ectopic pregnancy.pptx
- 2. An “ectopic” or “ectopic pregnancy” (graviditas extrauterine, S.ec-topica) implies the development of a fetal egg not in the uterine cavity, but outside it.
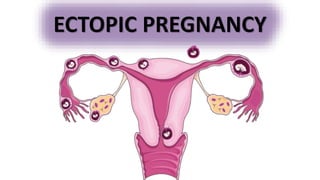
- 3. An ectopic pregnancy is an extrauterine pregnancy.Almost all ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube (>95%).
- 5. Sites of implantation of 1800 ectopic pregnancies from a 10-year population-based study. (Data from Callen, 2000; Bouyer, 2003.)
- 6. Two national guidelines are available covering the diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy: •RCOG/AEPU Joint Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Ectopic Pregnancy, Nov 16. •NICE Guideline 126: Ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage: diagnosis and initial management, Apr 19
- 8. The cause of ectopic pregnancy is either the delayed advancement of the egg or its accelerated maturation. The following factors contribute to this: • Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs(PID SIN); • Reconstructive plastic surgery on the fallopian tubes; • In vitro fertilization; • Tumors and tumor-like formations of the uterus and its appendages; • Endometriosis; • Tuberculosis • Sexual infantilism; • Anomalies in the position and development of the genital organs; • Irregularities in the migration of the fetal egg(migracio ovi externum); • Increased proteolytic activity of trophoblast; • Endocrine diseases. • Previous ectopic pregnancy (15% chances of next) ETIOLOGY
- 9. •Previous ectopic pregnancy (risk is around 15-18.5%) •IVF •Fallopian tube damage (may be secondary to infection, surgery) •Adhesions •Smoking •Intrauterine contraceptive device •Progestogen-only pill RISK FACTORS
- 10. Ectopic Pregnancy Triad: amenorrhea, vaginal spotting, and abdominal pain. NB!! Clinical Presentation differs if the patient has an ectopic or an ruptured ectopic Women has dubious and probable signs of pregnancy, there are changes in taste and appetite, nausea, salivation or vomiting, delayed menstruation, engorgement of the mammary glands may be observed !!
- 11. Symptoms • Abdominal/pelvic pain • Vaginal bleeding • Amenorrhoea • Shoulder tip pain (a sign of rupture and intra-abdominal bleeding, indicative of blood irritating the diaphragm) • Urinary discomfort • GI upset • Syncopal attacks Signs • Abdominal/pelvic tenderness • Rebound tenderness, peritonism • Abdominal distention • Pallor • Cervical motion tenderness (refers to pain on movement of the cervix during a bimanual examination, indicative of pelvic inflammation) • Cullen Sign Bruising around the umbilicus’s Turner sign Bruising around flanks Evidence of Hemoperitoneum
- 12. PRIMARY OVARIAN ECTOPIC Spiegelberg’s criteria
- 13. A. Transvaginal sonogram shows a gestational sac containing fetal parts of a 16-week gestation. The placenta is marked by a red asterisk.
- 14. B. Due to concern for extensive parasitic blood supply to the pregnancy, exploratory laparotomy was performed. Here, the right ovary is lifted by the surgeon, and the fallopian tube is the cordlike structure stretched across the top of the mass. Due to mass size and vascularity and scant normal ovarian stroma, this patient was treated by right salpingo-oophorectomy. (Photograph contributed by Dr. Kyler Elwell.)
- 15. PRIMARY ABDOMINAL ECTOPIC Studdiford criteria
- 16. Sagittal view of an abdominal pregnancy at term. The placenta is implanted on the posterior surface of the uterus and broad ligament. The enlarged, flattened uterus is located just beneath the anterior abdominal wall and to the level of the umbilicus. The cervix and vagina are pulled up and are dislodged anteriorly and superiorly by the large fetal head in the cul-de-sac. Placenta Uterus Bladder
- 17. NB! Primary ovarian/abdominal are much rarer as compared to secondary ovarian and abdominal ectopic Secondary ovarian ectopic Pregnancy coming out from uterus and settling in the ovary Secondary abdominal ectopic Pregnancy coming out from tube and settling in the abdomen #Term abdominal pregnancy is very rare- Delivered by laparotomy
- 18. CERVICAL ECTOPIC Cervical pregnancy. Transvaginal sonographic findings may include: (1) an hourglass uterine shape and ballooned cervical canal; (2) gestational tissue at the level of the cervix (black arrow); (3) absent intrauterine gestational tissue (white arrows); and (4) a portion of the endocervical canal seen interposed between the gestation and the endometrial canal
- 19. CESAREAN SCAR ECTOPIC A. Transvaginal sonogram of a uterus with a cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) in a sagittal plane. An empty uterine cavity is identified by a bright hyperechoic endometrial stripe (long, white arrow). An empty cervical canal is similarly identified (short, white arrow). Last, an intrauterine mass is seen in the anterior part of the uterine isthmus (red arrows). Healthy myometrium between the bladder and gestational sac is absent.
