Silabus fisika indo 2009 2014 indo+inggris-
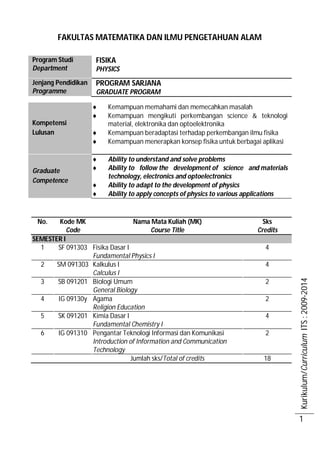
- 1. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 1 FAKULTAS MATEMATIKA DAN ILMU PENGETAHUAN ALAM Program Studi Department FISIKA PHYSICS Jenjang Pendidikan Programme PROGRAM SARJANA GRADUATE PROGRAM Kompetensi Lulusan Kemampuan memahami dan memecahkan masalah Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan science & teknologi material, elektronika dan optoelektronika Kemampuan beradaptasi terhadap perkembangan ilmu fisika Kemampuan menerapkan konsep fisika untuk berbagai aplikasi Graduate Competence Ability to understand and solve problems Ability to follow the development of science and materials technology, electronics and optoelectronics Ability to adapt to the development of physics Ability to apply concepts of physics to various applications No. Kode MK Code Nama Mata Kuliah (MK) Course Title Sks Credits SEMESTER I 1 SF 091303 Fisika Dasar I Fundamental Physics I 4 2 SM 091303 Kalkulus I Calculus I 4 3 SB 091201 Biologi Umum General Biology 2 4 IG 09130y Agama Religion Education 2 5 SK 091201 Kimia Dasar I Fundamental Chemistry I 4 6 IG 091310 Pengantar Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi Introduction of Information and Communication Technology 2 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 18
- 2. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 2 SEMESTER II 1 SF 091304 Fisika Dasar II Fundamental Physics II 4 2 SF 091305 Fisika Dasar III Fundamental Physics III 2 3 SF 091306 Metode Pengukuran Fisika Physical Measurement Method 3 4 SM 091304 Kalkulus II Calculus II 4 5 SK 091202 Kimia Dasar II Fundamental Chemistry II 3 6 IG 091308 Bahasa Inggris English 2 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 18 SEMESTER III 1 SF 091307 Elektronika Dasar I Fundamental Electronics I 3 2 SF 091309 Fisika Matematika I Mathematical Physics I 4 3 SF 091311 Termodinamika Thermodynamics 3 4 SF 091312 Fisika Modern Modern Physics 4 5 SF 091313 Mekanika Mechanics 4 6 IG 091306 Kewarganegaraan Civics 2 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 20 SEMESTER IV 1 SF 091205 Metode Numerik Numerical Method 2 2 SF 091308 Elektronika Dasar II Fundamental Electronics II 3 3 SF 091310 Fisika Matematika II Mathematical Physics II 4 4 SF 091314 Gelombang Wave 4 5 Pilihan Minat/Bidang Elective Courses 6 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 19
- 3. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 3 SEMESTER V 1 SF 091315 Medan Elektromagnet Electromagnetic Field 4 2 SF 091316 Fisika Laboratorium Laboratory Physics 2 3 SF 091317 Fisika Kuantum Quantum Physics 4 4 Pilihan Minat/Bidang Elective Courses 9 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 19 SEMESTER VI 1 SF 091206 Fisika Komputasi Computational Physics 4 2 SF 091318 Fisika Statistik Statistical Physics 3 3 IG 091306 Bahasa Indonesia Indonesian 2 4 Pilihan Minat/Bidang Elective Courses 9 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 18 SEMESTER VII 1 SF 091207 Seminar Seminar 2 2 SF 091319 Fisika Zat Padat Solid State Physics 4 3 SF 091320 Fisika Inti Nuclear Physics 4 4 IG 091311 Pengantar Technopreneur Introduction to Technopreneurship 2 5 Pilihan Minat/Bidang Elective Courses 6 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 18 SEMESTER VIII 1 SF 091321 Tugas Akhir Final Project 6 2 Pilihan Minat/Bidang Elective Courses 8 Jumlah sks/Total of credits 14
- 4. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 4 PILIHAN MINAT / BIDANG ELECTIVE COURSES 1 SF 091209 Fisika Keramik Physics of Ceramics 3 2 SF 091211 Fisika Logam Physics of Metals 3 3 SF 091213 Korosi Corrossion 3 4 SF 091215 Difraksi Kristal Crystal Diffraction 3 5 SF 091217 Fisika Semikonduktor Physics of Semiconductors 3 6 SF 091219 Elektronika Electronics 3 7 SF 091221 Perpindahan Panas Heat Transfer 3 8 SF 091223 Analisis Sistem Fisis Analysis of Physics System 3 9 SF 091225 Pengolahan Sinyal Signal Processing 2 10 SF 091227 Pengolahan Citra Image Processing 3 11 SF 091231 Instrumentasi Optik Instrumentation Optics 3 12 SF 091233 Komputasi Optik Optics Computation 4 13 SF 091235 Fisika Matematika Lanjut Advanced Mathematical Physics 3 14 SF 091237 Teori Relativitas Khusus Special Theory of Relativity 2 15 SF 091239 Teori Group Group Theory 3 16 SF 091241 Geodinamika Geodynamics 3 17 SF 091256 Fisika Batuan Rock Physics 3 18 SF 091245 Analisa Well-Log Well-Log Analysis 3 19 SF 091247 Eksplorasi Geothermal Geothermal Exploration 3
- 5. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 5 PILIHAN MINAT / BIDANG ELECTIVE COURSES 1 SF 091208 Pengantar Fisika Bahan Introduction to Material Physics 3 2 SF 091210 Fisika Polimer Physics of Polymers 3 3 SF 091212 Fisika Bahan Komposit Physics of Composite Materials 3 4 SF 091214 Fisika Bahan Lanjut Physics of Advanced Materials 3 5 SF 091216 Spektro-mikrografi Spectroscopy and Micrography 3 6 SF 091218 Elektro Akustik Acoustics Electronics 3 7 SF 091220 Elektro Digital Digital Electronics 3 8 SF 091222 Mekanika Fluida Fluid Mechanics 2 9 SF 091224 Fisika Instrumentasi Instrumentation Physics 3 10 SF 091226 Fisika Bangunan Building Physics 3 11 SF 091228 Intellegent Instrumen Intelligent Instrument 3 12 SF 091230 Optika Modern Modern Optics 3 13 SF 091232 Optika Serat Fiber Optics 3 14 SF 091234 Elektromagnetika Electromagnetics 2 15 SF 091236 Fotonika Photonics 3 16 SF 091238 Pengantar Fisika Partikel Introduction to Particel Physics 3 17 SF 091240 Pengantar Kosmologi Introduction to Cosmology 3 18 SF 091242 Kapita Selekta Selective Topics 2 19 SF 091244 Elektromagnetika Terapan Applied Electromgnetics 2 20 SF 091246 Seismologi Seismology 3 21 SF 091248 Eksplorasi Kelistrikan Bumi Elective Methods and Application 3
- 6. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 6 22 SF 091250 Vulkanologi Vulcanology 3 23 SF 091252 Eksplorasi Seismik Seismic Exploration 4 24 SF 091254 Eksplorasi Medan Potensial Bumi Potentials Filed Exploration 3
- 7. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 7 SILABUS KURIKULUM /COURSE SYLLABUS MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091303: Fisika Dasar I SF 091303: Fundamental Physics I Credits: 3/0/1 Semester: I TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN / LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan dan menggunakan rumusan hukum-hukum dasar fisika tentang mekanika, mekanika fluida dan kalor. Students are able to explain and use formulas of fundamental laws of physics about the mechanics, fluid mechanics and heat. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah Mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi Dapat menerapkan dasar-dasar fisika pada bidang lain Ability to solve problems. Following the development of science and technology Ability to apply fundamentals of physics in other fields POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Besaran dan vektor; Kinematika partikel: kecepatan, percepatan, gerak lurus, gerak parabola, gerak melingkar; Dinamika partikel: hukum Newton, gaya gesek; Kerja dan energi: konsep kerja, energi kinetik, energi potensial, kekekalan energi mekanik, momentum dan tumbukan; Gerak rotasi: kecepatan dan percepatan sudut, momen gaya dan momen inersia, gerak menggelinding; Getaran: gerak harmonis sederhana, gabungan getaran selaras; Mekanika fluida: hidrostatika, hidrodinamika. Materi praktikum berupa modul praktikum tentang: Gerak peluru, Gerak lurus percepatan konstan (Flecther Trolley), Gaya sentrifugal, Koefisien gesek, Momen inersia, Tetapan Pegas, Percepatan gravitasi bumi (bandul matematis, bandul fisis). Quantities and vectors, kinematics of particles:velocity, accelerati- on, straight motion, parabolic motion, circular motion, dynamics of particcles: Newton's laws, friction; Work and energy: the concept of work, kinetic energy, potential energy, conservation ofmechanical energy, momentum and collisions; Rotational motion: angular velocity and angular acceleration, moment of force and moment of inertia, rolling motion; Vibration: simple harmonic motion, the combined vibration in tune;
- 8. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 8 Fluid mechanics: hydrostatics, hydrodynamics. Materials laboratory experiment module of the form: Motion bullets, straight motion to constant acceleration (Flecther Trolley), centrifugal force, friction coefficient, moment of inertia, spring constant, the gravitational acceleration of the Earth (mathe- matical pendulum, physical pendulum). PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Halliday & Resnic; 'Fundamental of Physics'. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987 2. Alonso & Finn,"Fundamental University Physics", Addison Wesley Pub Comp Inc,1 3 `.ed, Calf, 1990 3. Tipler, PA,(ted. L Prasetio dan R.W.Adi), "Fisika : untuk Sains dan Teknik, Jilid 1", Erlangga, Jakarta, 1998 4. Giancoli, DC., (terj, Yuhilza H), 'Fisika, jilid 1', Ertangga, Jakarta, 2001 5. Tim Dosen, "Diktat Fisika I", ”Soal-soal Fisika I", Fisika FMIPA-ITS 6. -, "Petunjuk Praktikum Fisika Dasar", Fisika, MIPA-ITS MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SM 091303: Kalkulus I SM 091303: Calculus I Credits: 3/0/1 Semester: I TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Memahami konsep-konsep dasar fungsi satu variable, limit fungsi, diferensial dan turunan fungsi beserta aplikasinya, integral tak tentu serta teknik pengintegralan. Understanding the basic concepts of one variable functions, limit functions, differential and derivative of the function and its application, not necessarily integral and integration tehniques KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah; Mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi; Dapat menerapkan dasar-dasar Matematika pada bidang lain; Ability to solve problems. Following the development of science and technology Able to apply fundamentals of mathematics in other fields; POKOK BAHASAN/ Sistem bilangan dan topik-topik geometri analitik datar; Fungsi, limit, dan kekontinuan; Diferensiasi; Aplikasi Diferensiasi; Integral, Teorema fundamental Kalkulus I dan II Numbering system and analytic geometry topics of flat;
