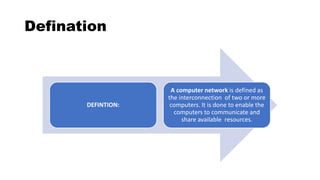
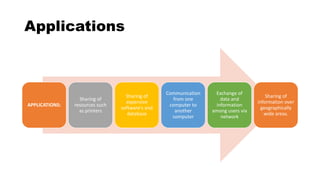
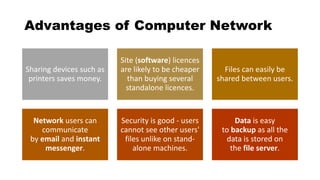
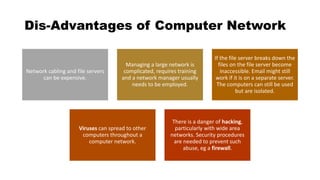
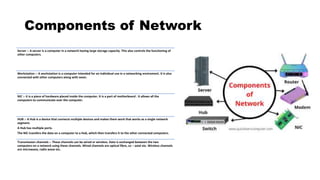
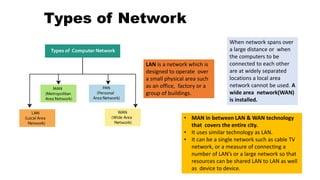
This document provides an overview of basic computer network concepts. It defines a computer network as interconnecting two or more computers to enable communication and sharing of resources. It describes common network applications like sharing printers, software, databases and exchanging information. It also outlines components of a network like servers, workstations, network interface cards, hubs and transmission channels. Additionally, it discusses different types of networks including LAN, WAN and MAN and various network topologies such as bus, star and ring configurations.