2.atomic structure and bonding
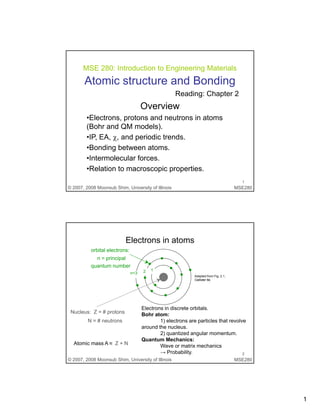
- 1. 1 MSE 280: Introduction to Engineering Materials Reading: Chapter 2 Atomic structure and Bonding g p Overview •Electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms (Bohr and QM models). •IP, EA, χ, and periodic trends. MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 1 •Bonding between atoms. •Intermolecular forces. •Relation to macroscopic properties. Electrons in atoms orbital electrons: n = principal quantum number 1 Nucleus: Z = # protons Adapted from Fig. 2.1, Callister 6e. Electrons in discrete orbitals. Bohr atom: n=3 2 1 MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 2 N = # neutrons Atomic mass A ≈ Z + N 1) electrons are particles that revolve around the nucleus. 2) quantized angular momentum. Quantum Mechanics: Wave or matrix mechanics → Probability.
- 2. 2 Comparison of Bohr and QM models MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 3 Figs. 2.2 and 2.3 from Callister 6 ed. Atomic orbitals dyz dxy MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 4 s px py pz dz2dx2-y2dxz • have discrete energy states (Quantized). • tend to occupy lowest available energy state. Electrons...
- 3. 3 Quantum numbers • Principal: n = 1, 2, 3, 4… • Angular momentum: l = 0, 1, 2, 3…, n – 1 = s, p, d, f… s = sharp, p = principal, d = diffuse, f = fundamental • Magnetic: ml = 0, ±1, ±2, ±3… , ±l Determines the number of states in a given l subshell (2l +1 total) • Spin: ms = ±1/2 e g MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 5 e.g. 1s n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = 1/2 n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = -1/2 2s n = 2, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = 1/2 n = 2, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = -1/2 Which atom is this? Be Electron Configuration - Shorthand notation to represent which states electrons occupy in an atom (without specifying electron spin). e.g. Carbon 1s 2s Electron configuration: 1s22s22p2 2p MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 6 Note - each energy level can only hold two electrons of opposite spin (Pauli exclusion principle). - for degenerate levels (e.g. 2p-orbitals), each orbital is filled with one electron before electrons are paired up.
- 4. 4 Electron configuration 1 electron in the s-orbital: Alkali metals Li, Na, K, Rb… 2 electrons in the s-orbital: Alkaline earths Be, Mg, Ca… Filled s-orbital and 4 electrons in p-orbital: Chalcogens O, S, Se… Filled s-orbital and 5 electrons in p-orbital: Halogens F Cl Br MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 7 F, Cl, Br… Partially filled d-orbital: Transition metals e.g. Mn, Fe, Co… Valence electrons determine which group atoms belong to. Stable configuration • have complete s and p subshells t d t b i t Stable electron configurations... • tend to be inert. Z Element Configuration 2 He 1s 2 10 Ne 1s 22s 22p 6 18 Ar 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p6 Adapted from Table 2.2, Callister 6e. MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 8 36 Kr 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p63d10 4s 24p6 Noble gases
- 5. 5 Valence electrons 2p 3s 2p 3s Filled shell} Valence electron 1s 2s p Na 1s 2s Na+ Filled shell leads to stability. } Lose an electron 3 3p 3s 3p Filled shell} Valence electrons MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 9 Gain an electron 1s 2s 2p 3s Cl 1s 2s 2p 3s Cl- leads to stability. How much energy does it require to take an electron out of an atom? Energy of an electron in vacuum Energy Valence electron IP MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 10 • Ionization potential (IP): Energy required to pull out a valence electron (in vacuum). By convention, IP is positive (i.e. need to put in energy to pull out the electron).
