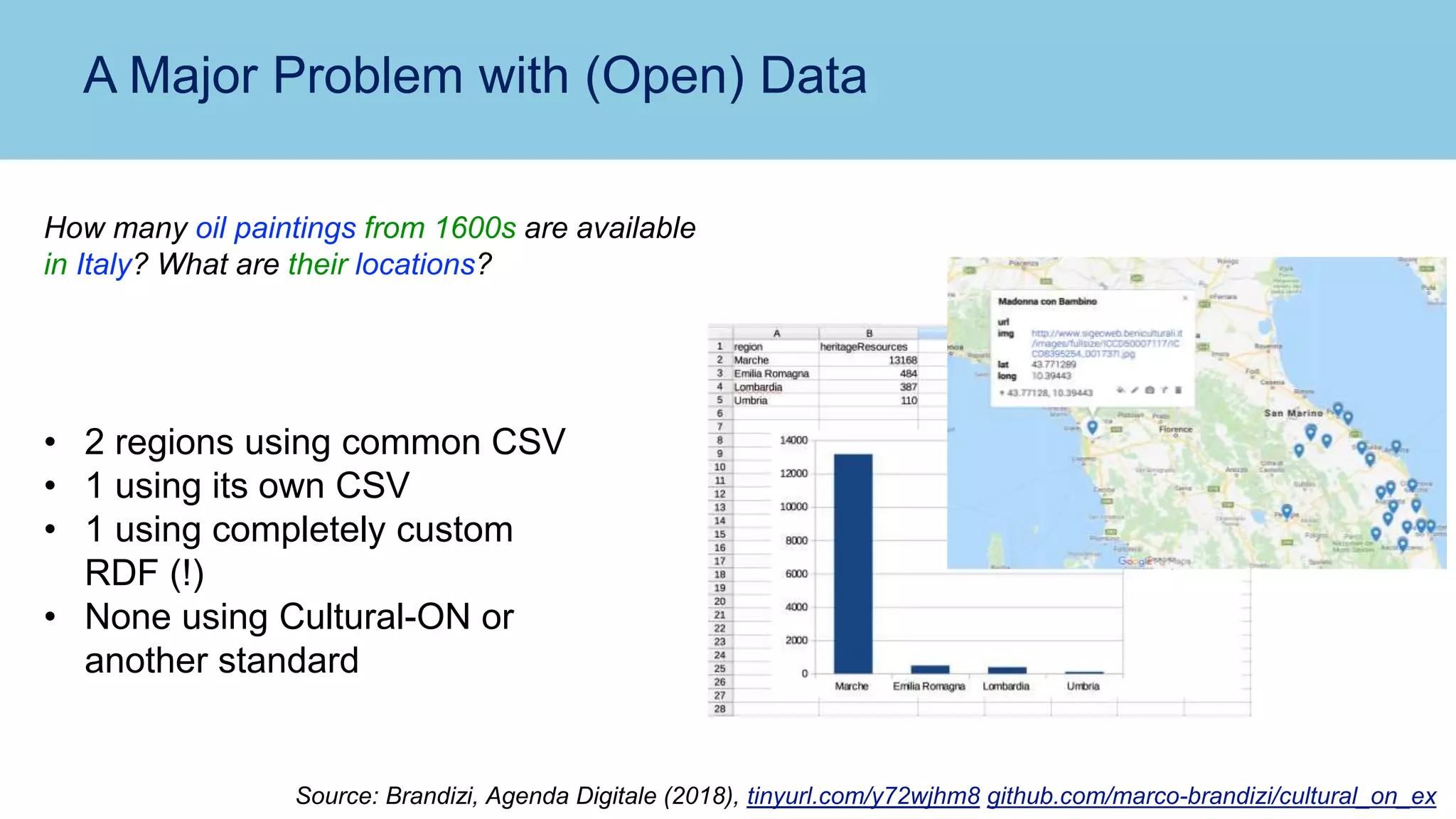
