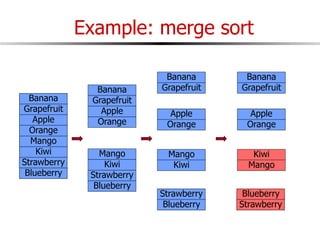
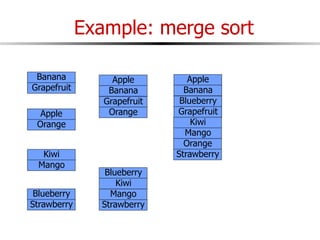
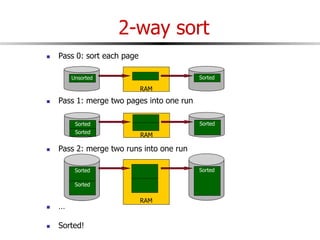
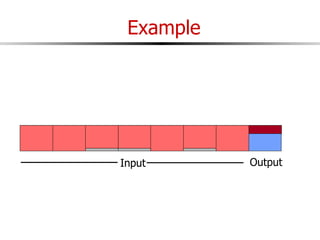
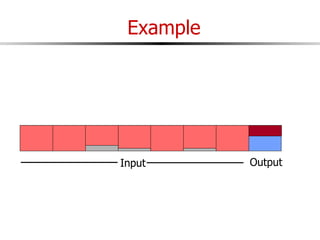
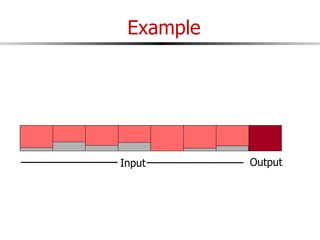
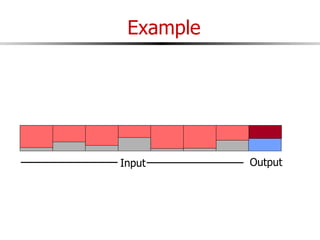
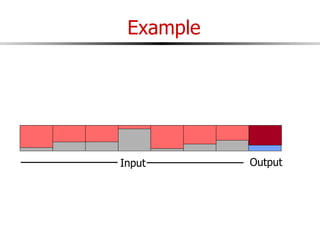
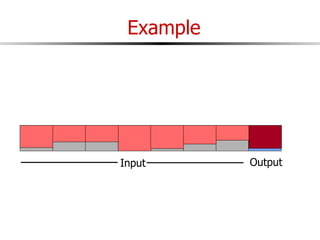
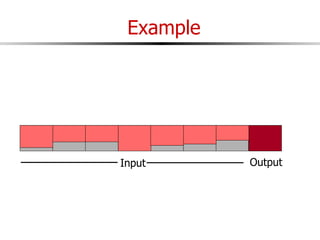
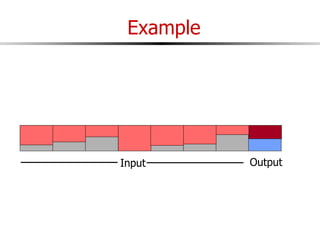
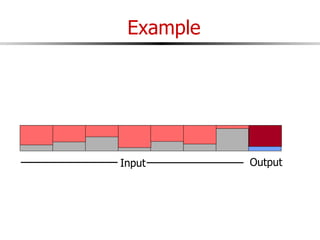
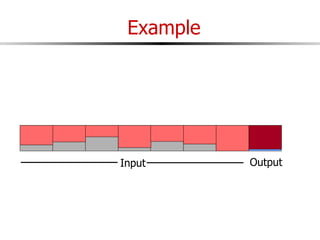
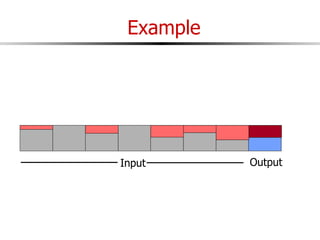
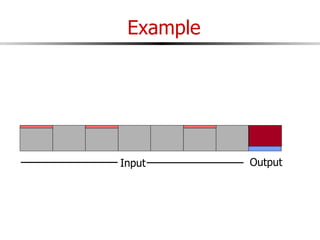
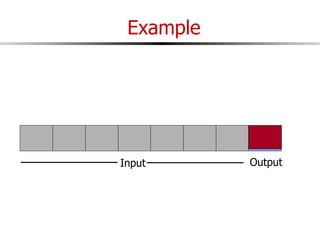
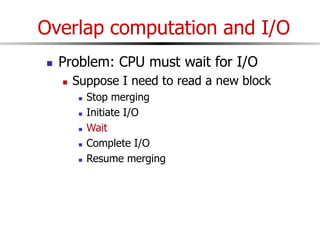
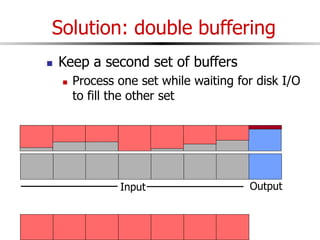
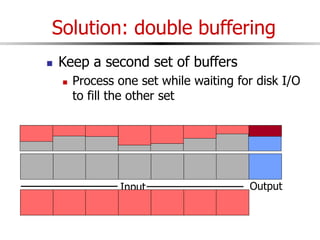
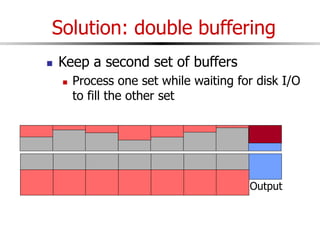
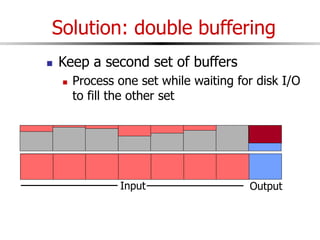