- 9. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 9 SUBJECTS Functions, limits, and continuity; Differentiation; Applications of Differentiation; The integral, fundamental theorem of Calculus I and II PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Dosen-dosen Jurusan Matematika ITS, “Buku Ajar Kalkulus I”, Jurusan Matematika FMIPA ITS, 2003. 2. Anton, H., “Calculus, with Analitic Geometry”, 6 th edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Singapore, 1999. 3. Purcell, J.E., Rigdon, S.E., Varberg, D., “Calculus”, 8 th edition, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2000. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SB 091201: Biologi Umum SB 091201: General Biology Credits: 2 Semester: I TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN / LEARNING OBJECTIVES Memahami dan menjelaskan konsep dasar kehidupan secara menyeluruh ciri morfologi, anatomi dan adaptasi secara integratif didalam proses kehidupan sebagai dasar untuk mempelajari ilmu biologi yang lebih tinggi Understand and explain basic concepts of life as a whole charac- teristic morphology, anatomy and adaptation are integrated within the life process as a basics for studying the higher biology sciences KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa mengerti dan memahami konsep hidup dari tingkat sel sampai individu yang meliputi morfologi dan anatomi, fisiologi, reproduksi, adaptasi dan evolusi Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan konsep hidup dari tingkat sel sampai individu yang meliputi morfologi dan anatomi, fisiologi, reproduksi, adaptasi dan evolusi Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan dan mempraktekkan konsep hidup dari tingkat sel sampai individu yang meliputi morfologi dan anatomi, fisiologi, reproduksi, adaptasi dan evolusi Students know and understand the concept of iving up to the individual cell level, including morphology and anatomy, physio- logy, reproduction, adaptation and evolution Students are able to explain the concept of living up to the individual cell level, including morphology and anatomy, physio- logy, reproduction, adaptation and evolution Students can explain and practice the concept of living up to the individual cell level, including, morphology and anatomy, physio- logy, reproduction, adaptation and evolution
- 10. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 10 POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Pendahuluan : karakteristik makhluk hidup dan molekul kehidupan; Asal usul makhluk hidup: struktur sel, jaringan dan organ, metabolisme; Keanekaragaman makhluk hidup: taksonomi, Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya; Genetika : mitosis dan meiosis, kromosom dan DNA, genetika Mendel; Evolusi : pandangan Darwinian, evolusi populasi, asal mula species, melacak filogeni; Bentuk dan fungsi tumbuhan : struktur dan fungsi, organ reproduksi, system control; Bentuk dan fungsi hewan : struktur dan fungsi, organ reproduksi, homeostatis; Ekologi : ekosistem dan biokonservasi; Pengantar bioteknologi Introduction: the characteristics of living things and the molecules of life: The origin of living things; The structure of cells, tissues and organs, metabolism; Diversity of living things: taxonomy, Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya; Genetics: mitosis and meiosis, chromosomes and DNA, Mendelian genetics; Evolution: Darwinian view, the evolution of populations, the origin of species, trace phylogeny; Form and function of plant: structure and function, reproductive organ, system control, shape and function of animals: structure and function, reproductive organs, homeostasis; Ecology: The ecosystem and biokonservasi; Introduction to biotechnology PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Campbell, N.A.; Reece J.B. and Mitchell L.G., 2000. Biology. 5 th ed., Addison Wisley Longman, Inc, California 2. Alters, S, 1996, Biology Understanding Life, Mosby Year Book, Inc, St Louis, Missouri, USA. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG 091301: PENDIDIKAN AGAMA ISLAM IG 091301: ISLAM EDUCATION Credits: 2 Semester: 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN / LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa akan memahami, meyakini, engamal- kan ajaran Islam dan mengaktualisasikan dalam kehidupan. Students are able to understand, believe, execute Islamic direction and put it their lives
- 11. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 11 KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY memiliki iman, taqwa, akhlak yang mulia memiliki penalaran yang baik, berpikir kritis, dan berwawasan luas menjadikan nilai-nilai Islam untuk mengenali berbagai masalah aktual dan mampu me-mecahkannya, mampu berkomunikasi dengan baik, bersikap mandiri dan toleran dalam mengembangkan kehidupan yang harmonis antar umat manusia. Having belief, taqwa, and good behavior. Having delicate logics, critical thinking, and broad horizon Applying Islamic values to identify various actual problems and solve them, having good communication skill, independent, tolerant, and encouraging to have harmonic life among humans POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Konsep ketuhanan dalam Islam Hakekat manusia menurut Islam Hukum, ham, demokrasi dalam Islam Etika, moral dan akhlak Iptek dan seni dalam Islam Theology of Islam Human existence in Islam Law, Human rights, democracy in Islam Ethics, Morale, and Behavior Science and technology and art in Islam PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Departemen Agama RI, Terjemah Al Qur-an, (Al Qur-an Translation) 2. TIM PAI ITS, Kuliah Al Islam, (Al Islam Course) 3. Departemen Agama RI Panduan Pendidikan Agama Islam di PTU, (Guidance of Islam Education in General Higher Education) 4. Muslim Nurdin Moral dan kognis (Islam, Islam Morale and Cognition) 5. Yusuf Qardawi, Karakteristik Islam, (Islam Characteristics) MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG. 091302: Agama Kristen IG.091302: Christian Credits: 2 Semester: 1 or 2 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN /LEARNING Mahasiswa mampu menghayati cinta kasih Tuhan Allah sehingga dapat tumbuh sebagai pribadi yang utuh dan dapat membuktikan dirinya sebagai manusia yang dewasa, bertanggung jawab kepada Tuhan Allah, sesama manusia, lingkungan hidup dan
- 12. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 12 OBJECTIVES bersedia mengabdikan hidup dan pekerjaannya demi kepentingan bangsa dan sesama manusia. Students are able to sense the love of God so that they become personaly matured and complete as they have to take charge to their God, their surroundings, as well as their environment; they also have to be aware that they have to have a willingness to use their livea and their occupations for the sake of the nations and others. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Hakekat manusia sebagai makhluk religius Keberadaan Tuhan serta peranan penting agama dalam kehiudpan manusia dan masyarakat. Hubungan timbal balik antara iman dan IPTEKNI The Essence of human beings as the religious creatures The existence of God and its important roles in the life of people and society Interrelationship between faith and Science and Technology. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Manusia : Sebagai makhluk religius yang bermartabat, sebagai makhluk religius yang menjalani kehidupannya secara utuh dalam semua dimensi kehidupan Tuhan : Konsep Tuhan Yang Maha Esa menurut Iman Kristen, Cinta Kasih Tuhan dalam kehidupan manusia, Agama Kristen dan peranannya dalam kehidupan manusia. Etika dan Moral : Hubungan antara etika, moral dan Iman Kristen. Sikap etis terhadap nilai-nilai kehidupan Ilmu Pengetahuan, Teknologi dan Seni (IPTEKNI): Hubungan timbal balik antara iman dan IPTEKNI, Landasan Iman Kristen untuk pengembangan IPTEKNI, Pengembangan IPTEKNI demi kesejahteraan umat manusia serta kelestarian alam Masyarakat :Tanggung jawab umat Kristen dalam masyarakat, Partisipasi umat Kristen dalam mewujudkan HAM, Partisipasi umat Kristen dalam mewujudkan civil society. Human: As a religious creature who has high dignity, and as a religious creature who can carry out this life in in a complete and overal dimensions of life. God : Concept of the Only God based on the Christianity, the love of God in the human life, Christianity and its roles in life. Ettiquatte and Moral Values : Relationdship between ettiquatte, moral value, Christianity. Ethical attitude towards the values of life Science and Technology: Interrelationship between science and
- 13. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 13 faith (i.e. Christianity), Christianity base to develop science and technology, development of science and technology for human and conservation of the nature. Society: the responsibity of Christian people in society, Christian people involvement in fostering human right, Christian people participation in promoting civil society PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Brownlee, M, ”Tugas Manusia Dalam Dunia Milik Tuhan” ( The Roles of People in The World of God), Jakarta: BPK Gunung Mulia, Jakarta.1987. 2. David Bergamini, ”Alam Semesta”,(the Universe) Jakarta: Tira Pustaka.1979, 3. Emanuel Gerrit Singgih, ”Bergereja, Bertheologi dan Bermsyarakat” (Worshipize, theologize, and Socilize) Yogjakarta:TPK. 1997 4. F. Magnis Suseno, ”Etika Politik”. (The Etiquette of Politics). Jakarta: Gramedia 1994, 5. F. Magnis Suseno. ”Kuasa dan Moral” (Power and Moral) Jakarta: Gramedia. 1995. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG .091303: AGAMA KATHOLIK IG .091303: CATHOLICS Credits: 2 Semester: 1 or 2 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN / LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu mengatasi persoalan dasar yang dihadapi dalam usahanya membangun hidup yang bermartabat. Mahasiswa mampu mengaktualisasikan hidup dan karya Yesus yang diwartakan Gereja dalam kehidupan sehari-hari. Mahasiswa mampu menyikapi secara benar IPTEKS dalam terang iman bagi kehidupan manusia dengan segala dinamikanya. Students are able to solve fundamental problems encountered along the attempt to carriout life with dignity Students are able to actualize the life and teachings of Jesus Christ as they are dispersed by Church in daily life. Students are able to perceive any development in science and technology in the light of Catholic faith for life and its dynamic changes. Mahasiswa memahami dan menggumuli persoalan dasar yang dihadapi manusia dalam usahanya membangun hidup yang bermartabat. Mahasiswa memahami dan menghayati konsep Tritunggal Yang
- 14. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 14 KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Maha Kudus, hidup dan karya Yesus yang diwartakan Gereja dan mengaktualisasikannya dalam kehidupan sehari-hari. Mahasiswa mampu memahami manfaat ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, dan seni bagi manusia beriman; bagaimana tanggung jawab manusia dalam mengejar nilai-nilai hidupnya berdasarkan karunia yang diberikan Tuhan kepadanya; memahami bagaimana tanggung jawab terhadap lingkungan hidup. Students are able to understand and merge into the problems facing by every human being in their attempt to cultivate lives in dignity. Students are able to perceive the Trinity doctrine, the life and teachings of Jesus Christ that Church has dispersed and then actualize them throughout the daily life. Students are able to make use of science, technology, and art of the living of religious people to seek values in their lives and able to bring the Lord’s blessing into their lives as the form of their responsibility towards their surroundings. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Manusia dan Moral: Pengantar, pengertian manusia dan moral, hubungan antara manusia dan moral berkaitan dengan persoalan dasar manusia, Martabat manusia, Hakikat dan tanggung jawab manusia. Ketuhanan yang Maha Esa: Pengantar, pengalaman religius dan pengalaman iman, pengertian Ketuhanan yang Maha Esa dalam kaitan dengan ke Tritungga-an, ke=Tritunggal-an dalam teladan Yesus Kristus Agama dan Kerukunan: Pengantar, Masalah-masalah agama, Makna agama dalam kehidupan, Hubungan antar umat beragama. Gereja: Pengantar, Sejarah, hakikat dan sifat-sifat Gereja dewasa ini, Gereja Katolik di Indonesia, Tugas-tugas Gereja Iman yang memasyarakat: Pengantar, Situasi masyarakat masa kini: Globalisasi, Tanggung jawab sosial, Kapita Selekta People and Moral: Introduction, Definitions, Definitions of human and moral, people and Moral in their relation to basic problems in human lives, people dignity, the essence and responsibility of a human being. The oneness of God: Introduction, Religious and faith experiences, Definitions of the Oneness of God in relation to the Trinity Doctrine, Trinity in the life of Jesus Christ. Religions and togetherness: Introduction, Problems in Religion, Meanings of Religion in life, relationships across religions. Church: Introduction, History, The Essence and Natures of Churce in today’s Era, Catholic Churches in Indonesia, the Roles of Church. Faith that is socializing: Introduction, Situation of today society:
