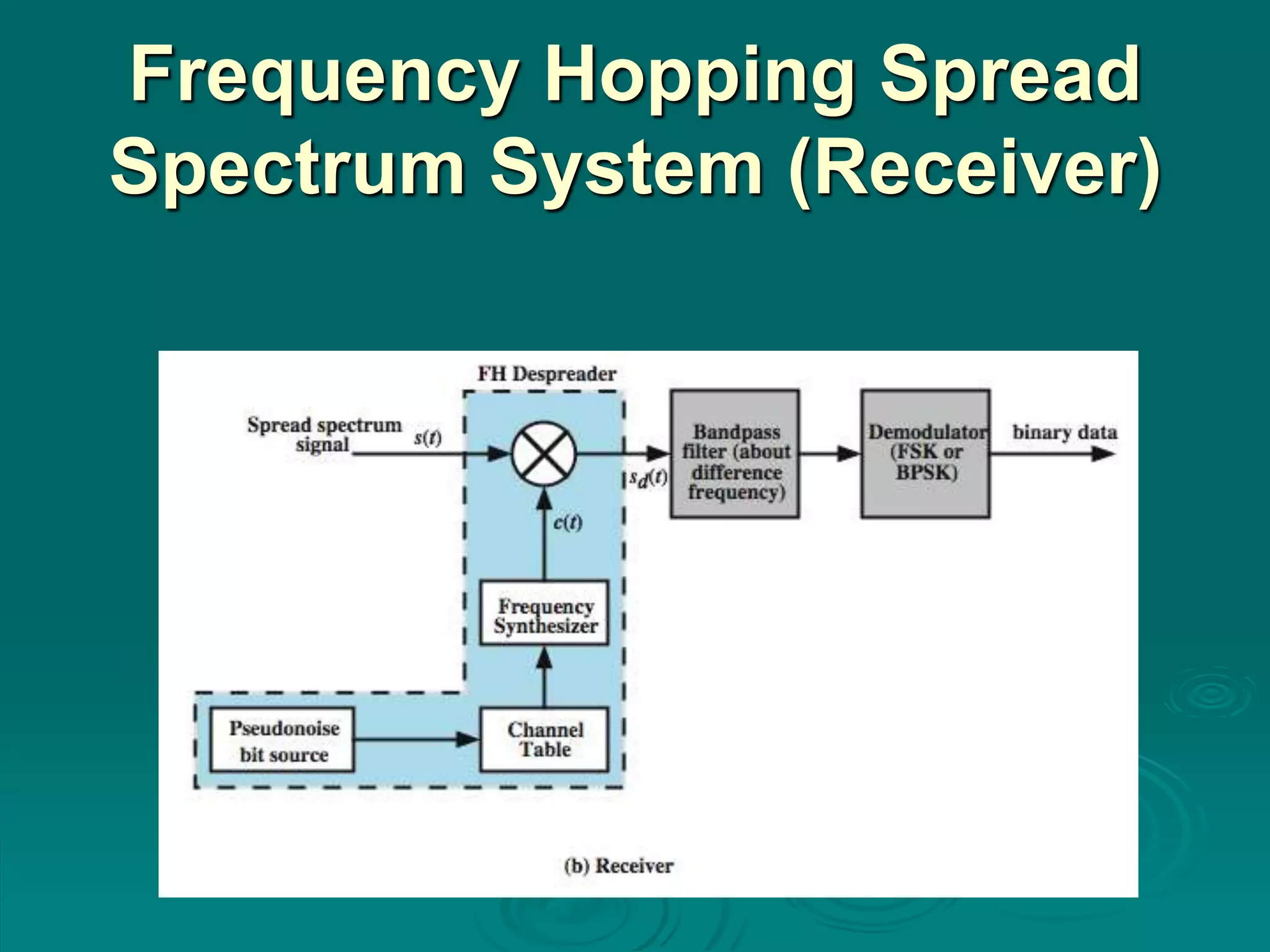
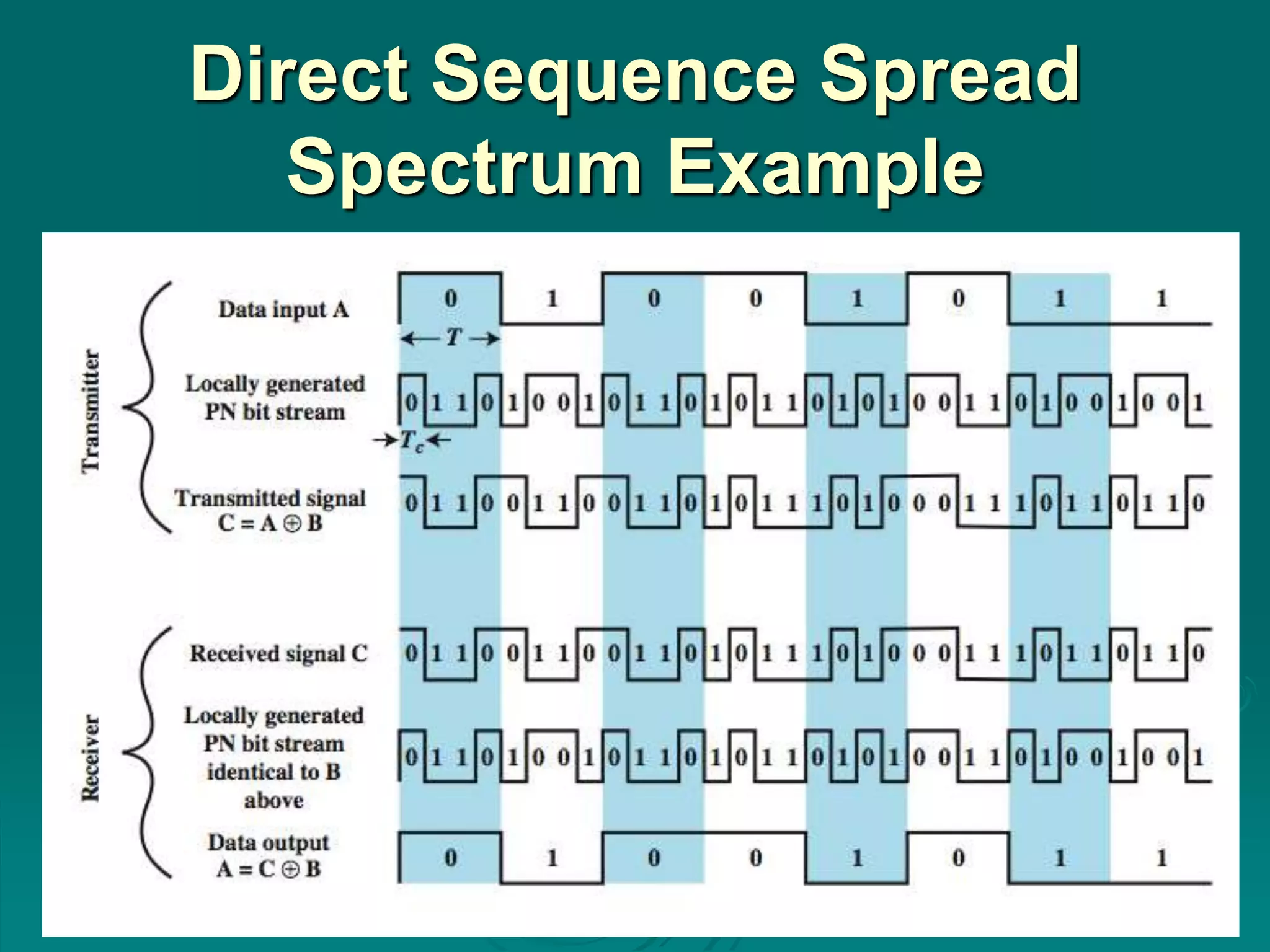
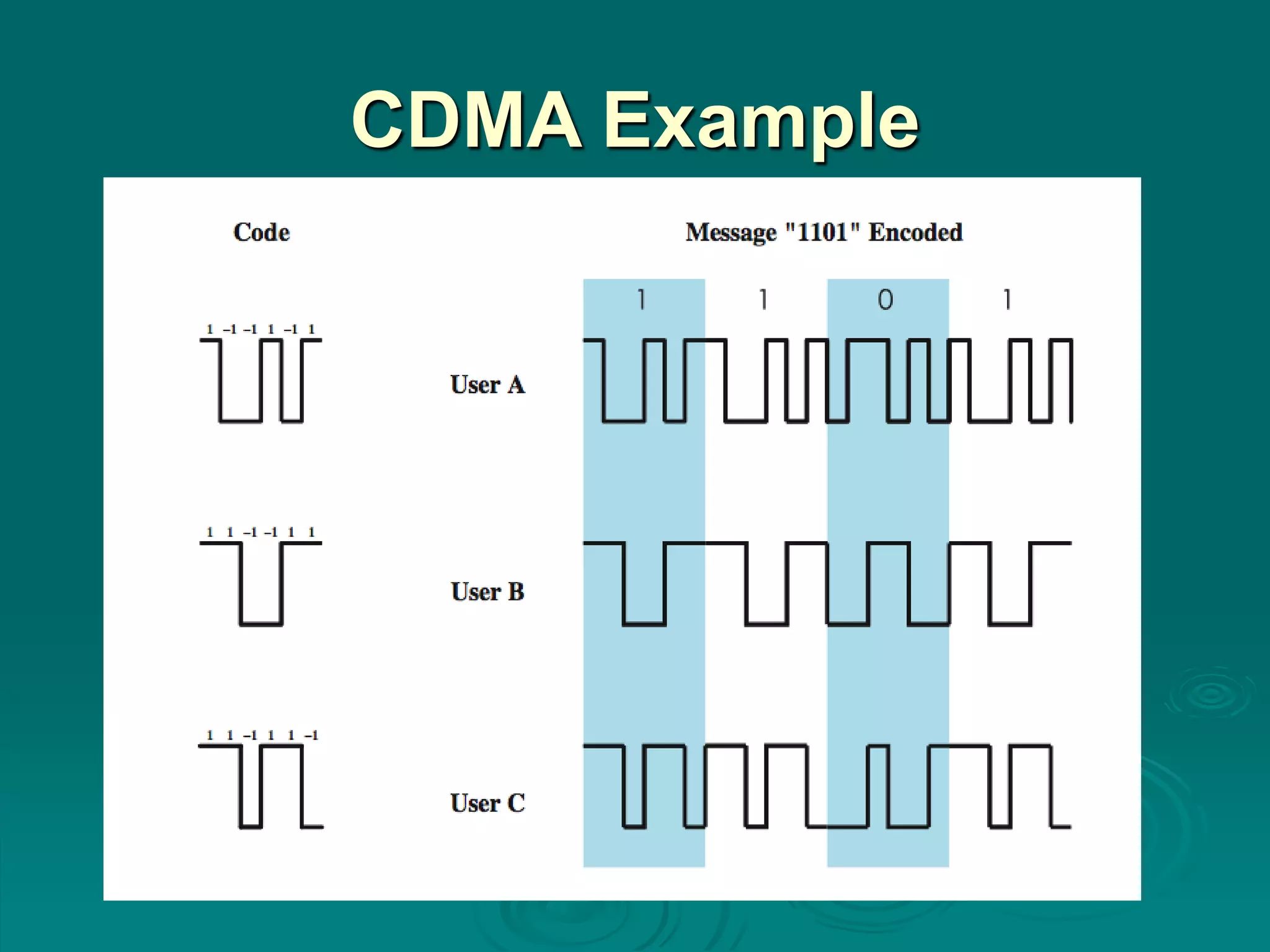
Spread spectrum encoding spreads data over a wide bandwidth to make jamming and interception harder. It uses either frequency hopping or direct sequence approaches. Some advantages of spread spectrum are immunity from noise and multipath distortion, ability to hide or encrypt signals, and allowing multiple users to share bandwidth with little interference. Pseudorandom numbers are used to determine hopping sequences or spreading codes, and must be known to decode the signal. Frequency hopping spreads a signal over different frequencies in sync between transmitter and receiver, while direct sequence represents each bit with multiple bits using a spreading code. Code division multiple access allows multiplexing using spreading codes unique to each user.