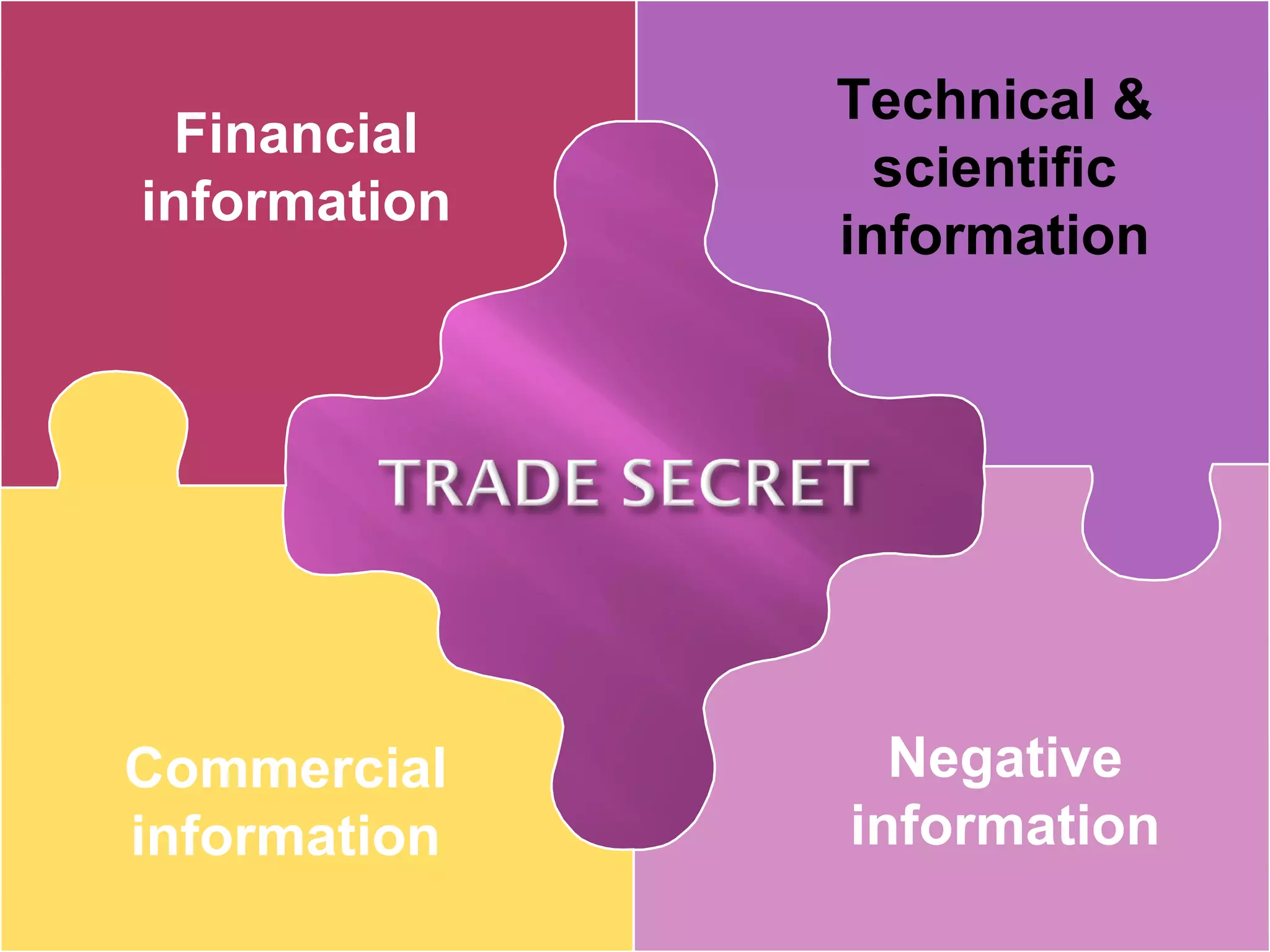
This document discusses intellectual property rights, specifically trade secrets. It defines a trade secret as confidential business information that provides a competitive advantage. Examples provided include formulas, recipes, and manufacturing techniques. It outlines best practices for maintaining secrecy such as limiting access, using non-disclosure agreements, and marking materials as proprietary. Trade secrets can potentially last indefinitely while providing worldwide protection without registration or fees. However, they can be lost through improper disclosure or discovery through legal reverse engineering. The document contrasts trade secrets with patents and discusses common ways trade secrets are stolen, such as by departing employees.