- 15. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 15 Globalisation, Social responsibility, Iman yang memasyarakat: Pengantar, Situasi masyarakat masa kini: Globalisasi, Tanggung jawab sosial, Kapita Selekta PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. KWI. Iman Katolik, Buku informasi dan referensi. (Catholic Faith, Books, Information, and References) Jakarta, Obor dan Yogyakarta: Kanisius.1990. 2. Dokumen Vatikan II. (Vatican Document) Jakarta: Penerbit Obor, 1993 3. Kumpulan Dokumen Ajaran Sosial Gereja ( Compilations of the Church Social Teachings) Jakarta: Dokpen KWI, 2001 4. Bernard T. Adeney. Etika Sosial Lintas Budaya. (Social Ettiquatte Across Cultures) Yogyakarta, Penerbit: Kanisius, 2000. 5. Pedoman Gereja Katolik Indonesia, KWI (Indonesia Catholic Church Guide) MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG 091304: PENDIDIKAN AGAMA HINDU IG 091304 : HINDU EDUCATION Credits: 2 Semester: 1 or 2 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN / LEARNING OBJECTIVES Setelah mengikuti kuliah mahasiswa dapat memahami tentang pengertian Ketuhanan, Tuhan YME yang Nirakara dan Akara, Catur Marga Yoga, sarana, tempat dan hari raya memujanya, konsepsi manusia dan martabat manusia, orang suci dan awatara aktualisasi etika dan moralitas dalam kehidupan, srada, jnana, karma sebagai kesatuan dalam yadnya, trihita karana dan tanggung jawab terhadap lingkungan, hakekat kebersamaan dalam pluralitas beragama, peran umat Hindu dalam mewujudkan masyarakat sejahtera, sumber ajaran Hindu tentang politik, peran agama Hindu dalam perumusan dan penegakan hukum. At the end of the course students are able to understand the meanings of God; the only God who is impersonal and personal; Four pathways to God; media, places and the days to praise the Gods, conception about human and human dignity, sacret people and awatara and how to actualize the etiquate and moral value in daily life, srada, jnana, karma as a form of unity in yadnya, trihita karana and social responsibilities, the essence of togetherness in plurality in terms of living side by side with various faith, the roles of Hindi in promoting wellbeing societies, political view in Hindu, the roles of Hindu to
- 16. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 16 formulating and upholding law. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa dapat memahami dan menjelaskan konsep ke Tuhanan dalam Agama Hindu {Brahma Widya}, catur marga yoga, hakekat manusia Hindu, etika dan moralitas, IPTEKS dalam perspektif Hindu, . kerukunan hidup umat beragama dalam pandangan Hindu,. sistem politik dalam pandangan Hindu dan refleksi nilai hukum Hindu dalam konteks masyarakat hukum Indonesia Students are able to state and describe the concept of God in Hindu,{Brahma Widya}, catur marga yoga, the essence of being Hindi, etiquete and moral value, Science and Technology from perspective of Hindu, political system from the point of view of Hindu, and reflection of value of law in the context of Indonesia rule governed society. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Konsepsi Ketuhanan (Brahma Widya), Pengertian Ketuhanan Tuhan Yang Maha Esa yang nirakara (impersonal) dan akara (personal) Catur Yoga Marga (empat jalan menuju kepada-Nya), Pengertian Catur Marga Yoga Sarana, tempat dan hari-hari raya memuja-Nya Hakekat Manusia Hindu , Konsepsi manusia Hindu, Eksistensi dan martabat manusia Tanggung jawab manusia sebagai ciptaan-Nya, Orang suci dan awataranya. Etika dan Moralitas, Konsepsi etika dalam perspektif Hindu, Aktualisasi etika dan moralitas dalam kehidupan, Misi untuk memperbaiki diri (manawa menuju madhawa). Implementasi kebenaran, kebajikan, kasih sayang, kedamaian, tanpa kekerasan. Ilmu Pengetahuan teknologi dan seni dalam perspektif Hindu, Sradha, Jnana dan Karma sebagai kesatuan dalam yadnya, Kewajiban menuntut ilmu dan mengamalkan ilmu Tri Hita Karana dan tanggung jawab terhadap alam dan lingkungan ,Seni keagamaan Conception of God (Brahma Widya), Definitions of The Only God who is impersonal and personal. Four Pathways to God, Definitions, the four pathways to God, media, place, and days to praise the Gods The Essence of Hindi, the Conception of Hindi, existence and human dignity, human responsibility to God, the creator, Sacred people and their awatara Ettiquate and Moral Values, Ettiquate Conception in the perspective of Hindu, Actuaisation of ettiquate and moral values in lives, missions for self reflection from manawa to madhawa, implementation of truth, kindness, love, and peace, without any
- 17. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 17 violence Science and Technology from the perspective of hindu, Sradha, Jnana and Karma as unity in yadnya, rights for learning and implementing studies on Tri Hita Karana and responsibilities towards nature and environment, the arts of religions PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Wiana,. 1994. Bagaimana Hindu Menghayati Tuha( How to Understand God from the Points of Hindu),. Manikgeni. 2. Wiana, .1982. Niti Sastra, Ditjen Hindu dan Budha. 3. Atmaja, 1974. Panca Sradha,. PHDI Pusat . 4. Titib, 1996. Veda Sabda Suci Pedoman Praktis Kehidupan (Veda Sabda Suci, Practical Guides for life), Paramita 5. Pudja, 1997, Teologi Hindu (Theology of Hindu), Mayasari MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG.091305: Agama Budha IG.091305 : Budha Credits: 2 Semester: 1 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa pengertian dan menghayati Hakekat Tuhan Yang Maha Esa serta mengamalkan Sila Ketuhanan Yang Maha Esa, Mahasiswa memiliki pengertian dan memahami adanya Dewa, Bodhisatva, Arahat dan Buddha sehingga mahasiswa mampu melaksanakan suri teladannya, Mahasiswa memahami tentang Bodhisatva dan Buddha serta menghayati dan mengamalkan Dharma, Mahasiswa dapat memahami dan mengerti tentang Hukum Ke – Sunyataan, sehingga mahasiswa dapat menyesuaikan diri dengan hukum Ke-Sunyataan tersebut, Mahasiswa dapat memahami dan mengerti hukum Karma sehingga mahasiswa dapat menerima, menerapkan serta melaksankan . Students are able to understand the essence of the Oneness of God and bring the first principle of Pancasila into the real life implementation. Students believe and perceive the existance of God, Bodhisatva, Arahat and Buddha as a consequence they are able to follow the teachings. Students believe and perceive Bodhisatva and Budha so that they are able to bring their darma in their lives. Students understand the rules of Sunyataan, so that they are able to adapt themselves into the rules. Students understand Karma, so that they are able to implement the rule in their lives. KOMPETENSI/ Mahasiswa dapat memahami dan melaksanakan ajaran agama
- 18. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 18 COMPETENCY Budha, sesuai ajaran yang dilaksanakan Sang Budha tentang pergaulan dalam masyarakat Students are able to understand as well as implement the Budha’s teachings on how to live in a real life. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Sila Ketuhanan Yang Maha Esa: Catur Paramita, Catur Mara, Brahma Vihara, Bhavana. Riwayat Hidup Sang Buddha: Kelahiran Bodhisatva, Ramalan Pertapa Asita, Ramalan Para Brahmana, Masa Remaja, Masa Berumah Tangga, Masa Pertapa, Mencapai Buddha, Masa Pembabaran Dharma, Terbentuknya Sangha. Tentang Bodhisatva: Dana Paramita Tentang proses tercapainya tingkat Bodisatva: Sila Paramita Tentang Sad- Paramita: Viriya Paramita The First Principle of Pancasila, The Oneness of God: Catur Paramita, Catur Mara, Brahma Vihara, Bhavana. Biography of Lord Budha: the born of Bodhisatva, Asita’s Prediction, the predictions of Brahmana, adolesence or teen age, period of family hood, the Hermit period, Achieving Buddha’s enlightment, times for learning Budhism together, Sangha achievement. About Bodhisatva: Dana Paramita About process of achieving Bodisatva level: Paramita Principles About Sad- Paramita: Viriya Paramita PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Dhamma Pada(Depag, 1904) 2. Dhamma Sari ( Depag, 1904) 3. Kuliah Agama Budha (Depag 1903) MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SK 091201: Kimia Dasar I SK 091201: Fundamental Chemistry I Credits: 4 Semester: I TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING Mahasiswa mampu menggunakan prinsip-prinsip dasar ilmu kimia untuk pengembangan kemampuan diri dalam memecahkan permasalahan pada kehidupan sehari-hari Students are able to use the basic principles of chemistry to
- 19. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 19 OBJECTIVES develop skills in solving problems ineveryday life KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa mampu menerangkan prinsip-prinsip dasar ilmu kimia meliputi hukum laju, kesetimbangan, elektrokimia, kimia inti dan aplikasinya dalam menjelaskan sifat, struktur, reaktivitas dan klasifikasi senyawa-senyawa/unsur-unsur organik dan anorganik. Mahasiswa dapat melakukan perhitungan-perhitungan dasar kimia. Mahasiswa dapat melakukan eksperimen-eksperimen dasar kimia serta mengaitkan hasil pengamatannya dengan teori-teori dasar kimia beserta aplikasinya. Students are able to explain the basic principlesof chemistry covering the legal rate, equilibrium, electrochemistry, chemical core and its applicationin explaining the nature, structure, reactivity and classification of the compounds/ elements oforganic and inorganic; Students can perform basic calculations of chemistry; Students can conduct experiments in basic chemistry and relate the observations with the basic theories of chemistry and its application POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Dinamika reaksi, Kesetimbangan Kimia, Elektrokimia, Kimia Inti, Pengenalan Unsur, Senyawa Organik dan Anorganik serta klasifikasinya. The dynamics of reaction, Chemical Equilibrium,Electrochemistry, Chemistry Core, Introductory Elements, Organic and Inorganic Compounds and classification. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG 091310: Pengantar Teknologi informasi dan Komunikasi IG 091310: Introduction of Information and Communication Technology Credits: 2 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa dapat mengenal dan menggunakan perangkat teknologi informasi dan komunikasi, sehingga dapat membantu proses pembelajaran pada jurusan masing-masing. Students can recognize and use information and communi- cation technology devices, which can help the learning process in each department.
