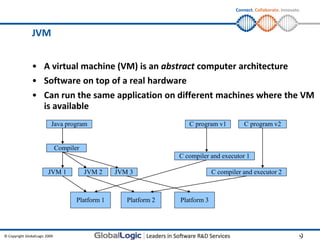
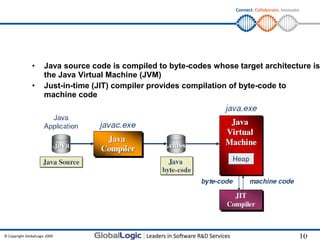
The document provides an overview of basic Java programming concepts. It discusses how Java enables software portability across different hardware systems and operating systems through the use of bytecode and the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It also covers Java language fundamentals like data types, packages, I/O, and garbage collection. The document includes examples and exercises for attendees to practice writing, compiling and running simple Java programs.



![Connect. Collaborate. Innovate.
• Example C program
void main()
{
int arr[2];
printf(“%dn”, arr*3+);
}
• Run this on windows (using turbo c)
• Run this on Unix (using gcc)
• Compare the results
© Copyright GlobalLogic 2009 7
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaprogrammingbasics-120628015528-phpapp01/85/Java-programming-basics-7-320.jpg)

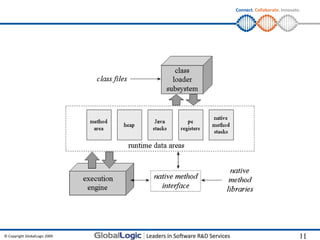




![Connect. Collaborate. Innovate.
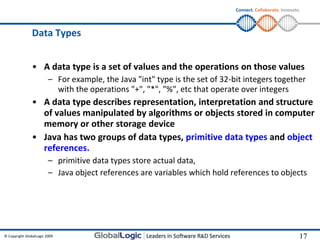
Data Types
• Arrays
int[] anArray;
anArray = new int[10];
OR
int[] anArray = new int[10];
• String
String greeting = "Hello world!";
character array
char[] helloArray = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '.'};
String helloString = new String(helloArray);
Basic operations
length
concat
substr
• int, float
© Copyright GlobalLogic 2009 18
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaprogrammingbasics-120628015528-phpapp01/85/Java-programming-basics-18-320.jpg)