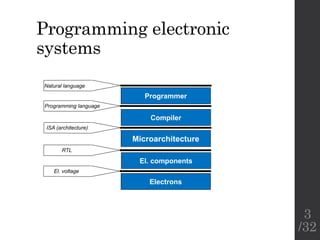
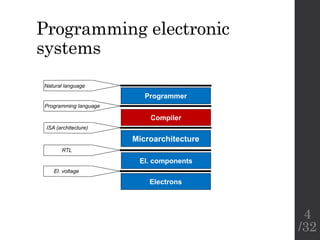
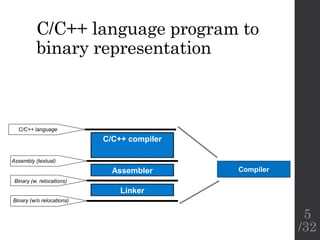
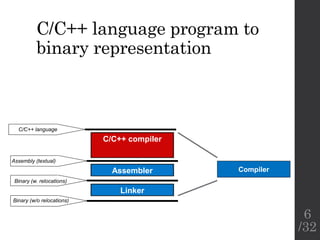
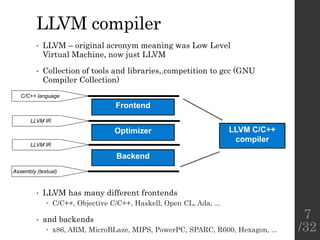
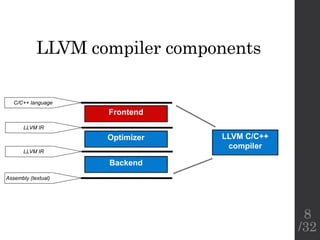
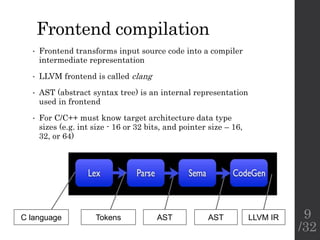
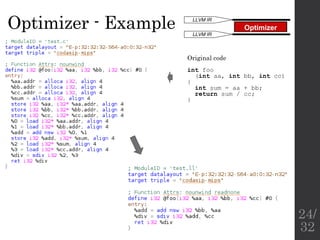
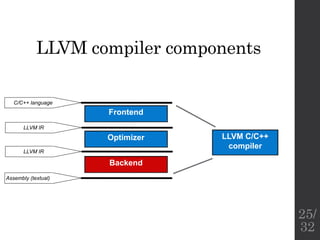
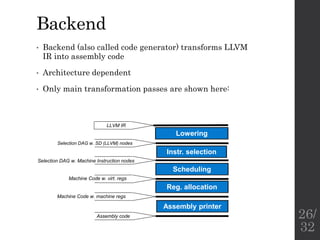
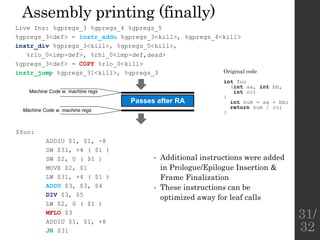
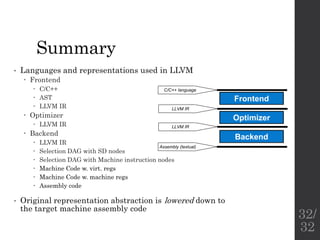
The document describes the languages and representations used at each stage of compilation in LLVM. It discusses how the C/C++ frontend transforms source code into an AST then LLVM IR. The optimizer performs optimizations on the LLVM IR. The backend lowers the LLVM IR into a selection DAG with machine instructions and finally emits assembly code. The compilation process translates from the original high-level language into target-specific assembly.

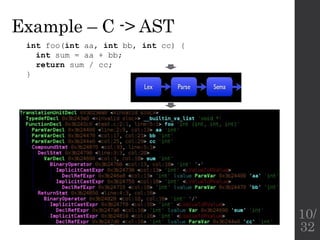

![(used slides from [2])
12/
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-140430-ipp-languagesusedinllvmduringcompilation-171129164034/85/07-140430-ipp-languages-used-in-llvm-during-compilation-12-320.jpg)
![(used slides from [2])
Source to source compilation
13/
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-140430-ipp-languagesusedinllvmduringcompilation-171129164034/85/07-140430-ipp-languages-used-in-llvm-during-compilation-13-320.jpg)

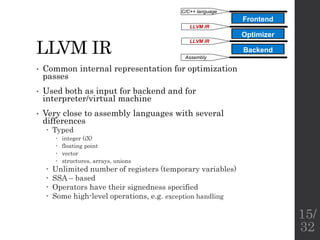


![(used slides from [1])
18/
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-140430-ipp-languagesusedinllvmduringcompilation-171129164034/85/07-140430-ipp-languages-used-in-llvm-during-compilation-18-320.jpg)
![(used slides from [1])
(used slides from [1])
19/
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-140430-ipp-languagesusedinllvmduringcompilation-171129164034/85/07-140430-ipp-languages-used-in-llvm-during-compilation-19-320.jpg)
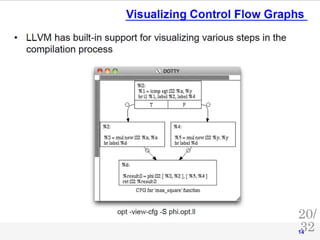
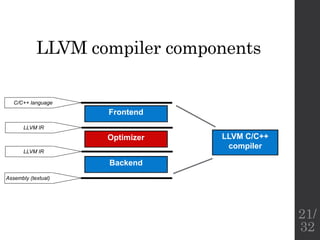


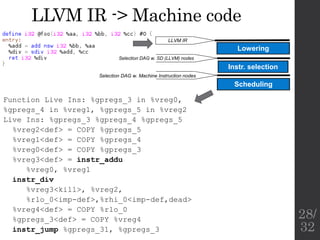
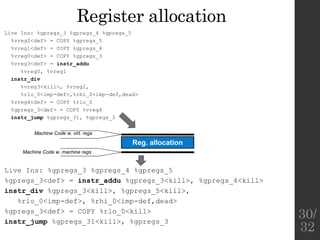
![Lowering, instruction
selection, and basic scheduling
• Switch to presentation Dan Gohman: SelectionDAG
Phases ([3])
Lowering
Instr. selection
Assembly printer
LLVM IR
Selection DAG w. SD (LLVM) nodes
Selection DAG w. Machine Instruction nodes
Assembly code
Scheduling
Machine Code w. virt. regs
Reg. allocation
Machine Code w. machine regs
27/
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-140430-ipp-languagesusedinllvmduringcompilation-171129164034/85/07-140430-ipp-languages-used-in-llvm-during-compilation-27-320.jpg)

![References
• [1] Christian Plessl: Introduction to the LLVM Compiler
Framework, Univ. of Paderborn, 2012
• [2] Olaf Krzikalla: Performing Source-to-Source Transformations
with Clang, European LLVM Conference Paris, 2013
• [3] Dan Gohman: SelectionDAG Phases- llvm.org/devmtg/2008-
08/Gohman_CodeGenAndSelectionDAGs.pdf
33/
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-140430-ipp-languagesusedinllvmduringcompilation-171129164034/85/07-140430-ipp-languages-used-in-llvm-during-compilation-33-320.jpg)