- 20. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 20 KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa mampu mendefinisikan Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan manfaat Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi Mahasiswa mampu menyelesaikan masalah dengan bantuan Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi Mahasiswa bisa menggunakan Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi untuk berbagi aplikasi Students are able to define Information and Communications Technology Students are able to explain the limits benefits of Information and Communication Technology Students are able to solve the problem by using Information and Communication Technology Students can use Information and Communications Technology for various applications POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Definisi, sejarah, karakteristik, manajemen Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi; Konten Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi; Peralatan Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi; Jaringan Komputer dan Komunikasi Data; Layanan Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi; Perangkat Lunak; Pengamanan dan Etika dalam Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi; Ketrampilan Praktek. The definition, history, characteristics, management of Infor- mation and Communication Technology Content of Information and Communication Technology Information and Communication Technology Equipment. Computer Network and Data Communication Information Technology and Communication Services Software Security and Ethics in Information Technology and Communica- tion Skills Practice PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Diktat PTIK ITS tahun 2009
- 21. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 21 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091304: Fisika Dasar II SF 091304: Fundamental Physics II Credits: 4 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan dan menggunakan rumusan hukum-hukum fisika tentang medan listrik dan medan magnet. Students are able to explain and use the formulation of physical laws about the electric and magnetic fields. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah; Mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi; Dapat menerapkan dasar-dasar fisika listrik magnet pada bidang lain; Ability to solving problems; Following the development of science and technology; Able to apply the basics of physics electricity magnetism in other fields; POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Muatan listrik, hukum Coulomb; Medan listrik: kuat medan listrik, garis gaya, perhitungan kuat medan listrik; Hukum Gauss: fluks, hukum Gauss dan aplikasinya; Potensial listrik energi potensial, medan dan potensial listrik; Kapasitor: Kapasitansi, dielektrik; Arus listrik: arus dan gerak muatan, hukum Ohm, energi dalam rangkaian listrik; Rangkaian arus searah: hukum Kirchoff, rangkaian RC; Medan magnet: gaya magnet, momen gaya, sumber medan magnet; Induksi magnetik: fluks magnet, GGL induksi, generator; Arus bolak balik: arus bolak-balik dalam resistor, induktor, kapasitor, rangkaian R-L, R-C, R-L-C. Electric charge, Coulomb's law, electric field: electric field strenght, lines of force, the calculation of electric field strength; Gauss'Law: flux, Gauss' law and its application; electric potential, potential energy field and electric potential; Capacitors: Capacitance, dielectric, electric current: current and movement of charge, Ohm's law, the energy in the electrical circuit; series of direct current: Kirchoff law, the RC circuit; Magnetic field: magnetic force, moment of force,the source of the magnetic field, magnetic induction: magnetic flux, induced emf, generators; ac: alternating current in the resistors, inductors, capacitors, circuit R-L, R-C, R-L-C. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ 1. Halliday & Resnick,"Fundamental of. Physics'. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987
- 22. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 22 REFERENCES 2. Alonso & Finn,"Fundamental University Physics", Addison Wesley PubLComp.lnc, 1990 3. Tipler, P.A.,(terj. B. Soegijono), °Fisika : untuk Sains dan Teknik, Jilid 2", Erlangga, Jakarta, 2001 4. Giancoli, DC., (terj, Yuhilza H), 'Fisika, jilid 1", Erlangga, Jakarta, 2001 5. Tim Dosen,"Diktat Fisika l1*,'Soal-soaf Fisika I!", Fisika FMIPA-ITS 6. . -, "Petunjuk Praktikum Fisika Dasar", Fisika, MIPA-ITS MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091305: Fisika Dasar III SF 091305: Fundamental Physics III Credits: 2 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan dan menggunakan rumusan hukum- hukum fisika tentang termo-dinamika, gelombang dan optik. Students are able to explain and use the formulation of physical laws of thermodynamics, waves and optics. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan untuk memecahkan masalah sederhana fisika Kemampuan untuk mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi Kemampuan untuk menerapkan dasar-dasar fisika pada bidang lain Ability to solving a simple problem of physics; Ability to follow the development of science and technology; Ability to apply the basics of physics in other fields POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Termodinamika: hukum gas ideal, hukum pertama dan hukum kedua termodinamika; Gelombang: fungsi gelombang, cepat rambat gelombang, energi dan intensitas gelombang, efek Dopler; Optika geometri: refleksi dan refraksi oleh permukaan datar dan lengkung, lensa tipis dan tebal, pembentukan bayangan pada lensa dan cermin, deviasi dan dispersi pada prisma, alat-alat optis; interferensi, difraksi dan polarisasi. Thermodynamics: law for ideal gas, the first law of thermody- namics; the second law of thermodynamics. Waves: wave function, wave velocity, energy and intensity of wave, Dopler effect; Geometry Optics: reflection and refraction on the surface of flat and curved surfaces, thin and thick lens , image formation by mirrors and lenses, deviation and dispersion in the prism, optical instruments; interference, diffraction and polarization.
- 23. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 23 PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Halliday & Resnick,"Fundamental of. Physics'. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1987 2. Alonso & Finn,"Fundamental University Physics", Addison Wesley PubLComp.lnc, 1990 3. Tipler, P.A.,(terj. B. Soegijono), °Fisika : untuk Sains dan Teknik, Jilid 2", Erlangga, Jakarta, 2001 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091306: Metode Pengukuran Fisika SF 091306: Physycal Measurement Method Credits: 3 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan cara pengukuran besaran-besaran fisis, mampu menggunakan metode pengukuran untuk menganalisis besaran fisis yang diperoleh dari hasil pengukuran sederhana di lapangan (laboratorium). Students are able to explain how the measurement of physical quantities, capable of using the measurement method to analyze the physical quantities obtained from the simple measurement in the field (laboratory) KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah; Kemampuan Mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi; Dapat menerapkan dasar-dasar metode pengukuran pada bidang lain; Ability to solving problems; Ability to follow the development of science and technology; Ability to apply the basics of measurement methods in other fields; POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Pengamatan dan pengukuran besaran-besaran fisika; Sistem pengukuran dan kalibrasi; Analisis pengukuran: ralat rambang, sistem matrik, perambatan ralat, Pengolahan data, statistik Poisson, model matematik, curve fitting; Observation and measurement of physical quantities; Measurement system and calibration; Analysis of measurements: erratum Rambang, matrix systems, propagation of error, Data processing, Poisson statistics, mathematical modeling, curve fitting; PUSTAKA UTAMA/ 1. Beer,J., “ Theory of Error”, Addison Wisley, 1957 2. Imron, A., "Diktat Analisa Pengukuran Fisis", Fisika, MIPA-ITS
- 24. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 24 REFERENCES 3. Dunn, ”Measurement and data analysis for engineering and science’, McGraw-Hill, 2005 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SM 091304: Kalkulus II SM 091304: Calculus II Credits: 4 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa dapat memahami konsep-konsep dasar tentang teknik pengintegralan fungsi satu peubah dan aplikasinya, fungsi transenden, limit-limit bentuk taktentu, deret takhingga, persemaan parametrik dan kutub, serta geometri dan vektor. Students can understand basic concepts about the function of one variable integration technique and its applications, transcen- dental functions, limits the form of not-necessarily, series no-till, parametric and polar equations, and the geometry and vector KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah Mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi Dapat menerapkan dasar-dasar Matematika pada bidang lain; Ability to solving problems. Following the development of science and technology Able to apply the basics of mathematics in other fields; POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Pengertian tentang teknik-teknik pengintegralan; penerapan integral tertentu; berbagai bentuk fungsi transenden, limit bentuk taktentu dan integral tak wajar, deret tak hingga; persamaan parametrik dan koordinat kutub; pengantar geometri datar dan ruang dengan pendekatan vektor. An understanding of the techniques of integration; The application of definite integrals; Various forms of transcendental functions, limits the form of not- necessarily and unnatural integral, infinite series; Parametric equations and polar coordinates; Introduction flat geometry and space vector approach. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Tim penyusun Buku Ajar Kalkulus Jurusan Matematika FMIPA ITS, “Buku Ajar Kalkulus II” edisi ke-4, 2005. 2. Anton, H., Calculus, A New Horison, 6 th ed., John Wiley & Sons. New York, 1999. 3. Purcell, J.E., Rigdon, S.E., Calculus, 8 th ed., Prentice-Hall, New Jersey,
- 25. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 25 2000. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SK 091202: Kimia Dasar II SK 091202: Fundamental Chemistry II Credits: 3 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menggunakan prinsip-prinsip dasar ilmu kimia untuk pengembangan kemampuan diri dalam memecahkan permasalahan pada kehidupan sehari-hari Students are able to use the basic principles of chemistry to develop skills in solving problems in everyday life KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa mampu menerangkan prinsip-prinsip dasar ilmu kimia meliputi hukum laju, kesetimbangan, elektrokimia, kimia inti dan aplikasinya dalam menjelaskan sifat, struktur, reaktivitas dan klasifikasi senyawa-senyawa /unsur-unsur organik dan anorganik. Mahasiswa dapat melakukan perhitungan-perhitungan dasar kimia. Mahasiswa dapat melakukan eksperimen-eksperimen dasar kimia serta mengaitkan hasil pengamatannya dengan teori-teori dasar kimia beserta aplikasinya. Students are able to explain the basic principles of chemistry covering the legal rate, equilibrium, electrochemistry, Nuclear chemistry and its application in explaining the nature, structure, reactivity and classification of the compounds / elements of organic and inorganic; Students can perform basic calculations of chemical; Students can perform basic chemical experiments and observa- tions relate to the basic theories of chemistry and its application. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Dinamika reaksi, Kesetimbangan Kimia, Elektrokimia, Kimia Inti, Pengenalan Unsur, Senyawa Organik dan Anorganik serta klasifikasinya. The dynamics of reaction, Chemical Equilibrium, Electrochemistry, Nuclear Chemistry, Introductory Elements, Organic and Inorganic Compounds and their classification. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES
- 26. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 26 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG 091308: Bahasa Inggris IG 091308: English Credits: 2 Semester: II TUJUAN PEMBELAJARA N/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa dapat memahami isi sebuah artikel/ jurnal/ teks akademik mengenai sains dan teknologi yang ditulis dalam bahasa Inggris. Mahasiswa dapat mendiskripsikan informasi atau isi dari argumentatif teks lisan setelah menyimak teks tersebut. Mahasiswa dapat mengungkapkan argumentasi atau ide-ide logis secara lisan atau tulisan. Students are able to understand the content of various acedemic texts in Science and Technology. Students are able to describe any information perceived from spoken argumentative articles. Students are able to express either oral or written the logical ideas. OMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa dapat menerapkan strategy membaca yang efektif untuk menafsirkan isi argumentatif teks berbahasa Inggris yang berbasis sains dan teknologi. Mahasiswa dapat menafsirkan isi berbagai jenis teks lisan yang berbahasa Inggris. Mahasiswa dapat menyampaikan secara lisan dan tulisan argumen-argumen atau ide-ide dalam bahasa Inggris. Students are able to employ effective reading strategies to understand any argumentative texts in Science and Technology Students are able to interpret concisely any spoken texts. Students are able to present either oral or written the ideas or argument they have. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Scanning: Scanning in everyday life; scanning tables; scanning academic articles/jurnals,; scanning encyclopedia entri. Previewing and Predicting: previewing and predicting book covers to foresee the contents; listen to spoken text and predict the suitable picture or figures; Say out loud the undelined reasons for predicting. Vocabulary Knowledge for Effective Reading and listening: guessing meaning from context in sentences; using grammar to guess word meaning; recognizing words connecting ideas.
