Lec17 mosfet iv
- 2. Substrate Channel Drain Insulator Gate Operation of a transistor VSG > 0 n type operation Positive gate bias attracts electrons into channel Channel now becomes more conductive More electrons Source VSD VSG
- 3. Some important equations in the inversion regime (Depth direction) VT = φms + 2ψB + ψox Wdm = √[2εS(2ψB)/qNA] Qinv = -Cox(VG - VT) ψox = Qs/Cox Qs = qNAWdm VT = φms + 2ψB + √[4εSψBqNA]/Cox Substrate Channel Drain Insulator Gate Source x
- 4. ECE 663 MOSFET Geometry x y z L Z S D VG VD
- 5. ECE 663 How to include y-dependent potential without doing the whole problem over?
- 6. ECE 663 Assume potential V(y) varies slowly along channel, so the x-dependent and y-dependent electrostats are independent (GRADUAL CHANNEL APPROXIMATION) i.e., Ignore ∂Ex/∂y Potential is separable in x and y
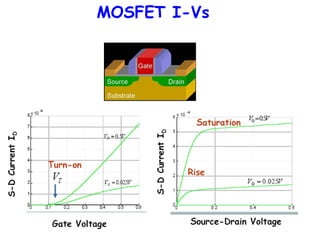
- 7. ECE 663 How to include y-dependent potentials? ψS = 2ψB + V(y) VG = ψS + √[2εSψSqNA]/Cox Need VG – V(y) > VT to invert channel at y (V increases threshold) Since V(y) largest at drain end, that end reverts from inversion to depletion first (Pinch off) SATURATION [VDSAT = VG – VT]
- 8. j = qninvv = (Qinv/tinv)v I = jA = jZtinv = ZQinvv ECE 663 So current: Qinv = -Cox[VG – VT - V(y)] v = -µeffdV(y)/dy
- 9. ECE 663 So current: I = µeff ZCox[VG – VT - V(y)]dV(y)/dy I = µeff ZCox[(VG – VT )VD- VD 2 /2]/L Continuity implies ∫Idy = IL
- 10. ECE 663 But this current behaves like a parabola !! ID VD IDsat VDsat I = µeff ZCox[(VG – VT )VD- VD 2 /2]/L We have assumed inversion in our model (ie, always above pinch-off) So we just extend the maximum current into saturation… Easy to check that above current is maximum for VDsat = VG - VT Substituting, IDsat = (CoxµeffZ/2L)(VG-VT)2
- 11. What’s Pinch off? 0 0 0 0 VG VG Now add in the drain voltage to drive a current. Initially you get an increasing current with increasing drain bias 0 VD VG VG When you reach VDsat = VG – VT, inversion is disabled at the drain end (pinch-off), but the source end is still inverted The charges still flow, just that you can’t draw more current with higher drain bias, and the current saturates
- 12. Square law theory of MOSFETs I = µeff ZCox[(VG – VT )VD- VD 2 /2]/L, VD < VG - VT I = µeff ZCox(VG – VT )2 /2L, VD > VG - VT J = qnv n ~ Cox(VG – VT ) v ~ µeffVD /L NEW
- 13. ECE 663 Ideal Characteristics of n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET
- 14. ECE 663 Drain current for REALLY small VD ( ) ( )[ ] ( )TGD DTGinD DDTGinD VVV VVVC L Z I VVVVC L Z I −<< −≈ −−= µ µ 2 2 1 Linear operation Channel Conductance: )( TGin VD D D VVC L Z V I g G −µ= ∂ ∂ ≡ Transconductance: Din VG D m VC L Z V I g D µ= ∂ ∂ ≡
- 15. ECE 663 In Saturation • Channel Conductance: • Transconductance: ( )2 2 TGinD VVC L Z satI −µ= 0= ∂ ∂ ≡ GVD D D V I g ( )TGin VG D m VVC L Z V I g D −µ= ∂ ∂ ≡
- 16. ECE 663 Equivalent Circuit – Low Frequency AC • Gate looks like open circuit • S-D output stage looks like current source with channel conductance gmdD G VG D D VD D D vgvgi V V I V V I I DG += δ ∂ ∂ +δ ∂ ∂ =δ
