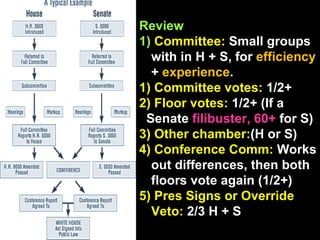
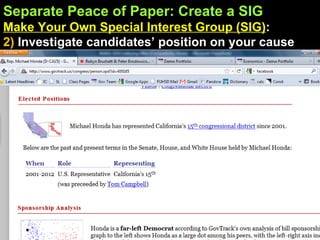
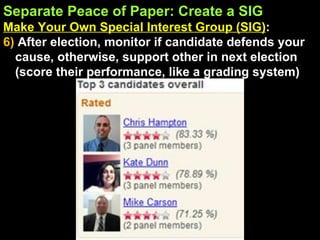
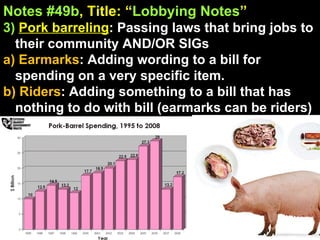
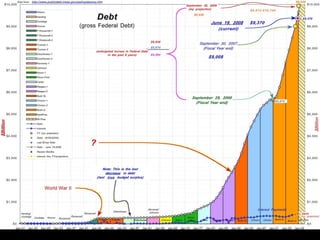
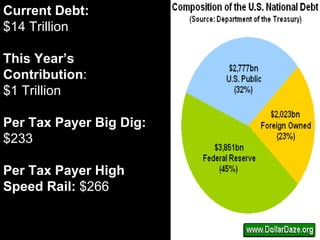
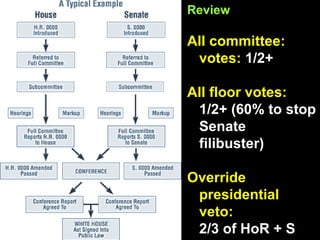
The document provides an overview of the legislative process in Congress and discusses lobbying. It defines key terms like earmarks, riders, and pork barrel spending. It also outlines the steps a bill takes through committees and floors votes in both the House and Senate. Special interest groups are introduced as organizations that lobby Congress by donating money, endorse candidates, and monitor politicians' performance on issues. The document contains notes, journal prompts, and a review of the legislative process and lobbying techniques.