- 27. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 27 Topics: stating and recognizing topics from a paragraph or a text in written and spoken text; working with the topics, finding and writing the topic sentence. Main Ideas: finding the main idea in the topic sentence, stating main ideas of a paragraph, develop topic to main ideas, develop supporting details for the main ideas, producing an outline. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Mikulecky and Jeffries. “More Reading Power” Addison-Wesley publishing Company, 1996 2. Supriyanto. ”Critical Reading” ITB. 2007. 3. Rooks. “ Paragraph Power: Communicating Ideas through Paragraphs.Prentice Hall Regents. 1999 4. Hayden, R.E., Pilgrim, D.W, and Haggard, A.Q. “Mastering American English. Prentice Hall, Inc. 2000. 5. Thomson and Martinet. “A Practical English Grammar. Oxford University Press.1995. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091307: Elektronika Dasar I SF 091307: Fundamental Electronics I Credits: 3 Semester: III TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu mengenal, memahami dan menganalisa model-model rangkaian serta dapat mengetahui respons rangkaian. Students are able to recognation, state and analysis circuits models, and knows about circuit respons KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah terkait dengan elektronika Mengikuti perkembangan sains dan teknologi Kemampuan menerapkan dasar-dasar elektronika pada bidang fisika dan yang lain Ability to solving the problem of electronic circuits Follow the develop of Science and technology Ability to application of fundamental electronics in physics problem and others POKOK Pembagi tegangan dan arus, Pengukuran tegangan dan arus, Penggunaan alat ukur tegangan dan arus; Jembatan Wheatstone, Percobaan Jembatan Wheatstone,
- 28. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 28 BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Rangkaian ekivalen; Praktikum: Galvonometer, rangkaian seri dan pararel Analisa rangkaian : metode titik dan metode mesh, Rangkaian ekivalen Thevenin dan Norton, Transfer daya maximum; Rangkaian kombinasi RLC, Respons orde 1 rangkaian RC dan RL, Respons alami dan step rangkaian RLC; Voltage and Curent devider, voltage and current measurement and the experiment Wheatstone bridge, Wheatstore bridge experiments, equivalen circuits, Galvonometer, paralel and serie Circuit; and the experiments Circuit analysis : node metods and mesh methods; Equivalen Circuit;Thevenin and Norton; Maximum of Power Transfer RLC Circuit combinations, Respons of circuit order for RC and RL Natural Respon and step of RLC circuit; Work laboratory; Serie and Pararel Circuit, PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. James W. Nilsson dan Susan A. Riedel, 2008, Electronic Circuit, Pearson Prentice Hall. 2. Petunjuk Praktikum Laboratorium Madya 3. Sutrisno, 1986, “ Elektronika”, Penerbit ITB MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091309: Fisika Matematika I SF 091309: Mathematical Physics I Credits: 4 Semester: III TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu mengaitkan fenomena fisis dengan formula matematis yang sesuai, mampu mengurai serta menyelesaikan dengan berbagai metode analitis yang ada. Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan teori matematis yang kemudian digunakannya untuk menyelesaikan persoalan-persoalan fisika. Students are able to link the physical phenomena with the appropriate mathematical formula, is able to parse and finish with a variety of existing analytical methods. Students are able to explain the mathematical theory which is then used to solve physics problems
- 29. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 29 KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan pemahaman masalah fisika Kemampuan penerapan matematika dalam bidang fisika Kemampuan penerapan matematika dalam perkembangan metode penyelesaian masalah fisis Ability understanding of physics problems The ability of the application of mathematics in physics The ability of the application of mathematics in the development of methods of solving physical problems POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Persamaan diferensial biasa dan transformasi Laplace; Analisis vektor (kalkulus vektor); Bilangan kompleks; Fungsi kompleks; Persamaan linier: vektor, matriks dan determinan; Deret; Deret Fourier; Fungsi variabel banyak; Diferensiasi Parsial. Differensial Equation and Laplace Trasfrom Vector analysis (Vector Calculus) Complex Variable; Complex Functions Serries; Fourier Serries; Multivariables Functions, Differensial Partials. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Purwanto, A.,"Diktat Fisika Matematika", Fisika, MIPA-ITS, Surabaya, 2003 2. Boas, M.L.,“Mathematical Methods in the Physical Science”, Edisi 3, John Wiley Sons, New York, 2006. 3. Arfken, G.B. dan Weber, H.J.,”Mathematical Methods for Physicists”, Edisi 3, Academic Press, 2001. 4. Butkov, B., “Mathematical Physics”, Addison Wesley, California, 1977. 5. Riley, K.F., Hobson, M.P. dan Bence, S.J.,”Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering”, Edisi 3, Cambridge University Press, 2006. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091311: Termodinamika SF 091311: Thermodynamics Credits: 3 Semester: III TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan pengertian dasar termodinamika, persamaan keadaan hukum-hukum termodinamika I dan II. Memahami konsep temperatur, kesetimbangan panas, keterkaitan kerja dan kalor, serta entropi. Memahami penerapan konsep-konsep termodinamika klasik.
- 30. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 30 Students are able to explain a basic understanding of thermody- namics, equation of state laws of thermodynamics I and II. Understand the concept of temperature, thermal equilibrium, the relationship of work and heat, and entropy. Understand the application of the concepts of classical thermo- dynamics KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan mahasiswa dalam analisis sistem termodinamika. Kemampuan penerapan hukum thermodinamika dalam berbagai persoalan. Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi. The ability of students in the analysis of thermodynamic systems. The ability of the application of thermodynamic laws in a variety of issues. Ability to follow developments in technology POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Pandangan makroskopik dan mikroskopik, lingkup termodinamika; kesetimbangan termal, temperatur, termokopel, kesetimbangan termodinamika, diagram PV dan PT, persamaan keadaan, perubahan differensial keadaan dan penerapannya, kerja, proses kuasi-statik, kalor dan hukum pertama termodi-namika, proses terbalikkan dan takterbalikkan, entropi, siklus Carnot, entalpi, fungsi Helmholtz dan Gibbs, kapasitas panas, perubahan fase. Macroscopic and microscopic view, the scope of thermodynamics; Thermal equilibrium, temperature, thermocouple, thermodynamic equilibrium, PV and PT diagrams, equation of state, differential changes in circum stances and its application, Work, the process of quasi-static, heat and first law of thermo- dynamics, Reverse the process and no-reverse out, entropy, Carnot cycle, enthalpy, Helmholtz function and Gibbs, heat capacity, phase changes. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Zemansky, M.W, & R. H. Dittmann (terj: The Houw Liong, Ph.D)," Kalor dan Termodinamika", penerbit ITB, 1986. 2. Sears. F.W., “An Introduction to Thermodynamics: the Kinetic Theory of Gases and Statistical Mechanics”, Addison Wesley, 1963.
- 31. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 31 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091312: Fisika Modern SF 091312: Modern Physics Credits: 4 Semester: III TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan konsep-konsep fisika modern agar mahasiswa mempunyai pengetahuan dasar bagi kuliah fisika kuantum Students are able to explain the concepts of modern physics for students to have basic knowledge of quantum physics lecture KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memahami konsep fisika modern Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi kuantum; Ability to understand the concepts of modern physics Ability to follow the development of quantum technology; POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Teori relativitas khusus, Radiasi benda hitam, Efek fotolistrik, Praktikum efek fotolistrik, Praktikum milikan; Efek Compton, Postulat de Broglie, Dualitas partikel – gelombang Ketaktentuan Heisenberg, Teori atom Bohr, Praktikum spektrum atom; Kaidah kuantisasi, Atom mirip-hidrogen, Atom banyak –elektron, Molekul; Zat padat, Pengantar Fisika Inti : inti atom, radioaktivitas dan reaksi inti; The theory of special relativity, black body radiation, photoelectric effect, photo electric effect Practicum, Practicum appropriation; Compton effect, de Broglie's postulates, particle duality – wave Heisenberg uncertainty, Bohr's atomic theory, atomic spectra of the practicum; Rule quantization, hydrogen atom-like, many-electron atom, mole- cule; Solids, Introduction to Physics Nucleus: the nucleus, radioactivity and nuclear reaction; PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Beiser, A. (terj: The How Liong), “Konsep Fisika Modern”, Erlangga, cetakan ke-dua, Jakarta, 1992 2. Eisberg, R. & Resnicks, R., “Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei, and Particles”, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2 nd Ed., 1985. 3. Krane, S.K (terj: Hans J. Wospakrik), “Fisika Modern”, UI Press, Jakarta, 1992. 4. Serway, R.A, Moses, C.J and Moyer, C.A, “Modern Physics”, third edition, 2005
- 32. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 32 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091313: Mekanika SF 091313: Mechanics Credits: 4 Semester: III TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan dan menggunakan rumusan- rumusan tentang berbagai jenis gerak dari suatu partikel ,gerak sistem partikel, gerak benda kontinyu (fluida dan padatan) serta penyelesaian persamaan gerak yang tidak sederhana. Students are able to explain and use formulas of various types of motion of a particle, motion of particle systems, motion of the continuous (fluidand solids) and the resolution of equations of motion are not simple. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memahami permasalan mekanik Kemampuan analisis bidang fisika Kemampuan beradaptasi dengan perkembangan teknologi Ability to understand mechanical problems Ability to analyze the field of physics Ability to adapt to technological developments POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Gerak partikel satu, dua dan tiga dimensi; Konservasi energi; Konservasi momentum; Medan Gravitasi; Gerak gaya sentral; Gerak sistem partikel; Gerak sistem koordinat; Rotasi disekitar sumbu, Rotasi benda kaku, Mekanika media kontinyu; Kinematika fluida; Dinamika fluida; Persamaan Lagrange; Persamaan Hamilton; Tensor Inersia; The motion of particles one, two and three dimensions; Conservation of energy, conservation of momentum; Gravity field; central force motion; Motion particle system; motion coordinate system; rotation around the axis, rotation of rigid bodies, mechanics of continuous media; Kinematics of fluid; fluid dynamics; Lagrange equation, Hamilton equation; Inertia Tensor; PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Arya, Atam Parkash, “Introduction to Classical Machanics”, Allyn and Bacon, Boston, 1990 2. Barger, V. & M. Olsson, “Classical Mechanics : A Modern Perspective”, McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, 1995
- 33. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 33 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG 091306: Kewarganegaraan IG 091306: Civics Credits: 2 Semester: III TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Membantu mahasiswa mengembangkan potensinya untuk menguasasi ilmu pengetahuan, ketrampilan, dan sikap kewarganegaraan dan nilai-nilai yang diperlukan dalam rangka penerapan ilmu, profesi dan keahliannya serta berpartisipasi dalam kehidupan masyarakat dari komuniti setempat, bangsa dan dunia.. Menjadi warga Negara yang cerdas, demokratik dan berkeadaban, dan bertanggung jawab, menggalang kemampuan kompetitif bangsa di era globalisasi, yang efektif mencakup: Pemahaman dasar tentang cara kerja demokrasi dan lembaga-lemabaganya. Pemahaman tentang “rule of law” dan HAM seperti tercermin dalam rumusan- rumusan perjanjian dan kesepakatan internasional dan local. Penguatan ketrampilan partisipatif yang akan memberdayakan peserta didik untuk merespons dan memecahkan masalah-masalah masyarakat secara demokratis. Pengembangan budaya demokrasi dan perdamaian pada lembaga-lembaga pendidikan dan seluruh aspek kehidupan masyarakat. To help the students to develop their potencies in mastering sciences skills, and citizenship attitudes and values. Which are required in the applications / implemen-tations of sciences, profession and profi-ciency, and also to participate in the local communities, nation and world., to help the students to be intelligent, democratic and civilized citizen, and to be citizens having respon sibilities, and capabilities in mobilizing the abilities, of national competitiveness in the globalization era that effectively cover:. Basic understanding with the working law/way of democracy and its institutions.. Understanding with the rule of low and human rights , such as they are reflected in the formula of agreements, and also in the local and international accords.. Improving participative skills which will strengthen participants to respond and solve social problems democratically. Improving democratic and peaceful cultures in the institutions of education and all aspects of social life. Menjadi ilmuwan dan professional yang memiliki rasa
- 34. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 34 KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY kebangsaan dan cinta tanah air, demokratis yang berkeadaban menjadi warga Negara yang memiliki daya saing; berdisiplin; dan berpartisipasi aktif dalam membangun kehidupan yang damai berdasarkan sistem nilai Pancasila. To become scientists and professionals having nationalism and patriotism spirits, democratic and civilized citizens ; To become citizens having competitive powers, and disciplines, and taking part actively in the development of peaceful life based on the system of Pancasila values. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Filsafat Pancasila Identitas Nasional Hak dan Kewajiban warga negara Negara dan Sistem Konstitusi Demokrasi di Indonesia The Philoshophy of Pancasila National identity Citizen’s rights and obligation State and system of constitution Democracy in Indonesia PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Armaidy Armawi, Geostrategi Indonesia, (Indonesian Geostrategy) Jakarta, Direktorat jenderal Pendidikan Tinggi, 2006 2. Azyumardi Azra, Paradigma Baru Pendidikan Nasional dan Rekonstruksi dan Demokratisasi, (A new Paradigm of National Education and reconstruction and Democratization) Penerbit Kompas, Jakarta, 2002 3. Bahar, Dr. Saefrodin, Konteks Kenegaraan, Hak Asasi Manusia, (State Context on Human Rights) Pustaka Sinar Harapan, Jakarta, 2000. 4. Cassesse, Antonio, Human Right In a Change Word, Hak-Hak Asasi Manusia Di dunia Yang Berubah (terjemahan R.Zainudin), Yayasan Obor Indonesia, Jakarta, 1994. 5. Kaelan, Pendidikan Kewarganegaraan, (Citizenship Education) UGM Press, Yogyakarta 2005.Perspective”, McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, 1995 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091205: Metode Numerik SF 091205: Numerical Method Credits: 2