- 17. ECE 663 • Input stage looks like capacitances gate-to-source(gate) and gate-to-drain(overlap) • Output capacitances ignored -drain-to-source capacitance small Equivalent Circuit – Higher Frequency AC
- 18. ECE 663 • Input circuit: • Input capacitance is mainly gate capacitance • Output circuit: ( ) ggateggdgsin vfCjvCCji π≈+ω= 2 gmout vgi ≈ gate m in out fC g i i π = 2 Din VG D m VC L Z V I g D µ= ∂ ∂ ≡ Equivalent Circuit – Higher Frequency AC
- 19. ECE 663 Maximum Frequency (not in saturation) • Ci is capacitance per unit area and Cgate is total capacitance of the gate • F=fmax when gain=1 (iout/iin=1) 2max max 22 2 L V ZLC CV L Z f C g f Dn i iDn gate m π µ = π µ = π = ZLCC igate =
- 20. ECE 663 Maximum Frequency (not in saturation) 2max 2 L V f Dn π µ = LVv vL D / / 1 max µ ω = = (Inverse transit time) NEW
- 21. ECE 663 Switching Speed, Power Dissipation ton = CoxZLVD/ION Trade-off: If Cox too small, Cs and Cd take over and you lose control of the channel potential (e.g. saturation) (DRAIN-INDUCED BARRIER LOWERING/DIBL) If Cox increases, you want to make sure you don’t control immobile charges (parasitics) which do not contribute to current.
- 22. ECE 663 Switching Speed, Power Dissipation Pdyn = ½ CoxZLVD 2 f Pst = IoffVD
- 24. ECE 663 CMOS NOT gate (inverter) Positive gate turns nMOS on Vin = 1 Vout = 0
- 25. ECE 663 CMOS NOT gate (inverter) Negative gate turns pMOS on Vin = 0 Vout = 1
- 26. ECE 663 So what? • If we can create a NOT gate we can create other gates (e.g. NAND, EXOR)
- 27. ECE 663 So what? Ring Oscillator
- 28. ECE 663 So what? • More importantly, since one is open and one is shut at steady state, no current except during turn-on/turn-off Low power dissipation
- 29. ECE 663 Getting the inverter output Gain ON OFF
- 30. ECE 663 0= ∂ ∂ ≡ GVD D D V I g ( )TGin VG D m VVC L Z V I g D −µ= ∂ ∂ ≡ What’s the gain here?
- 32. ECE 663 BJT vs MOSFET • RTL logic vs CMOS logic • DC Input impedance of MOSFET (at gate end) is infinite Thus, current output can drive many inputs FANOUT • CMOS static dissipation is low!! ~ IOFFVDD • Normally BJTs have higher transconductance/current (faster!) IC = (qni 2 Dn/WBND)exp(qVBE/kT) ID = µCoxW(VG-VT) 2 /L gm = ∂IC/∂VBE = IC/(kT/q) gm = ∂ID/∂VG = ID/[(VG-VT)/2] • Today’s MOSFET ID >> IC due to near ballistic operation NEW
- 33. ECE 663 What if it isn’t ideal? • If work function differences and oxide charges are present, threshold voltage is shifted just like for MOS capacitor: • If the substrate is biased wrt the Source (VBS) the threshold voltage is also shifted i BAs B i f ms i BAs BFBT C qN C Q C qN VV )2(2 2 )2(2 2 ψε +ψ+ −φ= ψε +ψ+= i BSBAs BFBT C VqN VV )2(2 2 +ψε +ψ+=
- 34. ECE 663 Threshold Voltage Control • Substrate Bias: i BSBAs BFBT C VqN VV )2(2 2 +ψε +ψ+= ( )BBSB i As T BSTBSTT V C qN V VVVVV ψ−+ψ ε =∆ =−=∆ 22 2 )0()(
- 35. ECE 663 Threshold Voltage Control-substrate bias