- 6. 6 How much energy does it require to place an electron in an atom? Energy of electron in vacuum Energy Valence electrons EA Lowest available state MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 11 • Electron Affinity (EA): Energy gained by putting an electron in (from vacuum). By convention, EA is negative (i.e. electron goes from higher energy state in vacuum to lower energy state in atom). How do we determine when an atom will accept an electron or give one up? y EA IP Vacuum level • Electronegativity (χ): a measure of how likely an atom will take up or give up an electron EAIP + Energy Valence electrons EA Lowest available state IP χ MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 12 A simple (and intuitive) definition: -When two atoms are brought together, the atom with larger χ will have higher electron density around its nucleus. -Larger Δχ more ionic bond. 2 ~ EAIP x +
- 7. 7 MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 13 Bonding Primary Ionic E Covalent Metallic Secondary Dipole-dipole H bonds E MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 14 H-bonds Dipole-induced-dipole Fluctuating dipoles Equilibrium bond length
- 8. 8 Ionic Bonding • Occurs between + and - ions. • Requires electron transfer. Na (metal) unstable Cl (nonmetal) unstable electron • Large difference in electronegativity required. • Example: NaCl 3s 3p MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 15 electron + - Coulombic Attraction Na (cation) stable Cl (anion) stable Na (χ = 0.9) 3s 3p Cl (χ = 3.0) Ionic Bonding Na (metal) unstable Cl (nonmetal) unstable electron +Na (cation) Cl (anion) ezz EA 4 2 21 =+ - Coulombic Attraction Na (cation) stable Cl (anion) stable ro A πε4 Since z1 = +1 for Na+ and z2 = -1 for Cl- r A r e E o A −=−= πε4 2 Negative energy means attraction only. Will the atoms collapse on themselves? MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 16 No, there is also repulsive energy (e.g. e-e repulsion) nR r B E = B and n depend on atoms involved. In many cases n ~ 8.
- 9. 9 Ionic Bonding E r A E nR r B E = Bond energy MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 17 r EA −= Equilibrium bond length gy Note: Other types of bonds can also be described in a similar manner Ionic Bonding: examples • Predominant bonding in Ceramics M O NaCl He - Ne - Ar - Kr - Xe - F 4.0 Cl 3.0 Br 2.8 I 2.5 Li 1.0 Na 0.9 K 0.8 Rb 0.8 H 2.1 Be 1.5 Mg 1.2 Ca 1.0 Sr 1.0 Ti 1.5 Cr 1.6 Fe 1.8 Ni 1.8 Zn 1.8 As 2.0 Cs Cl MgO CaF 2 O 3.5 MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 18 Give up electrons Acquire electrons Rn - At 2.2 Cs 0.7 Fr 0.7 Ba 0.9 Ra 0.9 Adapted from Fig. 2.7, Callister 6e. (Fig. 2.7 is adapted from Linus Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd edition, Copyright 1939 and 1940, 3rd edition. Copyright 1960 by Cornell University. From Callister 6e resource CD.
- 10. 10 Covalent Bonding 1s 1s HH Molecular orbitals • “Sharing” of electrons • Why do some atoms want to share electrons? • Example2: CH4 C: has 4 valence e, needs 4 more • Example1: H2 shared electrons from carbon atom H CH4 H H HH Atomic orbitals MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 19 H: has 1 valence e, needs 1 more Electronegativities are same or comparable. Adapted from Fig. 2.10, Callister 6e. shared electrons from hydrogen atoms HH H C an s-orbital three p orbitals Atomic Orbitals atomic orbitals for carbon: 1s 2s 2p 4 valence electrons but two different types orbitals. H’s on CH4 should be equivalent. x y z px py pz an s-orbital p Hybridization sp3 hybridization for C in CH4 MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 20 x y z 1s + 2p = sp2-orbitals 1s + 3p = sp3-orbitals 60° 60° x y z y x y z 1s + 1p = sp-orbitals sp3 hybridization for C in CH4