- 35. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 35 Semester: IV TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa dapat memahami pemecahan numerik, persoalan- persoalan matematika yang digunakan dalam fenomena fisika, dan membuat program sederhana untuk menyelesaikan persoalan- persoalan itu. Students can understand the numerical solution, the problems of mathematics used in physical phenomena, and create a simple program to solve those problems. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan melakukan pemrograman dari algoritma matematika; Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi pemrograman matematika; Ability to do programming from mathematical algorithms; Ability to follow the development of programming technology mathematics POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Akar persamaan, persamaan linier, persamaan tak-linier; Nilai dan vektor eigen; Interpolasi polinomial, integrasi numerik; Persamaan diferensial biasa; Fungsi-fungsi khusus, masalah beda-hingga; The roots of equations, linear equations, non-linear equations; The value and eigen vectors; Polynomial interpolation, numerical integration; Ordinary differential equations; Special functions, finite difference problem. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Suli, E. dan Mayers, D.’”Introduction to Numerical Analysis”, Cambridge University Press, 2003. 2. Karris, S.T.,”Numerical Analysis using Matlab and Spreadsheet”, Edisi 2, Orchard Publications, MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091308: Elektronika Dasar II SF 091308: Fundamental Electronics II Credits: 3 Semester: IV TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu memahami dan menjelaskan arus bolak- balik, analisis dan pemakaiannya (aplikasi). Mahasiswa mampu mengaplikasikan prinsip induksi elekromagnetik. Students are able to state and describe the alternating
- 36. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 36 current, analysis and applications. Students are able to application electromagnetic inductions KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memahami dan menjelaskan sumber sinusoida Kemampuan analisis masalah dalam elektronik Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi elektronika Ability to state and describe sinusoidal source Ability to analysis in electronic problems Ability to follow the develop of electronic technologies POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Analisis keadaan mantap (steady state), Perhitungan daya dalam kondisi mantap; Rangkaian tiga fasa Pengantar transformasi laplace, Analisa rangkaian menggunakan transformasi laplace; Teori Semikonduktor: ikatan kovalen, semikonduktor intrinsik, semikonduktor ekstrinsik; Dioda semikonduk-tor; Transistor sambungan: terbentuk-nya transistor sambungan, komponen arus transistor, stabilitas dan titik kerja transistor, model h transistor, persamaan penguat. Praktikum : (Transformator arus, Transformasi tegangan, Induksi elektromagnetik, Wattmeter, Histerisis) Steady State analysis, Power of Steady State Condition; Three Phasa Circuit; Introduction of Laplace transform; Circuit analysis using Laplace transform; Semiconductor Teory, Covalen bounded, intrinsics & extrinsics semiconductor; Semiconductor dioda, Transistors functions; Component of current intransistor, statility and central point of transistor; transistor model op-amp equations Laboratory work; Current transformation, voltage transformator, electromagnetic induction, Watt meter, histeresys PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. James W. Nilsson dan Susan A. Riedel, 2008, Electronic Circuit, Pearson Prentice Hall. 2. Petunjuk Praktikum Laboratorium Madya 3. Sutrisno, 1986, “ Elektronika”, Penerbit ITB MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091310: Fisika Matematika II SF 091310: Mathematical Physics II Credits: 4 Semester: IV
- 37. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 37 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu mengaitkan fenomena fisis dengan formula matematis yang sesuai, mampu mengurai serta menyelesaikan dengan berbagai metoda analitis yang ada. Students are able to link the physical phenomena with the appropriate mathematical formula, is able to parse and finish with a variety of existing analytical methods. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan pemahaman masalah fisika Kemampuan penerapan matematika dalam bidang fisika Kemampuan penerapan matematka dalam perkembangan metode penyelesaian masalah fisis Ability understanding of physics problems; The ability of the application of mathematics in physics; Ability matematka application in the development of methods of solving physical problems POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Fungsi gamma; Fungsi beta; Rumus stirlling; Solusi deret (metoda Frobenius); Fungsi-fungsi khusus (Polinomial Legendre, Bessel, Weber, Hermite, Laguerre); Persamaan differensial parsial (boundary value problems); Transformasi integral; Kalkulus variasi; Persamaan integral. The function of gamma, beta functions; Formulas stirlling; Solutions series (Frobenius method); Special functions (Legendre Polynomial, Bessel,Weber, Hermite, Laguerre); Partial differential equations (boundary valueproblems); Transformation of the integral; calculus variations, integral equations. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Boas, M.L.,“Mathematical Methods in the Physical Science”, Edisi 3, John Wiley Sons, New York, 2006. 2. Arfken, G.B. dan Weber, H.J.,”Mathematical Methods for Physicists”, Edisi 3, Academic Press, 2001. 3. Butkov, B., “Mathematical Physics”, Addison Wesley, California, 1977. 4. Riley, K.F., Hobson, M.P. dan Bence, S.J.,”Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering”, Edisi 3, Cambridge University Press, 2006. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091314: Gelombang SF 091314: Wave Credits: 4 Semester: IV
- 38. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 38 TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu memahami konsep dasar gelombang dan sifat-sifatnya, serta mampu meng-gunakannya pada gelombang elastik & gelombang elektromagnetik. Students are able to understand the basic concepts of wave and its properties, and able to use them on elastic waves and electro- magnetic waves KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memahami fenomena gelombang Kemampuan memahami konsep dasar gelombang Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi konsep dasar gelombang Ability to understand the phenomenon of wave; Ability to understand the basic concept of wave; Ability to follow the development of the basic concepts of wave technology POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Getaran Harmonis, Getaran Teredam, Getaran Paksa; Perambatan Gelombang 1 dimensi sampai 3 dimensi; Gelombang Elastik, Gelombang EM (pengantar gelombang EM) Refleksi dan Transmisi Gelombang, Interferensi Gelombang, Modulasi Gelombang, SWR, Analisa Fourier; Praktikum : Kisi diffraksi, polarisasi cahaya, spektro-meter, refraktometer, polarimeter, cincin Newton, Harmonic vibration, damped vibration, Forcedvibration; One-dimensional wave propagation through 3-dimensional; Elastic Waves, EM waves (EM wavesintroduction); Reflection and Transmission of Waves, Interference Wave, Wave Modulation, SWR, Fourier Analysis; Practical: Grid diffraction, polarization of light, gamma-meter, refractometer, polarimeter, Newton's rings, PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Prasetio, L. dkk. “Diktat Gelombang”, Fisika, MIPA-ITS, Surabaya 2003 2. Crawford, F.S. ; “Waves”, Berkeley Physics Course, vol 3, Me Graw-Hill, 1968 3. Pain, I.G., “Vibration and Wave in Physics”, Cambrindge University Press, 87 4. Peny, G., “Fourier Series and Optical Transform and Technique in Contemporary Optics”, John Wiley & Sons, Canada, 1995. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091315: Medan Elektromagnetik SF 091315: Electromagnetics Field
- 39. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 39 Credits: 4 Semester: V TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan hukum-hukum dasar medan elektromagnetik didalam hampa dan di dalam bahan. Mahasiswa dapat merumuskannya dalam bentuk integral maupun differensial, memahami sifat-sifat gelombang elektromagnetik dan pemakaiannya, serta mampu memcahkan persoalan-persoalan medan elektromagnetik. Student can explain and understand the fundamental rules of electromagnetic fields in vacum and matter. Student can formulate it in integral an differential forms, unstand the property of electromagnetic waves and its applications. Student can solve electromagnetic problems KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan analisis medan elektronika magnet Kemampuan memiliki melakukan implementasi dengan konsep dasar elektromagnetik The ability of electronic magnetic field analysis; Ability to have implemented with the basic concepts of electromagnetic POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Analisa vektor, Medan listrik, rotasi dan divergensi medan listrik Hukum Gauss, Potensial dan energi listrik, persamaan Laplace, persamaan Poisson, Metode bayangan, ekspansi multi kutub, medan listrik didalam bahan, perpindahan listrik; Medan magnet, rotasi dan divergensi medan magnet, potensial vektor dan skalar magnetik, medan magnet dalam bahan, induksi magnetik, hukum Faraday, Persamaan Maxwell; Hukum-hukum konservasi, persamaan kontinuitas, momentum, momentum sudut; Gelombang Elektromagnetik di dalam vakum dan didalam bahan, Absorbsi dan dispersi, pemandu gelombang; Vector Analysis, Electrostaties, electric field, divergence and cure of electric fields. Gauss law, electric potential, work and energy, Laplace’s equation, Poissoin’s equation, The Method of images, electric fields inmatter. Magnet staties, divergence and cure of magnetic field, magnetic field in matter, electromagnetic induction, Faraday’s law, Maxwell’s equation, The laws of conservation, the continuity equation, momentum, angular momentum. Electromagnetic in vacuum and in matter, Absorption and
- 40. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 40 dispersion, wave guide. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Griffith, D.J., “Introduction to Electrodynamics”, 2 nd , Prentice Hall, 1986 2. Nayfeh, M.H. & M.K Brussel, “Electricity and Magnetis’m, John Wiley & Sons, 1983 3. Reitz, J.R., F.J Milford, & R.W. Christy, “Foundations of Electromagnetic Theory”, 2 nd , Addison Wesley, 1993 4. Wangsness, R.K.,“Electromagnetic Fields”, John Wiley & Sons, 1986. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091316: Fisika Laboratorium SF 091316: Laboratory Physics Credits: 2 Semester: V TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu melakukan praktikum mandiri di laboratorium dengan merancang dan mempersiapkan kegiatan praktikum di laboratorium fisika lanjut. Students are able to conduct independent lab in the lab by designing and preparing for practical activities in the advanced physics laboratory. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Memiliki kemampuan skill di laboratorium untuk peralatan elektronika, fisika modern dan optoelektronika Strong skills in the laboratory for electronics equipment, modern physics and optoelectronics POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Perancangan dan pelaksanaan kegiatan praktikum di laboratorium , kelompok minat Fisika Bahan (laboratorium Fisika Zat Padat, laboratorium Semikonduktor, laboratorium Spektroskopi); Optika (laboratorium Optika dan optoelektronika), Instrumentasi (laboratorium akustik, laboratorium elektronika); Fisika Teori (laboratorium fisika teori dan filsafat alam). Design and implementation of practical activitiesin the laboratory, interest groups Materials Physics (Physics Laboratory of Solid Substances, Laboratory Semiconductor, Spectroscopy Laboratory); Optics (Optics and optoelectronics laboratory),instrumentation (ac oustic lab, electronics lab); Physics Theory (physics laboratory theory andnatural philosophy). PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Petunjuk Praktikum Fisika madya
- 41. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 41 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091317: Fisika Kuantum SF 091317: Quantum Physics Credits: 4 Semester: V TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menerangkan prinsip-prinsip kuantum, memahami sistem kuantum sederhana, metoda perumusan dan solusinya untuk memecahkan persoalan atomik dan molekular. Students can describe quantum principles, understand some simple quantum systems, formulation and solution of atomic and molecular problems KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memecahkan masalah tentang permasalahan atomik dan molekuler Kemampuan menerapkan fisika kuantum dalam berbagai bidang Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi yang menggunakan konsep dasar kuantum Ability to solve problems concerning the atomicand molecular problems; Ability to apply quantum physics in different fields; Ability to follow developments in technology that uses basic concepts of quantum; POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Lompatan dari mekanika klasik ke teori kuantum, paket gelombang, prinsip ketaktentuan, persamaan Schroedinger, fungsi dan nilai eigen, gerak partikel dalam potensial satu dimensi, metoda operator, gerak partikel dalam ruang tiga dimensi, momentum angular, persamaan radial, polar dan azimutal, atom hidrogen, interaksi elektron dengan medan elektromagnetik, metoda matriks, spin, penjumlahan momentum angular, teori gangguan bebas waktu, teori gangguan bergantung waktu, atom hidrogen nyata, atom helium, molekul, radiasi atom dan teori hamburan. Transition from classical to quantum theory, wave packets, uncertainty principle, Schrodinger equation, eigen functions and eigen values, particle in one dimensional potential, three dimensional systems: angular momentum, radial potential and hydrogen atom, operator method, spin and the addition of angular momentums, time independent perturbation theory. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. S. Gasiorowicz, “Quantum Physics”, 3 rd Ed., Wiley Internat. Ed.,USA, 2003. 2. Libofs, R.L,“Introductory Quantum Mechanics” Wesley Publishing Company, 2 nd .th, New York, 1992 3. A. Purwanto, “Fisika Kuantum”, Gava Media, Yogyakarta, 2006.