- 20. CESAREAN SCAR B. Hysterectomy specimen containing a cesarean scar pregnancy. C. This same hysterectomy specimen is transversely sectioned at the level of the uterine isthmus and through the gestational sac. The uterine body lies to the left, and the cervix is on the right. A metal probe is placed through the endocervical canal to show the eccentric development of this gestation. Only a thin layer of myometrium overlies this pregnancy, which pushes anteriorly through the uterine wall
- 21. CORNUATE ECTOPIC
- 24. OTHER RARE PARTS
- 25. Time of rupture: • Isthmus ectopic- 4-6 weeks • Ampullary ectopic- 6-8 weeks • Interstitial/ Cornual ectopic- 12-16 weeks
- 26. Pain is the most common complaint +/- vaginal bleeding. A ruptured ectopic will present with signs of shock and signs of peritonism. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- 28. Pain can be divided as being epigastric, umbilical or suprapubic (hypogastric). Ectopic typically presents as suprapubic pain but pain but may radiate to other areas, especially if ruptured.
- 29. Referred pain is important to understand. Certain areas of the abdomen can refer pain else where. A good example is in ectopic is in ectopic pregnancy when irritation of the diaphragm can diaphragm can cause shoulder tip pain.
- 30. Rapid onset severe constant pain differentials
- 31. Differential Diagnosis for ectopic pregnancy •Acute salpingitis •Abortion •Ruptured corpus luteum •Acute appendicitis •Dysfunctional uterine bleeding •Adnexal torsion •Degenerating leiomyomata •Endometriosis
- 32. For any pregnant lady presenting with abdominal pain and/or vaginal bleeding the most important investigations: •FBC •EUC •Urine analysis •β-hCG – Pregnancy test is almost always +ve, but serum β-HCG levels are lower than expected for normal pregnancy •Transvaginal Ultrasound/sonography Remember Levels of hCG that plateau in the first 8 weeks of pregnancy indicate an abnormal pregnancy, which may either be a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. INVESTIGATION
- 33. Other Investigations to support or rule out differentials” •Progesterone •Amylase/Lipase •LFT •ESR/CRP
- 34. Hormonal changes in pregnancy. Note First trimester bHCG peaks then drops
- 35. When the hCG level equals or exceeds 1500 to 2000 mIU/mL, an intrauterine gestational sac is usually seen on transvaginal ultrasound; in fact, when the hCG level meets or exceeds this threshold and no gestational sac is seen, the patient has a high Likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy β-HCG levels and correlation β-HCG rising normally β-HCG rising but not normally β-HCG is decreasing Failed pregnancy (eg, spontaneous abortion, tubal abortion, spontaneously resolving ectopic pregnancy).
- 36. STANDARD INVESTIGATION Transvaginal Ultrasound/sonography
- 40. Treatment for ectopic pregnancy should be comprehensive. It consists of the following stages: 1. Surgery- stopping bleeding; 2. Restoring blood loss and combating shock; 3. Rehabilitation of reproductive function. TREATMENT
- 41. MANAGEMENT Management of ectopic pregnancy falls into three main types; 1.Expectant your condition is carefully monitored to see whether treatment is necessary 2.Pharmacological a medicine called methotrexate is used to stop the pregnancy growing 3.Surgical surgery is used to remove the pregnancy, usually along with the affected fallopian tube
- 43. Expectant management This may be considered in carefully selected patients. They should be well, with only minor pain and low or declining B-hCG. Patients must also be willing and able to attend follow-up. NICE guidelines 126 advise the following women are offered expectant management: •Clinically stable and pain-free and •Unruptured tubal ectopic pregnancy measuring less than 35 mm with no visible heartbeat on transvaginal ultrasound scan and •Serum B-hCG levels of 1,000 IU/L or less and •Able to return for follow-up They also state it may be considered in women with serum B-hCG levels above 1,000 IU/L and below 1,500 IU/L. Serum B-hCG should be measured at days 2, 4 and 7 and then weekly. Levels should fall by 15% at each measurement, if they do not arrange senior review.
- 44. Pharmacological management Single-dose methotrexate (though some may require subsequent doses) can be considered as an alternative to surgery. NICE guidelines 126 advise the following women are offered methotrexate: •Have no significant pain and •Have an unruptured tubal ectopic pregnancy with an adnexal mass smaller than 35 mm with no visible heartbeat and •Have a serum B-hCG level less than 1,500 IU/litre and •Do not have an intrauterine pregnancy (as confirmed on an ultrasound scan) and •Able to return for follow-up A choice of either methotrexate or surgical management should be offered to women with a B-hCG level 1,500-5,000 IU/litre, who are able to return for follow-up and meet all of these criteria: •No significant pain •Unruptured ectopic pregnancy with an adnexal mass smaller than 35 mm with no visible heartbeat •No intrauterine pregnancy (as confirmed on an ultrasound scan) Those managed with methotrexate should have serum B-hCG measured at days 4 and 7 and then weekly. If levels plateau or rise arrange senior review.
