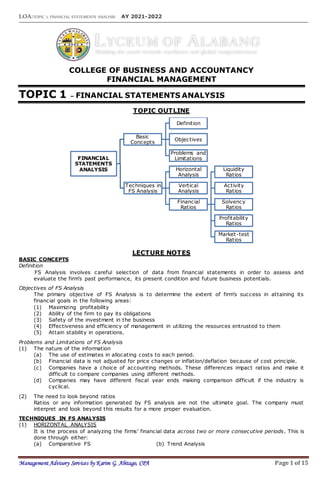
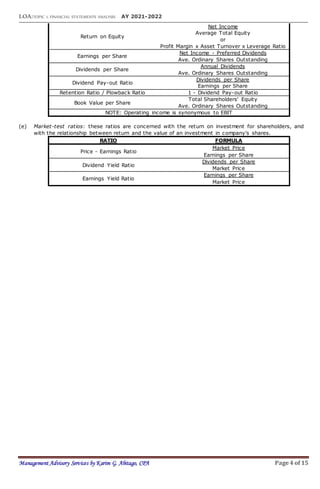
This document provides an overview of financial statement analysis techniques including horizontal analysis, vertical analysis, and calculating various financial ratios. It defines key terms, outlines objectives and limitations of financial statement analysis, and provides formulas and explanations for various liquidity, activity, solvency, profitability, and market-test ratios. Examples and exercises are also included to demonstrate applying these techniques.