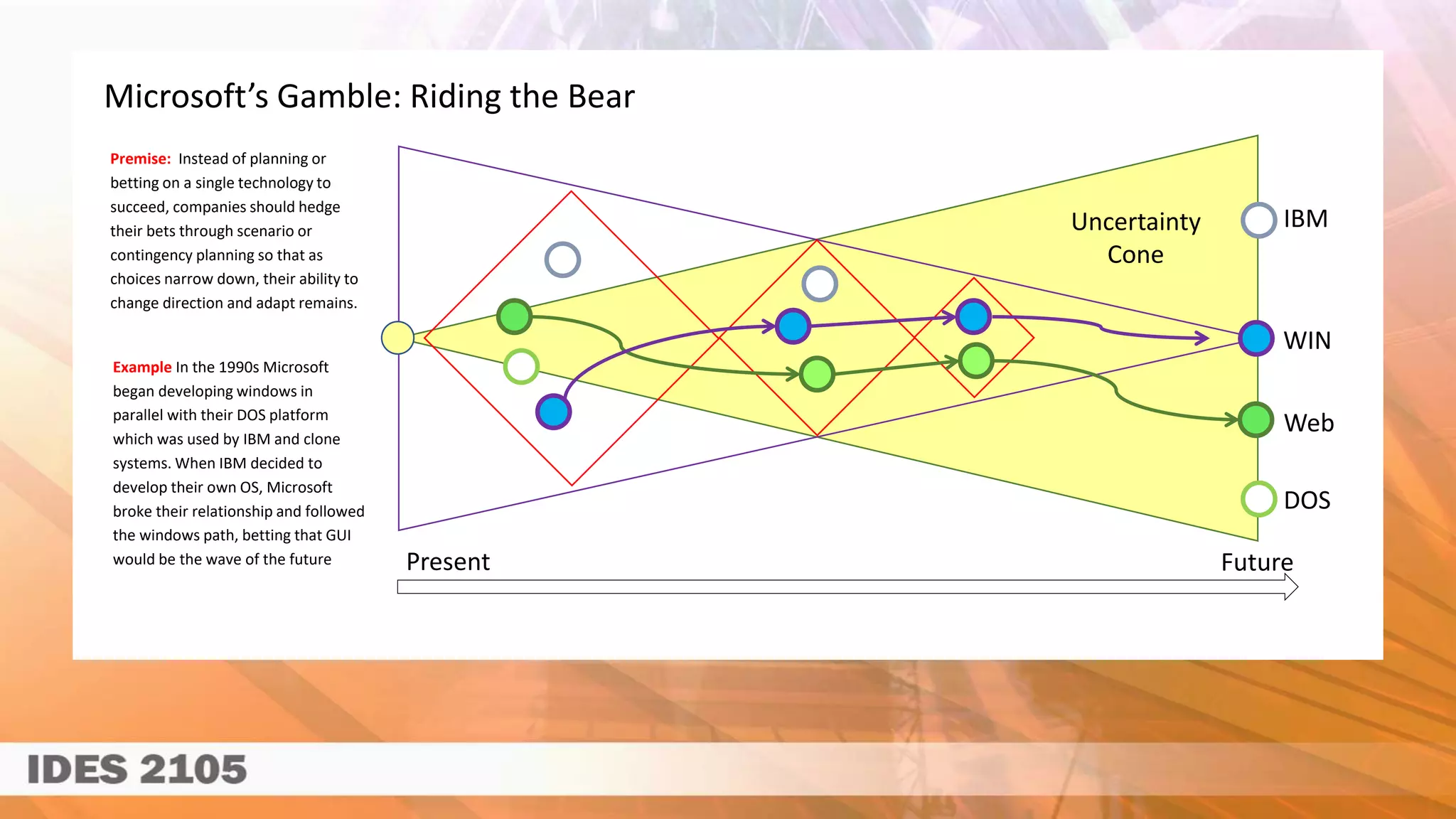
This document discusses different strategic approaches and schools of thought. It contrasts deliberate strategies that involve extensive planning versus emergent strategies that emphasize adapting to changes. It provides examples of companies like Sony that committed to an inflexible strategy with their Beta format and Microsoft that hedged their bets by developing Windows alongside DOS. The document also discusses balancing deliberate and emergent strategies depending on the type of innovation and risk involved.