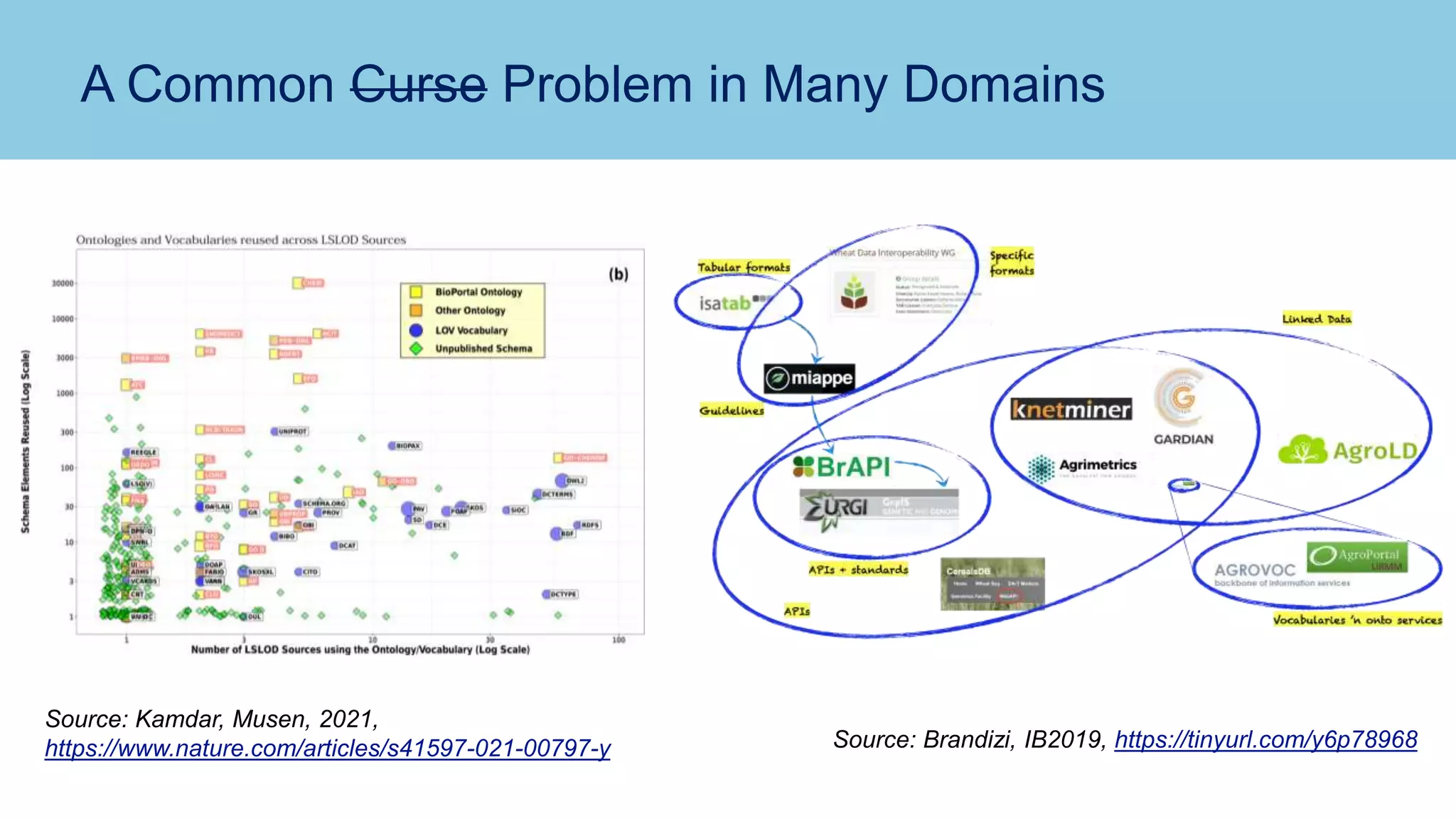