- 36. ECE 663 It also affects the I-V VG The threshold voltage is increased due to the depletion region that grows at the drain end because the inversion layer shrinks there and can’t screen it any more. (Wd > Wdm) Qinv = -Cox[VG-VT(y)], I = -µeffZQinvdV(y)/dy VT(y) = ψ + √2εsqNAψ/Cox ψ = 2ψB + V(y)
- 37. ECE 663 It also affects the I-V IL = ∫µeffZCox[VG – (2ψB+V) - √2εsqNA(2ψB+V)/Cox]dV I = (ZµeffCox/L)[(VG–2ψB)VD –VD 2 /2 -2√2εsqNA{(2ψB+VD)3/2 -(2ψB)3/2 }/3Cox]
- 38. ECE 663 We can approximately include this… Include an additional charge term from the depletion layer capacitance controlling V(y) Q = -Cox[VG-VT]+(Cox + Cd)V(y) where Cd = εs/Wdm Q = -Cox[VG –VT - MV(y)], M = 1 + Cd/Cox ID = (ZµeffCox/L)[(VG-VT - MVD/2)VD]
- 39. ECE 663 Comparison between different models Square Law Theory Body Coefficient Bulk Charge Theory Still not good below threshold or above saturation
- 40. ECE 663 Mobility • Drain current model assumed constant mobility in channel • Mobility of channel less than bulk – surface scattering • Mobility depends on gate voltage – carriers in inversion channel are attracted to gate – increased surface scattering – reduced mobility
- 41. ECE 663 Mobility dependence on gate voltage )(1 0 TG VV −θ+ µ =µ
- 42. ECE 663 Sub-Threshold Behavior • For gate voltage less than the threshold – weak inversion • Diffusion is dominant current mechanism (not drift) L Lnon qAD y n qADAJI nnDD )()( − −≈ ∂ ∂ −== kTVq i kTq i DBs Bs enLn enn /)( /)( )( )0( −ψ−ψ ψ−ψ = =
- 43. ECE 663 Sub-threshold ( ) kTqkTqV kT in D sD B ee L enqAD I // / 1 ψ− ψ− −= We can approximate ψs with VG-VT below threshold since all voltage drops across depletion region ( ) ( ) kTVVqkTqV kT in D TGD B ee L enqAD I // / 1 −− ψ− −≈ •Sub-threshold current is exponential function of applied gate voltage •Sub-threshold current gets larger for smaller gates (L)
- 44. ECE 663 Subthreshold Characteristic ( )( )GD VI S ∂∂ ≡ log 1 Subthreshold Swing
- 45. Tunneling transistor – Band filter like operation J Appenzeller et al, PRL ‘04 Ghosh, Rakshit, Datta (Nanoletters, 2004) (Sconf)min=2.3(kBT/e).(etox/m) Hodgkin and Huxley, J. Physiol. 116, 449 (1952a) Subthreshold slope = (60/Z) mV/decade Much of new research depends on reducing S !
- 46. Much of new research depends on reducing S ! • Increase ‘q’ by collective motion (e.g. relay) Ghosh, Rakshit, Datta, NL ‘03 • Effectively reduce N through interactions Salahuddin, Datta • Negative capacitance Salahuddin, Datta • Non-thermionic switching (T-independent) Appenzeller et al, PRL • Nonequilibrium switching Li, Ghosh, Stan • Impact Ionization Plummer
- 47. ECE 663 More complete model – sub-threshold to saturation • Must include diffusion and drift currents • Still use gradual channel approximation • Yields sub-threshold and saturation behavior for long channel MOSFETS • Exact Charge Model – numerical integration ∫ ∫ βψ µε = ψ ψ β−βψD s B V p p V D ns D p n VF e LL Z I 0 0 0 ,,
- 48. ECE 663 Exact Charge Model (Pao-Sah) – Long Channel MOSFET http://www.nsti.org/Nanotech2006/WCM2006/WCM2006-BJie.pdf
- 49. ECE 663