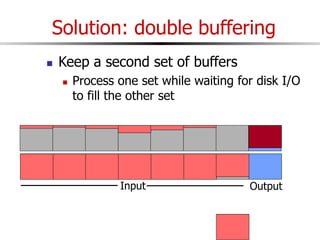
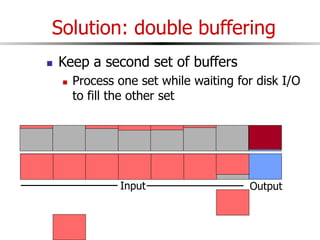
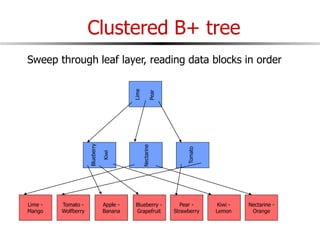
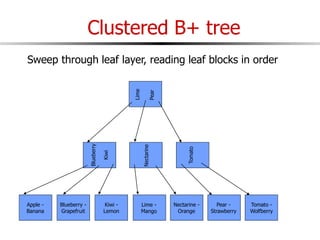
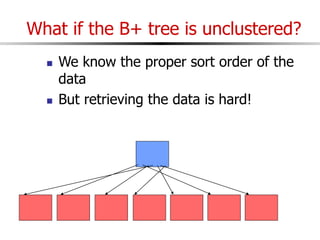
The document discusses external sorting techniques for large datasets that do not fit in memory. It describes the problem with standard in-memory sorting algorithms and introduces external merge sort as a solution. External merge sort works by sorting pages of data on disk in multiple passes, merging runs of sorted pages in each pass to reduce the number of disk I/Os needed. Various optimizations are discussed like using more buffers to process more pages per pass, blocking I/Os to improve sequential access, and double buffering to overlap I/O and computation. When data is indexed by a clustered B+ tree, it may already be sorted, avoiding the need for external sorting.