- 47. Pharmacology Methotrexate is a folic acid antagonist widely used for treatment of neoplasia, severe psoriasis and Rheumatoid arthritis. Side effects of methotrexate is conjunctivitis and gastrointestinal upset. Methotrexate therapyThe optimal candidates for MTX treatment of ectopic pregnancy are hemodynamically stable, willing and able to comply with post-treatment follow-up, have a human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentration ≤5000/mL, and no fetal cardiac activity. Contraindications for ectopic include renal failure, immunodeficiency, allergy, heterotopic pregnancy heterotopic pregnancy with coexisting viable intrauterine pregnancy, breastfeeding, unable to complete methotrexate management
- 48. Surgical management There are a number of indications for surgery, when indicated the laparoscopic approach should be used over open surgery when possible. There are two main terms to be aware of in the surgical management of tubal ectopics: •Laparoscopic salpingectomy: laparoscopy refers to 'key-hole' surgery. Salpingectomy refers to the removal of a fallopian tube, in this case, the tube affected by the ectopic pregnancy. This is generally the preferred treatment. •Laparoscopic salpingotomy: this refers to a procedure that aims to preserve the fallopian tube. The tube is opened and the ectopic is removed. It is generally considered if the contralateral tube is damaged or there are other fertility-based concerns. NB! The difference between salpingostomy and salpingotomy!!! Is that salpingostomy is (surgery) the surgical unblocking of a blocked fallopian tube while salpingotomy is the operation of making an incision into a fallopian tube to remove an ectopic.
- 49. Salpingectomy is removal of the fallopian tube (uterine tube). Salpingostomy is removing a section of the fallopian tube (uterine tube) Indications for salpingectomy: • Recurring ectopic pregnancies or are > 5 cm • Severely damage tubes • No future childbearing is planned
- 52. NICE guidelines 126 advise the following women are offered surgery as first-line management: •Unable to return to follow up or •An ectopic pregnancy and significant pain or •An ectopic pregnancy with an adnexal mass of 35 mm or larger or •An ectopic pregnancy with a foetal heartbeat visible on an ultrasound scan or •An ectopic pregnancy and a serum hCG level of 5,000 IU/litre or more Patients who have required salpingotomy require weekly serum B-HCG measurements until negative. Approximately 1 in 5 will need further treatment (e.g. methotrexate, salpingectomy). Women who have had a salpingectomy should conduct a urinary pregnancy test at three weeks and contact the gynaecology department if positive.
- 53. Emergency Haemodynamically unstable patients (ruptured ectopic) Signs and symptoms •Acute abdomen with worsening pain •Abdominal distention •Shoulder tip pain (Kehr’s sign) •Signs of shock Management - Resuscitation •Two large-bore IV line and IV fluids •Cross match 6U blood •Call senior help and aesthetics assistance urgently Surgery – Laparotomy with salpingectomy
- 54. Emergency surgery is indicated in patients with a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. If the patient is unstable, assess in an ABCDE manner, escalate with peri-arrest and/or major haemorrhage call.
- 55. Anti-D rhesus prophylaxis Rhesus D (RhD) negative women may require anti-D rhesus prophylaxis. Anti-D immunoglobulin is given to reduce the risk of maternal sensitisation in events where FMH is likely. The advice from NICE and the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) is as follows (each trust will have local guidelines): 1. NICE guidance 126 states anti-D rhesus prophylaxis should be offered to all RhD-negative women who have surgery to manage an ectopic pregnancy. 2. RCOG/AEPU Joint Guideline advises anti-D rhesus prophylaxis should be offered to all RhD-negative women who have surgery to manage an ectopic pregnancy or where bleeding is repeated, heavy or associated with abdominal pain. Rhesus (Rh) refers to a group of red cell antigens, the most important being RhD. Problems arise when RhD- negative mothers have RhD-positive foetuses. Feto- maternal haemorrhage (FMH) can expose the mother to RhD-positive blood. In response, a RhD-negative mother generates anti(D) antibodies. In subsequent pregnancies anti(D) antibodies can cross the placenta and lead to haemolytic disease of the newborn.
- 56. Side effects of methotrexate is conjunctivitis and gastrointestinal upset. COMPLICATION AND PROGNOSIS
- 58. REFERENCES • https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng126/resources/ectopic-pregnancy-and- miscarriage-diagnosis-and-initial-management-pdf-66141662244037 • https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/1471-0528.14189 • https://app.pulsenotes.com/specialities/gynaecology/notes/ectopic-pregnancy • https://armandoh.org/disease/ectopic-pregnancy/ • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RoBohoUrx4c • https://meduniver.com/Medical/Akusherstvo/1155.html • Books- Williams, Saveleva
- 59. Thanks For Your Attention!
Editor's Notes
- PID- Pelvic infl. Disease SIN-salphingitis isthimica nodosa
- EUC-ELECTROLYTE UREA CREATININE
- FHB- fetal heart beat