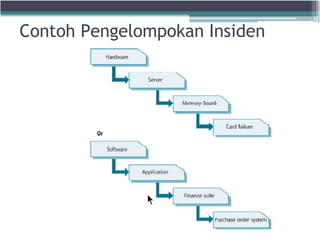
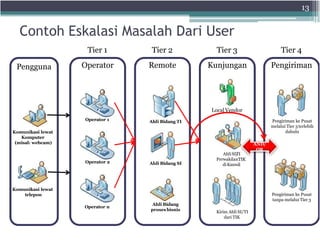
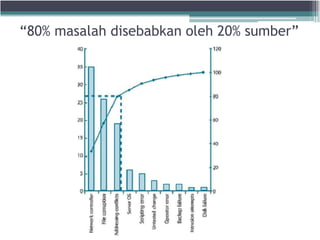
The document discusses the key processes and functions of Service Operation according to ITIL v3. It describes the purpose of Service Operation as delivering agreed service levels to users while managing supporting applications, technology, and infrastructure. Key processes covered include incident management, problem management, request fulfillment, access management, and event management. The roles of the service desk and IT operations management in ensuring service quality and value are also summarized.