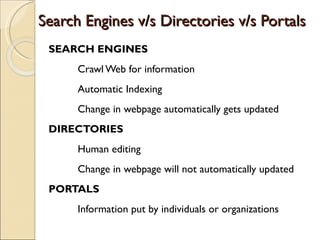
The document provides an overview of search engines, including their basics, functioning, types, advantages, disadvantages, and limitations. It defines a search engine as a tool that indexes websites and builds databases to help retrieve information from the internet based on keyword queries. The document discusses different types of search engines such as general, meta, subject-specific, intelligent/specialized, deep/invisible web, and scholarly literature search engines. It also compares search engines to directories and portals.
![Search Engines Shamprasad Pujar IGIDR, Mumbai [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sengine-110502073729-phpapp02/85/Search-Engines-1-320.jpg)