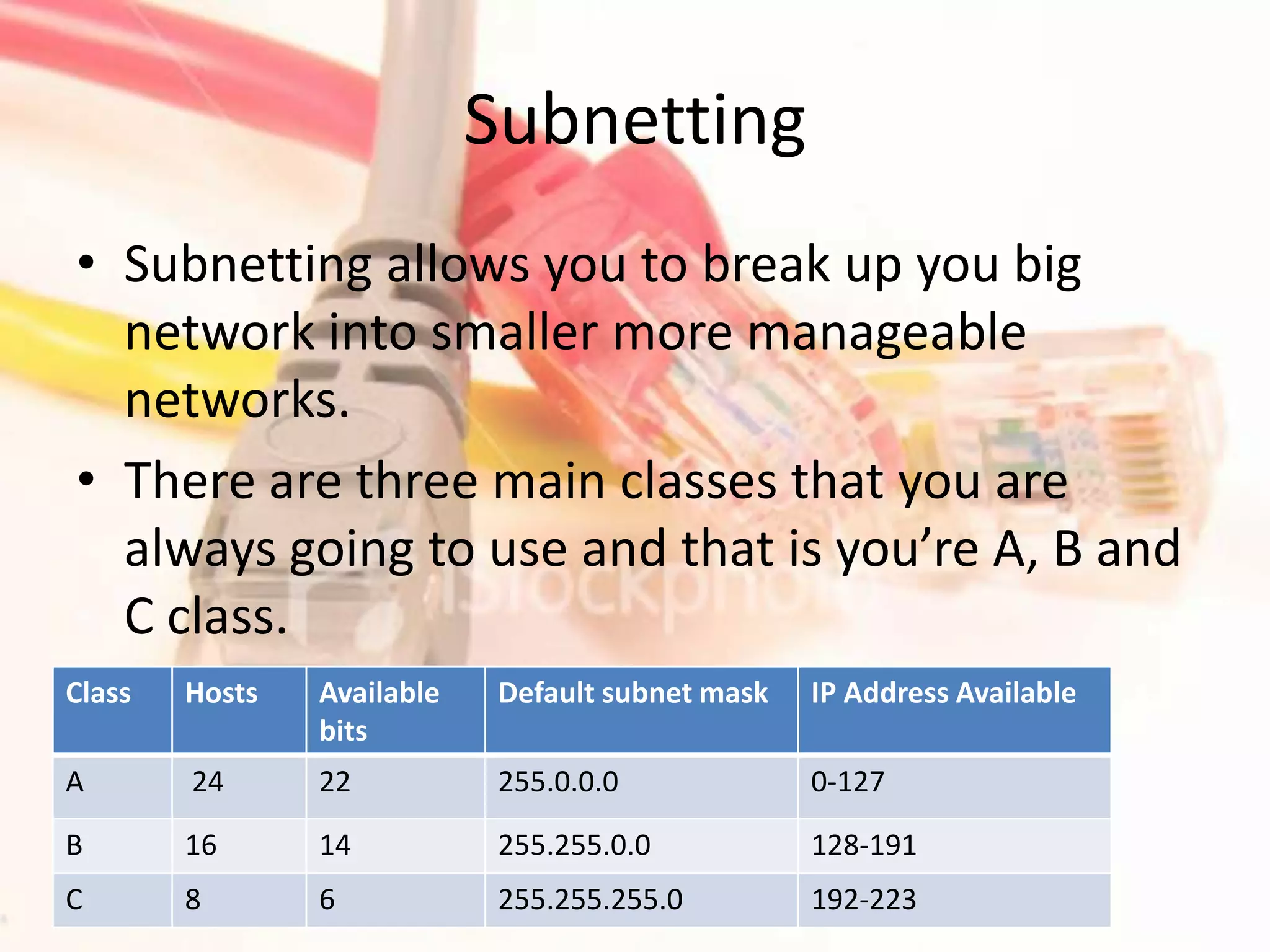
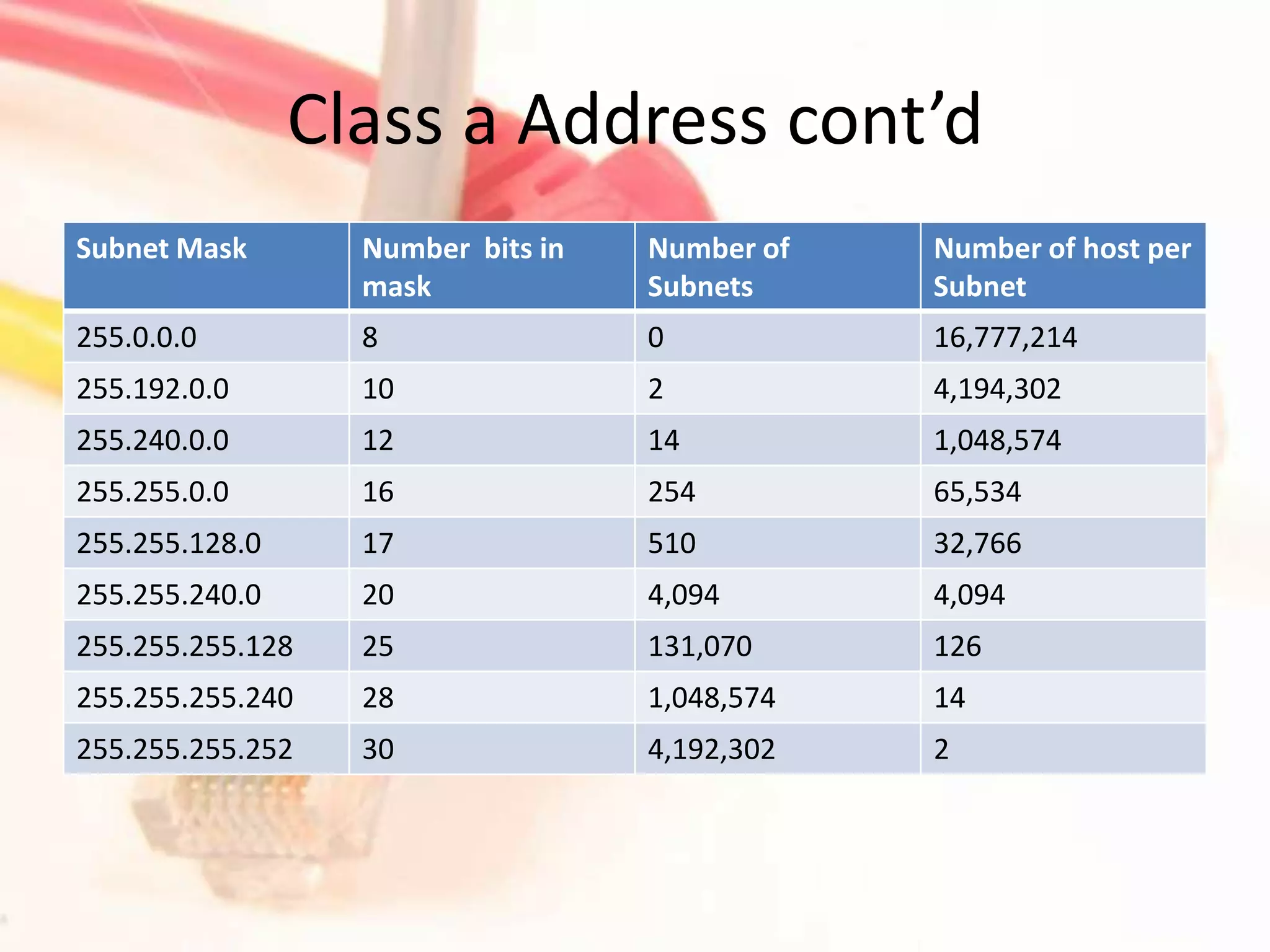
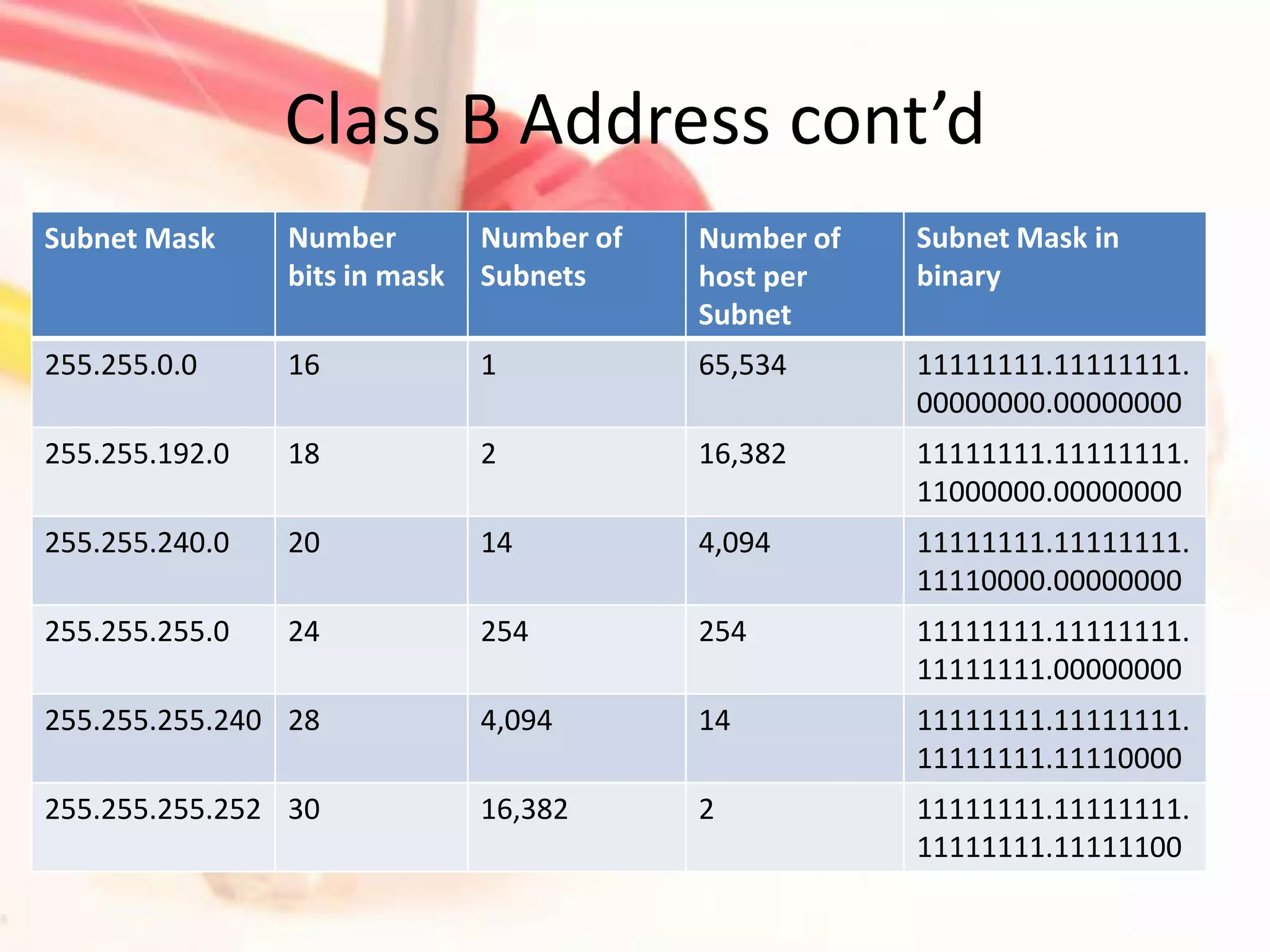
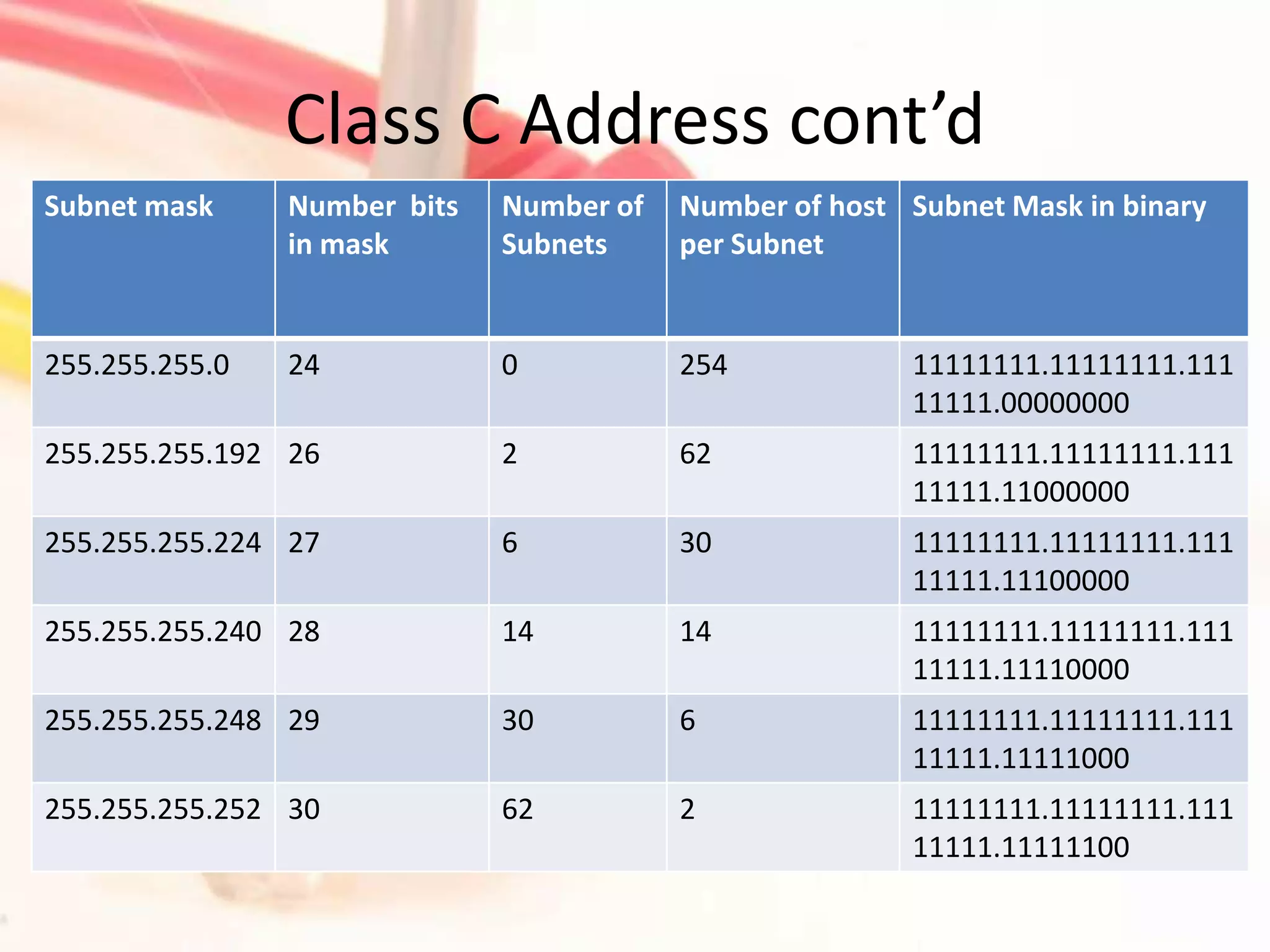
This document discusses how to subnet class A, B, and C IP addresses. It explains that IP addresses are made up of 32 bits divided into four octets. It also provides information on binary numbering and how subnetting allows you to break up large networks into smaller, more manageable subnets. For each address class, it notes the default subnet mask and host range, and that bits need to be borrowed from the host portion of the mask to create additional subnets.