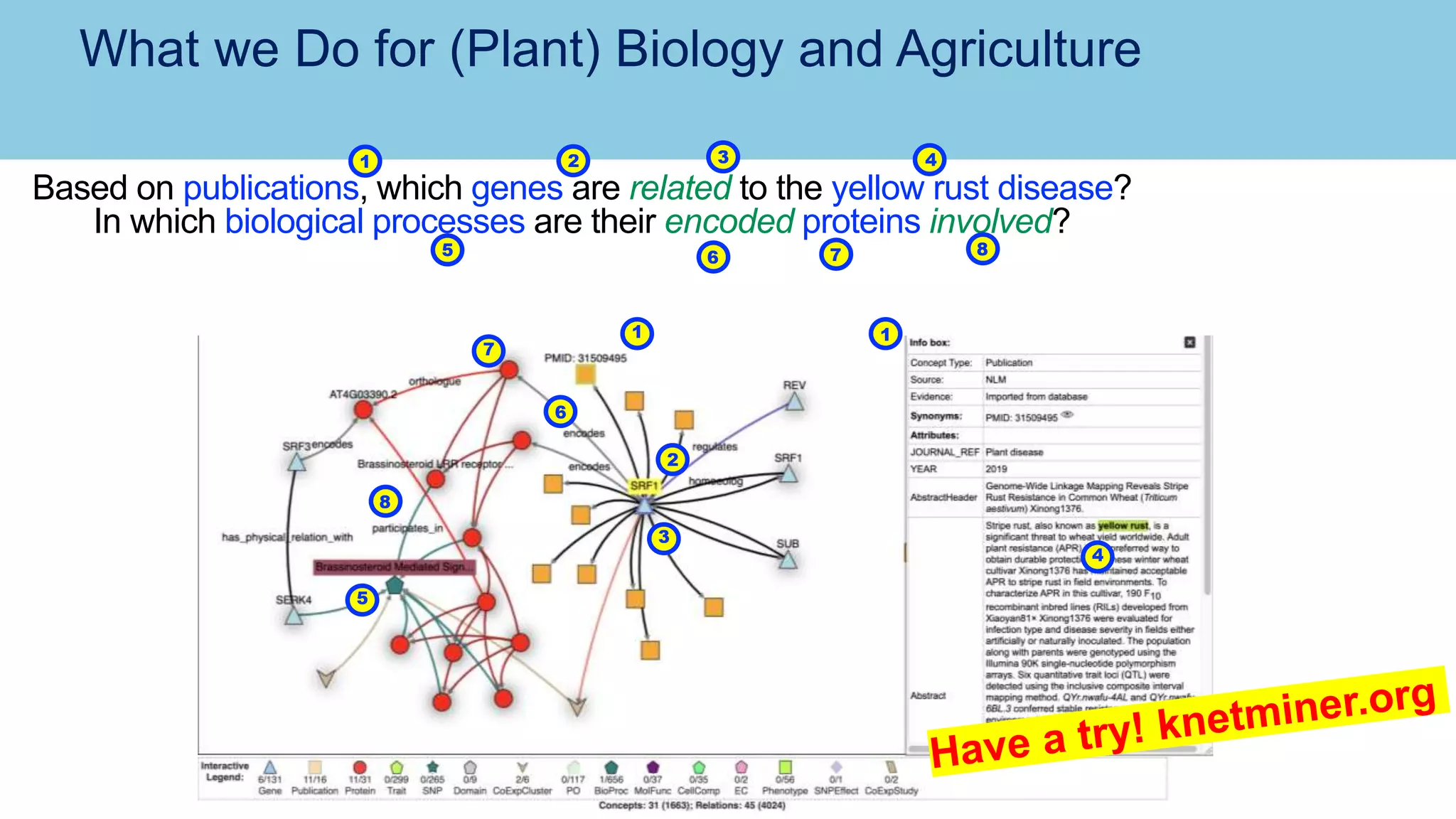
