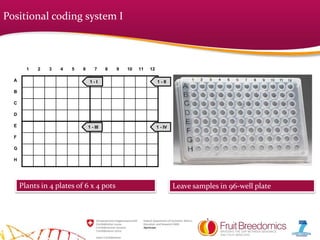
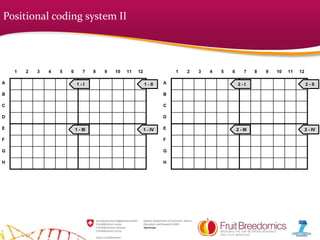
The document summarizes a technical session on fruit tree sampling procedures for genomic analysis. It describes using a 96-well format for efficiency and two coding systems for identifying individual plants without labeling - positional coding using the layout of pots in plates and a combination number system. The demonstration showed efficient procedures for puncturing leaves and expediting plates for analysis, though the whole process took more time than expected. Costs are relatively low compared to DNA extraction and analysis, requiring close work with partner companies.