- 11. 11 EXAMPLES: COVALENT BONDING He - H 2 1 SiC C(diamond) H2O H2 Cl2 F2 columnIVA Ne - Ar - Kr - Xe - Rn - F 4.0 Cl 3.0 Br 2.8 I 2.5 At 2.2 Li 1.0 Na 0.9 K 0.8 Rb 0.8 Cs 0.7 Fr 0.7 2.1 Be 1.5 Mg 1.2 Ca 1.0 Sr 1.0 Ba 0.9 Ra 0.9 Ti 1.5 Cr 1.6 Fe 1.8 Ni 1.8 Zn 1.8 As 2.0 SiC C 2.5 Cl2 Si 1.8 Ga 1.6 GaAs Ge 1.8 O 2.0 c Sn 1.8 Pb 1.8 Adapted from Fig. 2.7, Callister 6e. (Fig. 2.7 is MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 21 • Molecules with nonmetals • Molecules with metals and nonmetals • Elemental solids (RHS of Periodic Table) • Compound solids (about column IVA) 0.9 p g , ( g adapted from Linus Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd edition, Copyright 1939 and 1940, 3rd edition. Copyright 1960 by Cornell University. % ionic character Most bonds between two different types of atoms are somewhere in between ionic and covalent.between ionic and covalent. % ionic character = ]})(25.0exp[1{ 2 BA χχ −−− χj = electronegativity of atom j MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois χj electronegativity of atom j KEY POINT: Larger electronegativity difference more ionic
- 12. 12 Example problem • Order the following semiconductors from t l t t t i imost covalent to most ionic. 1) ZnS, GaP, CuCl 2) ZnS, ZnSe, ZnO MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 23 What’s so important about ionicity of bonds? • Chemical properties NaCl (highly ionic solid) dissolves readily in water but– NaCl (highly ionic solid) dissolves readily in water but Si (covalent solid) does not. • Electronic properties – Ionicity of the bonds will have a strong influence on the band gap and other electronic properties. • All properties of materials are largely determined MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 24 All properties of materials are largely determined by the types and strength of bonds between the constituent atoms.
- 13. 13 Metallic Bonding • Arises from a sea of donated valence electrons Fixed ion cores (nuclei + + + + + + Fixed ion cores (nuclei and inner electrons) “sea” of electrons MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 25 • Primary bond for metals and their alloys. • Large atomic radius and small IP will more likely lead to metallic bonding. + + + Adapted from Fig. 2.11, Callister 6e. Secondary Bonds: Intermolecular Forces • Dipole-dipole interaction: secondary bond between molecules with permanent dipole moments Van der Waals + - secondary bonding + - H Cl H Clsecondary bonding secondary bonding -general case: -ex: liquid HCl -ex: polymer Adapted from Fig. 2.14, Callister 6e. Adapted from Fig. 2.14, Callister 6e. From Callister 6e resource CD. MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 26 • Hydrogen bonding H O H H O H H O H
- 14. 14 • Dipole-induced-dipole interaction: secondary bond between molecules with permanent dipole moments + - + - + - • Fluctuating dipoles H2 H2 ex: liquid H 2asymmetric electron clouds secondary bonding polar Nonpolar (e.g. atom) MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 27 HH HH H2 H2 secondary bonding clouds + - + -secondary bonding Adapted from Fig. 2.13, Callister 6e. SUMMARY: BONDING Type Ionic Bond Energy Large! Comments Nondirectional (ceramics)Ionic Covalent Large! Variable large-Diamond small-Bismuth Variable Nondirectional (ceramics) Directional (semiconductors, ceramics polymer chains) MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 28 Metallic Secondary large-Tungsten small-Mercury smallest Nondirectional (metals) Directional inter-chain (polymer) inter-molecular From Callister 6e resource CD.
- 15. 15 • Bond length, r F F • Melting Temperature, Tm Energy (r) PROPERTIES FROM BONDING: TM • Bond energy, Eo r Energy (r) unstretched length r larger T smaller T m ro MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 29 Eo= “bond energy” ro r u st etc ed e gt larger T m Tm is larger if Eo is larger. From Callister 6e resource CD. • Elastic modulus, E cross sectional area A o length, Lo undeformed ΔLF Elastic modulus PROPERTIES FROM BONDING: E • E ~ curvature at ro ΔL F undeformed deformed ΔLF Ao = E Lo Energy unstretched length E is larger if curvature at MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 30 r larger Elastic Modulus smaller Elastic Modulus ro unstretched length E is larger if curvature at ro is larger. From Callister 6e resource CD.
- 16. 16 Ceramics (Ionic & covalent bonding): Large bond energy large Tm large E small α SUMMARY: BONDING and Materials’ properties Metals (Metallic bonding): Polymers small α Variable bond energy moderate Tm moderate E moderate α Directional Properties MSE280© 2007, 2008 Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois 31 Polymers (Covalent & Secondary): secondary bonding Directional Properties Secondary bonding dominates small T small E large α From Callister 6e resource CD.