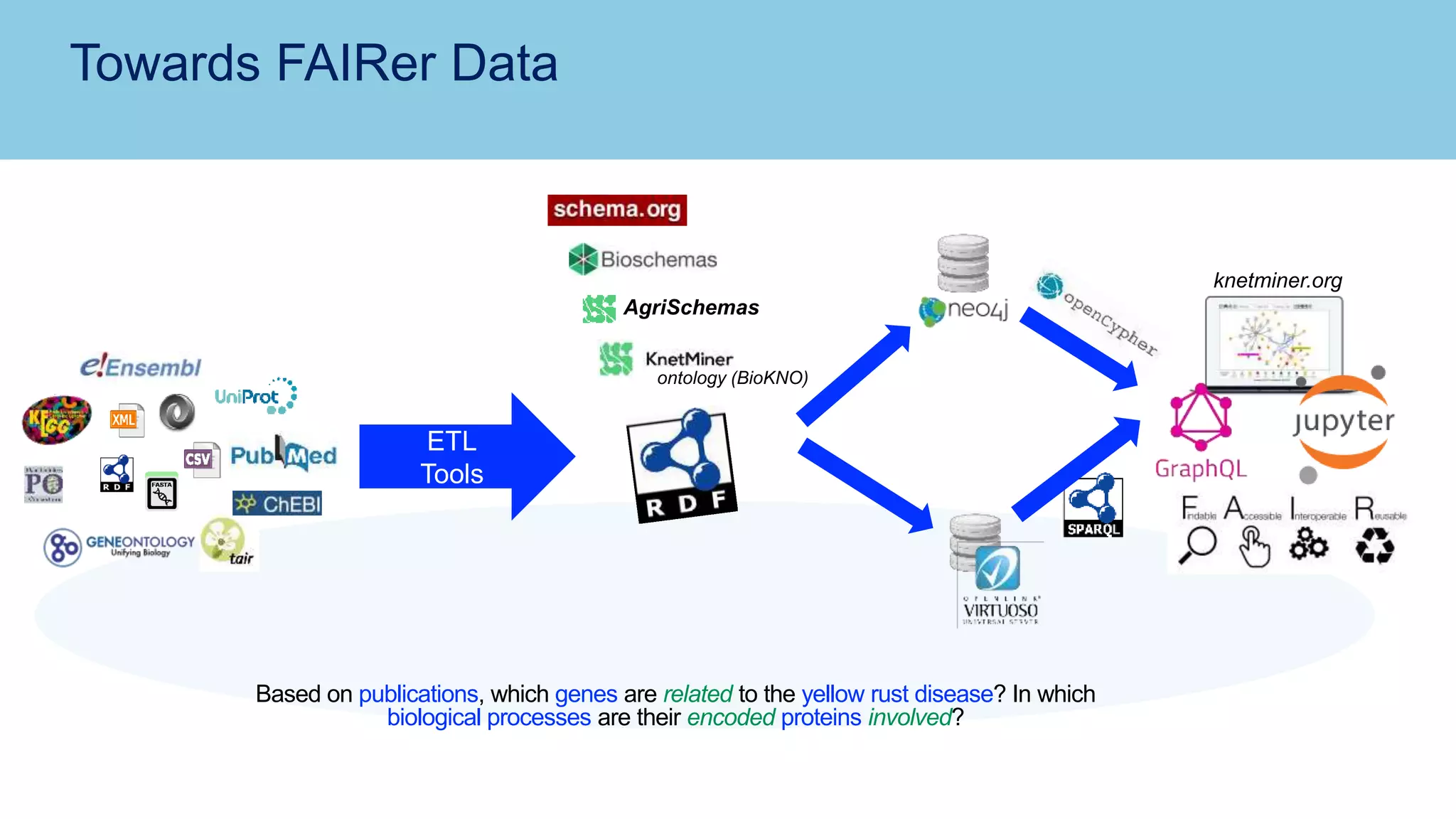
