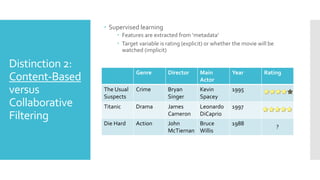
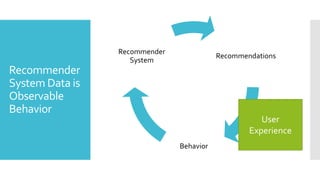
Mark Graus gave a presentation on recommender systems and the importance of considering the human factor. He discussed how recommender systems use machine learning algorithms like collaborative filtering and content-based filtering to make predictions, but that machine learning alone is not enough. User behavior data from recommender systems is limited and does not capture things like user preferences, privacy concerns, or choice overload. It is important to conduct A/B testing and user experience evaluations to understand how users actually interact with and feel about recommendation systems. The key takeaway is that recommender systems require both strong machine learning and a focus on the human perspective.