- 42. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 42 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091206: Fisika Komputasi SF 091206: Computation Physics Credits: 4 Semester: VI TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menggunakan cara-cara numerik untuk menyelesaikan persoalan-persoalan fisika melalui pemrograman komputer. Students can use numerical methods to solving physics problems through computer programming. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan pemrograman numerik persoalan fisika Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi komputasi fisika; The ability of numerical programming problems physics; Ability to follow the development of physics computing technology POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Estimasi kesalahan empirik, pencocokan kurva (fitting), Metode kuadrat terkecil, aplikasi persamaan diferensial biasa (bandul terpaksa, persamaan Schrodinger), Aplikasi matriks (masalah nilai eigen, struktur elektronik dalam atom, sistem banyak benda), analisis spektra, Aplikasi persamaan diferensial parsial, dinamika molekuler, sistem kontinyu, Pengantar simulasi Monte-Carlo. Estimation of the empirical error, curve-fitting (fitting), Method of least squares, the application ofordinary differential equations (forced pendulum,Schrodinger equation), The application matrix (eigen value problem, the electronic structure of atoms, the many objects),spectral analysis, The application of partial differential equations, molecular dyna- mics, continuous system, Introduction to Monte-Carlo simulation. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Pang, T.,”An Introduction to Computational Physics”, Cambridge University Press, 2006. 2. Landau, R.H. dan Paez, M.J.,”Computaional Physics, Problem Solving with Computers”, John-Wiley & Sons, 1997. 3. Ehrlich, R.,“Physics & Computers: Problems, Simulations & Data Analysis”, Haughton Mifflin Company, 1973. 4. Dom & McCrachen,“Numerical Methods with Fortran IV Case Studies”, John Wiley & Sons, 1972. 5. Hornan,S.E.,“Computational Physics”, Addison Vesley, 1986
- 43. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 43 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091318: Fisika Statistik SF 091318: Statistics Physics Credits: 3 Semester: VI TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan fenomena termodinamika (makroskopis) dari tinjauan mikroskopis melalui model-model distribusi statistik Maxwell-Boltzmann, Bose-Einstein dan Fermi-Dirac. Students can describe thermodynamical phenomena from microscopical point of view using Maxwell-Boltzmann, Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac distribution. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Kemampuan memahami masalah termodinamika secara lebih mendalam Kemampuan analisis masalah probabilistik distribusi dalam termodinamika Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi Ability to understand issues in more depth thermodynamics; Ability to analyze problems in thermodynamics probabilistic distribution; Ability to follow developments in technology POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Konsep dasar probabilitas dan distribusi binomial, karakteristik sistem termodinamika (makrokroskopik) dari sudut pandang mikroskopik; Lingkup fisika statistik, ensembel dan ruang fase, statistik Maxwell-Boltzmann, fungsi partisi Boltzmann, paradoks Gibbs; statistik Bose-Einstein, gas foton, gas fonon, statistik Fermi-Dirac, gas elektron, paramagnetisme Pauli, pancaran termionik. Basic concepts of probability and binomial distributions, specifications of microscopic states, characteristics of thermodynamical systems from microscopic point of view, ensemble and phase space, entropy and temperature, partition function, Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics and Gibbs paradox, Bose-Einstein statistics: photon dan phonon gas, Fermi-Dirac statistics: electron gas, Pauli paramagnetism, thermionic emission. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ 1. Purwanto, A.(2007).’Fisika Statistik’, GavaMedia, Yogyakarta. 2. Greiner, W., Neise, L. dan Stocker H..(1997).’Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics’, Springer, Berlin.
- 44. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 44 REFERENCES 3. Pointon, A.J.,“An Introduction to Statistical Physics”, Longman Grup Ltd., London, 1978. 4. Sears. F.W. & G.L. Salinger,“Thermodynamic, Kinetic Theory and Statistical Thermodynamics”, Addison Wesley, 1975. 5. Rei, F., “Statistical Physics”, Berkeley Physics Course, MC Graw- Hill. 1978 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE IG 091306: Bahasa Indonesia IG 091306: Indonesian Credits: 2 Semester: VI TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa memperoleh kemahiran dalam menggunakan bahasa Indonesia untuk menguasai, menerapkan dan mengembangkan ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi dan seni dengan penuh rasa tanggung jawab sebagai warga negara yang berkepribadian mulia. Students gain skills to use Indonesian Language to acquire, apply and develop science, technology and art accountably as noble citizens. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa mampu menggunakan bahasa Indonesia untuk mengungkapkan fakta, gagasan, metode, konsep, dan prinsip- prinsip ilmiah ke dalam karya ilmiah yang berkualitas (memenuhi syarat lugas, logis, sistematis, cendekia, efektif, efisien, dan menarik). Mahasiswa mampu memanfaatkan kemahiran bahasa Indonesia untuk mengembangkan diri sepanjang hidupnya. Students are able to use Indonesian Language to express fact, ideas, method, concept and scientific principles in a quality scientific work (simple, logic, systematic, educated, effective, efficient, and interesting). Students are able to make use of their Indonesian Language skills for their own longlife self-development. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Pendahuluan: Pengantar, bahasa Indonesia ilmiah, analisis kesenjangan dalam karya ilmiah (gap analysis). Komposisi Bahasa: komposisi kalimat efektif, syarat-syarat keefektifan, paragraf dan teknik pengembangan paragraf (komposisi paragraf). Menulis Akademik: menulis pendahuluan, metodologi, tinjauan pustaka dan/atau analisis/ pembahasan, serta daftar pustaka. Format penulisan karya ilmiah: proposal, makalah, dan atau laporan ilmiah.
- 45. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 45 Konsep Presentasi: teknik presentasi, penyiapan materi, kejelasan alur pikir, penyampaian materi. sikap berpresentasi, ringkasan dan jawaban berpresentasi. Introduction: Indonesian Language for scientific purposes, Language gap analysis of scientific article. Language Composition: Effective sentence, paragraph and paragraph composition Academic Writing: Introduction, methodology, literature review/analysis/discussion, bibliography. Scientific Writing: Proposal, Article, Scientific writing report. Presentation: Presentation techniques, outlining, delivery, attitude, summary, question-answer session. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Alwi, Hasan. 2000. Tata Bahasa Baku Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian Language Grammar). Jakarta: Balai Pustaka 2. Arifin, E. Zaenal. 1987. Penulisan Karangan Ilmiah dengan Bahasa Indionesia yang Benar (Writing Scientific Article Uisng Correct Indonesian Languge). Jakarta: Mediyatama Sarana Perkasa. 3. Brotowidjojo, Mukayat D. 1995. Penulisan Karangan Ilmiah (Writing Scientific Article). Jakarta: Akademika Presindo. 4. Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. 1998. Pedoman Ejaan Bahasa Indonesia yang Disempurnakan (Guidance of Official Indonesian Spelling System). Jakarta: Balai Pustaka 5. Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan.1998. Pedoman Umum Pembentukan Istilah (General Guidance of Terminology Formation). Jakarta: Balai Pustaka. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091207: Seminar SF 091207: Seminar Credits: 2 Semester: VII TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu membaca dan meringkas beberapa artikel jurnal ilmiah berbahasa Inggris, selanjutnya menyusun ringkasan dan kritik atas artikel tertentu serta mempresentasikannya di depan kelas. Students are able to read and summarize several scientific journal articles in English, then compile a summary and critique of certain articles andpresented it in front of the class. KOMPETENSI/ Mahasiswa mampu melakukan presentasi, menyampaikan hasil penelitian, dan menyapaikan pendapat.
- 46. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 46 COMPETENCY Students are able to make presentations, deliver results, and express opinion. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Membaca dan meringkas artikel jurnal ilmiah berbahasa Inggris Menyusun ringkasan dan kritik atas dua buah artikel ilmiah Menyajikan hasil kerjanya di depan kelas menggunakan multimedia. Read and summarize the scientific journal articles in English; Develop a summary and critique of two scientific articles; Presenting their work in front of the class using multimedia. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Academic writing and publishing, J. Hartley, Taylor and Francis e- Library, 2008. 2. Writing for science and engineering, H. Sylin-Roberts, Butterworth -Heinemann 2002. 3. Measurement Uncertainties in Science and Technology, M. Grabe, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2005 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091319: Fisika Zat Padat SF 091319: Solid State Physics Credits: 4 Semester: VII TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan dan menerapkan prinsip-prinsip fisika dalam memahami struktur dan sifat-sifat zat padat serta penerapannya. Students are able to explain and apply the principles 0f physics in understanding the structureand properties of solids and its appli-cation. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa dapat memahami struktur kristal, difraksi dalam kristal, vibrasi kisi kristal Mahasiswa dapat memahami elektro dalam logam dan struktur elektronik zat padat Mahasiswa dapat memahami semikonduktivitas dan piranti sekonduktor Mahasiswa dapat memahami sifat optik dan magnetik zat padat Mahasiswa dapat memahami superkonduktivitas dan material nano. Students can understand the crystal structure, diffraction in the crystal, the crystal lattice vibrations; Students can understand electrical and electronic structure in metallic solids;
- 47. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 47 Students can understand the semiconductivity and semiconduc-tor devices; Students can understand the optical and magnetic properties of solids; Students can understand superconductivity andnano materials. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Struktur kristal (keadaan kristalin, kisi Bravais, arah dan bidang kristal) dan Gaya antar atom; Difraksi sinar-x (Hk bragg, hambuaran atom dan kristal, kisi balik, penerapan sinar-x) difraksi neutron dan elektron; Kisi vibrasi (kapasitas panas model Einstein dan debye, kapasitas panas, konduktivitas panas, hamburan sinar-x, neutron, dan cahaya oleh fonon). Elektron dalam logam (elektron konduksi, konduktivitas dan resistivitas listrik, permukaan Fermi, konduktivitas panas dalam logam); struktur elektronik zat padat (struktur pita zat padat, zone Brillouin, pita energi dan penerapannya) Semikonduktivitas (bahan semikonduktor, semikonduktor intrinsik dan ekstrinsik, semikon- duktor tipe-p dan tipe-n, gejala difusi), piranti semikonduktor (sambungan p-n, transistor sambungan, jenis-jenis dioda, rangkaian terpadu) Dielektrika dan sifat optik zat padat (perumusan dielektrika dan tetapan dielektrik, polarisasi dan polarisabilitas, pizoelektrik, ferroelektrik), Magnetisme dan Resonansi magnetik (gejala kemagnetan, suseptibilitas magnet, klasifikasi bahan magnet, resonansi paramagneti dan resonansi magnetik inti) Superkonduktivitas (gejala superkonduktivitas dan super- konduktor, konduksi ion, semi-konduktor amorfus, kristal cair), material nano (.................) Crystal structure (crystalline state, Bravais lattice,the direction and the crystal field) and style between atoms; x-ray diffraction (Hk Bragg, scattering atoms and crystals, lattice back, the appli- cation of x-rays), neutron and electron diffraction, lattice vibra- tions (capacity Einstein and Debye model of heat, heat capacity, thermal conductivity, x-ray scattering, neutron, and light by phonons). Electrons in the metal (electron conduction, conductivity and elec- trical resistivity, Fermisurface, thermal conductivity in metals); electronicstructure of solids (band structure of solids, Brillouin zones, energy bands and their application) Semi-conductivity (semiconductor materials, intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, semiconconductor p-type and n-type, diffusion phenomena), semiconductor devices (pn junction, the transistor connection, the types of diodes, integrated circuits) Dielectric and optical properties of solids (the formulation of dielectric and dielectric constant, polarization and polarization- mobility, pizoelektrik, ferroelectric), Magnetism and Magnetic
- 48. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 48 Resonance (symptoms of magnetism, magnetic susceptibility, classification of magnetic materials, paramagnetic resonance and nuclear magnetic resonance) Superconductivity (phenomenon of superconductivity and super- conductors, ionconduction, amorphous semi-conductors, liquid crystals), nano materials. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. M.A Omar, “Elementary Solid State Physics”, Addison Wesley, New York, 1975 2. S.W Winata, Z Arifin, “Fisika Zat Padat I” Diktat Kuliah Jurusan Fisika FMIPA-ITS, Surabaya, 2001 3. S.W Winata, Darminto, dan Z Arifin, “Fisika Zat Padat II” Diktat Kuliah Jurusan Fisika FMIPA-ITS, Surabaya, 2002 4. F Blackmore, “Solid State Physics” John Willey and Sons, New York, 1976 5. Kittel, “Introduction Solid State Physics” John Willey and Sons, New York, 1991 6. J.R Christman, “Fundamentals of Solid State Physics” John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1988 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091320: Fisika Inti SF 091320: Nuclear Physics Credits: 4 Semester: VII TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan sifat-sifat inti , memahami interaksi inti yang dapat terjadi dan memahami struktur inti. Students are able to explain the properties of the core, the core of understanding interactions that can occur and understand the core structure KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Memiliki kemampuan memahami tentang fisika inti Kemampuan memahami penetahuan radiioaktif Kemampuan mengikuti perkembangan teknologi nuklir Strong understanding of core physics; Ability to understand penetahuan radiioaktif; Ability to follow the development of nuclear technology POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Gejala radioaktivitas, peluruhan radioaktif, massa inti, energi ikat inti, model dan struktur inti, spin dan momen magnetik inti, model reaksi inti, fisi dan fusi, reaksi berantai, reaktor dan jenisnya, interaksi radiasi dan materi, deteksi radiasi, peluruhan alfa, beta
- 49. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 49 dan gamma, radioisotop dan aplikasinya. Symptoms of radioactivity, radioactive decay, the core mass, core binding energy, and model corestructure, spin and magnetic moment of the core, the model of nuclear reaction, fission and fusion, chain reaction, and reactor type, the interaction ofradiation and matter, radiation detection, alphadecay , beta and gamma, radioisotopes and their applications. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Krane, K.S., “Introductory Nuclear Physics”, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1988. 2. Eisberg, R., & R. Resnick, “Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei, and Particles”, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2nd Ed., 1985. 3. Arya, A.P., “Fundamental Nuclear Physics”, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1983 4. Wong,S.S.M., “Introductory Nuclear Physics”, PTR Prentice Hall, Englewood, New Jersey, 1990 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091317: Pengantar Technopreneur SF 091317: Introduction to Technopreneur Credits: 2 Semester: VII TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Merubah mindset mahasiswa dari job seeker menjadi job creator serta membekali mahasiswa dengan kemampuan untuk menyusun sebuah rencana/proposal bisnis (Business Plan) Students are able to change their mindset from being job seekers to being job creators and are able to make a business plan KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Memiliki mindset sebagai seorang teknopre-neurship Mampu menyusun Rencana/Proposal Bisnis (Business Plan) yang baik. Having technopreneur mindset Being able to make business plan well POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Pendahuluan (Defininsi, jenis, orientasi, spirit, dan perilaku enterpreneur dalam menghadapi resiko, Kecerdasan emosional menuju kesuksesan, Perbedaan enterpreneur, teknopreneur, dan usaha kecil). Perubahan Mindset (Pola pikir positip, Mengubah perspektif dengan game, Memunculkan alternatif solusi). Sukses Story membangun karir Teknopreneurship (Alasan memilih
- 50. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 50 bidang usaha, Keuntungan sebagai teknopreneurship,Soft skill faktor yang dibutuhkan, Bagaimana membangun kompetensi dan jaringan). Peluang Usaha (Teknik-teknik mengidentifikasi peluang usaha, Kendala dan resiko produk atau usaha baru, Identifikasi jenis usaha yang sedang trend). Pemasaran Usaha (Proses pembentukan strategi pemasaran (STP dan 4P), Identifikasi persaingan, Menerobos kendala persaingan). Introduction (Definition,types, orientation, spirit, and attitudes of enterpreneur in dealing with risks.Emosional quotient towards success, The differencebetween enterpreneur, technopreneur, and small business). Changing Mindset (Positive mindset, Changing perspective through game, Generating alternative solution) Success Story: Developing Technopreneurship Career ; Reason for choosing business career, Advantages of being technopreneurship, Soft skill factor, How to develop competencies and network. Business Opportunities ; Business opportunity identification techniques, Problems and risks of new product or new business, Identifying booming business. Marketing ; Process of marketing strategy (STP and 4P), Identifying competition, Break through competition problems PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Tim Teknoprenersip ITS, Diktat “Teknoprenersip” (Technopreneurship, textbook ) 2. Yoseph Murphi, Membangkitkan Kekuatan Bawah Sadar (Arousing Subconscious Power) , Pioner Jaya, 2002 3. Carol Draeck, Change Your Mindset Change Your Life, Serambi, 2006 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091321: Tugas Akhir SF 091321: Final Project Credits: 6 Semester: VIII TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Melatih mahasiswa melakukan penelitian sesuai ilmu yang telah dimiliki dan selanjutnya melaporkan hasil penelitiannya baik secara tertulis maupun dengan cara presentasi. Train students to do research based on science that has been learned and subsequently reported the findings either in writing or by presentation. KOMPETENSI/ Mampu menyusun Rencana/Proposal penelitian yang baik
- 51. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 51 COMPETENCY Memiliki kemampuan melaksanakan penelitian Memiliki kemampuan melaporkan hasil penelitian secara sistematik. Able to develop proposal good research; Have the ability to do research; Have the ability to report the results of systematic research. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Menyusun proposal penelitian terprogram Melaksanakan penelitian berdasarkan proposal yang disusun Menyusun laporan berupa buku tugas akhir Mempresentasikan hasil penelitiannya Develop proposal programmed; Carry out research based on proposals prepared; Prepare report form book; Presenting research as final projrct book. PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Academic writing and publishing, J. Hartley, Taylor and Francis e- Library, 2008. 2. Writing for science and engineering, H. Sylin-Roberts, Butterworth-Heinemann 2002. MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SG091205: BAHASA INGGRIS LANJUT SG091205: ADVANCED ENGLISH Credits: 2 Semester: V/VI/VII/VIII TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa akan dapat memahami percakapan pendek, percakapan panjang dan monolog pada bagian LISTENING COMPREHENSION Part A, B, and C, penggunaan tata bahasa Inggris dan memilih jawaban yang tepat pada bagian STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION, dan bacaan-bacaan dalam Paper-based TOEFL pada bagian READING COMPREHENSION dan memilih jawaban yang tepat dalam Paper-based TOEFL. The students are going to be able to understand short conversation, longer conversation, and monolog, at LISTENING COMPREHENSION Part A, B, and C, the usage of English structure at STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION , and texts at READING COMPREHENSION and select the most appropriate answer in paper- based TOEFL KOMPETENSI/ Mahasiswa akan dapat memahami percakapan pendek,
- 52. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 52 COMPETENCY percakapan panjang dan monolog dan memilih jawaban yang tepat dalam Paper-based TOEFL bagian LISTENING COMPREHENSION Part A, B, and C Mahasiswa akan dapat memahami penggunaan tata bahasa Inggris dan memilih jawaban yang tepat dalam Paper-based TOEFL bagian STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION Mahasiswa akan dapat memahami bacaan dan memilih jawaban yang tepat dalam Paper-based TOEFL bagian READING COMPREHENSION The students are going to be able to understand short conversation, longer conversation, and monolog, at LISTENING COMPREHENSION Part A, B, and C and select the most appropriate answer in paper-based TOEFL The students are going to be able to understand the usage of English structure at STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION and select the most appropriate answer in paper-based TOEFL The students are going to be able to understand texts at READING COMPREHENSION and select the most appropriate answer in paper-based TOEFL POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Percakapan pendek, percakapan panjang dan monolog dalam Paper-based TOEFL bagian LISTENING COMPREHENSION Part A, B, and C Tata bahasa Inggris dalam Paper-based TOEFL bagian STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION Bacaan-bacaan dalam Paper-based TOEFL bagian READING COMPREHENSION Short conversation, longer conversation, and monolog, at LISTENING COMPREHENSION Part A, B, and C in paper-based TOEFL The usage of English structure at STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION in paper-based TOEFL Texts at READING COMPREHENSION n paper-based TOEFL PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. Phillips,,D.,Longman Preparation Course for the TOEFL Test,. New York, Pearson Education 2003. 2. Phillips,,D., Longman Preparation Course for the TOEFL Test, Introductory Course ,New York Pearson Education, 2004. 3. Mahnke,M.K. and Duffy, C.B.TOEFL Preparation Course ,New Jersey, Macmillan Heineman ELT 2006
- 53. Kurikulum/CurriculumITS:2009-2014 53 MATA KULIAH/ COURSE TITLE SF 091209: Fisika Keramik SF 091209: Physics of Ceramics Credits: 3 Semester: TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan struktur dan sifat bahan keramik serta contoh penggunaannya. Students can explain the structure and properties of ceramic materials as well as examples of its use. KOMPETENSI/ COMPETENCY Mahasiswa dapat mendiskripsikan struktur dan cacat bahan keramik. Mahasiswa dapat peran cacat terhadap sifat bahan. Mahasiswa dapat memahami sifat keramik utamanya konduksi, permitivitas, kekerasan, keuletan. Mahasiswa dapat mengerti proses pembuatan keramik. Students can describe th e structur e and defects of ceramic material. Students may role of defects on material properties. Students can understand the nature of its mainconduction ceramics, permittivity, hardness, ductility. Students can understand the process of making ceramics. POKOK BAHASAN/ SUBJECTS Definisi dan ruang lingkup kajian bahan keramik, struktur keramik, cacat dalam keramik, gejala difusi, konduksi listrik, diagram fasa, tranformasi fasa, proses keramik, reaksi padat, kalsinasi, sintering, fracture, kriteria Grifith, creep, fatigue, dielektrik. Definition and scope of the study of ceramicmaterials, ceramic structure, defects in ceramics, diffusion phenomena, electrical conductivity, phase diagram, phase transformation, the process ofceramics, solid reaction, calcination, sintering, fracture, Grifith criteria, creep, fatigue, dielectric PUSTAKA UTAMA/ REFERENCES 1. M.W. Barsoum, “Fundamental of Ceramics”, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1997. 2. Suasmoro, "Fisika Keramik", Jurusan Fisika MIPA ITS, Surabaya, 1999.