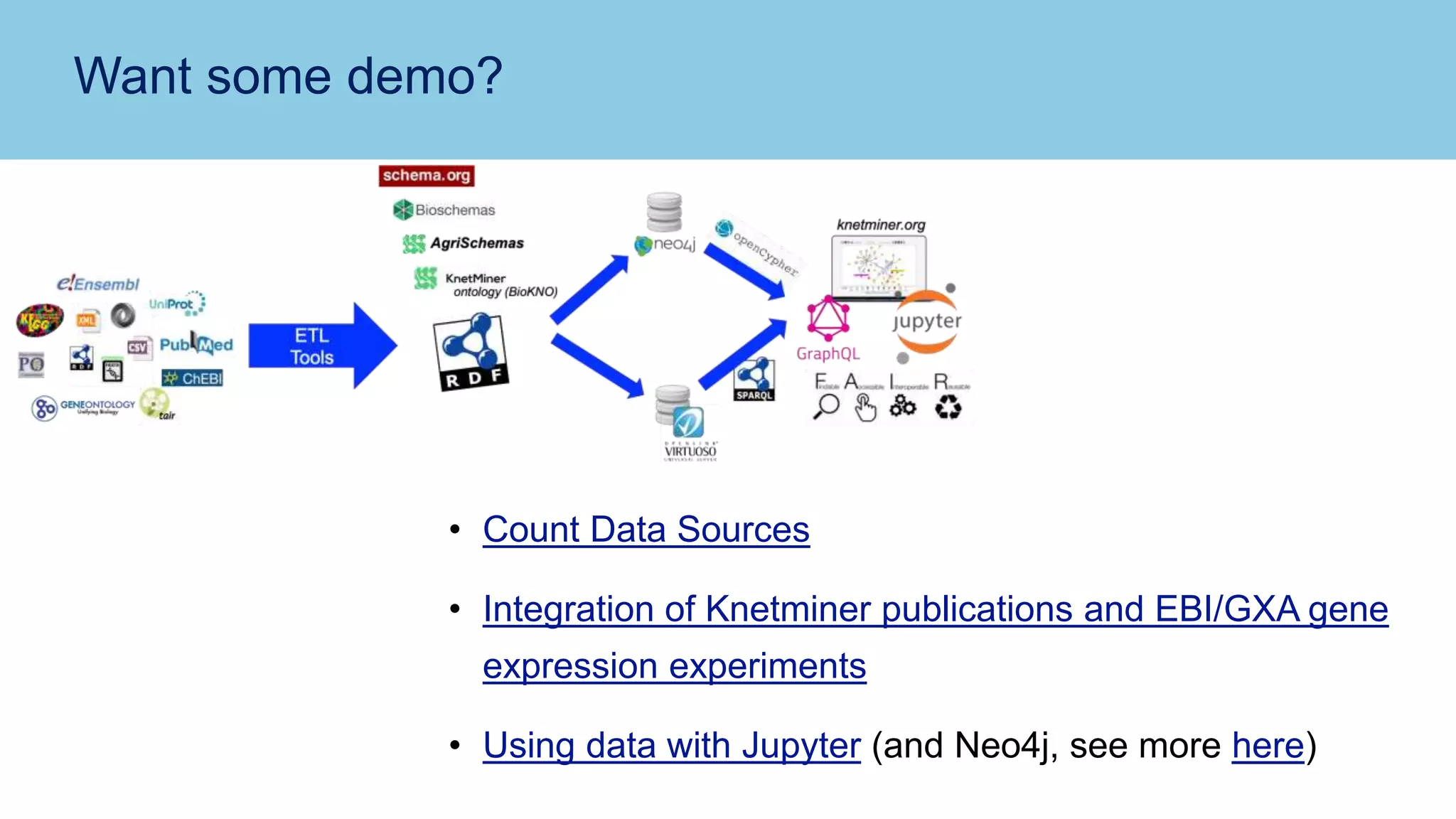
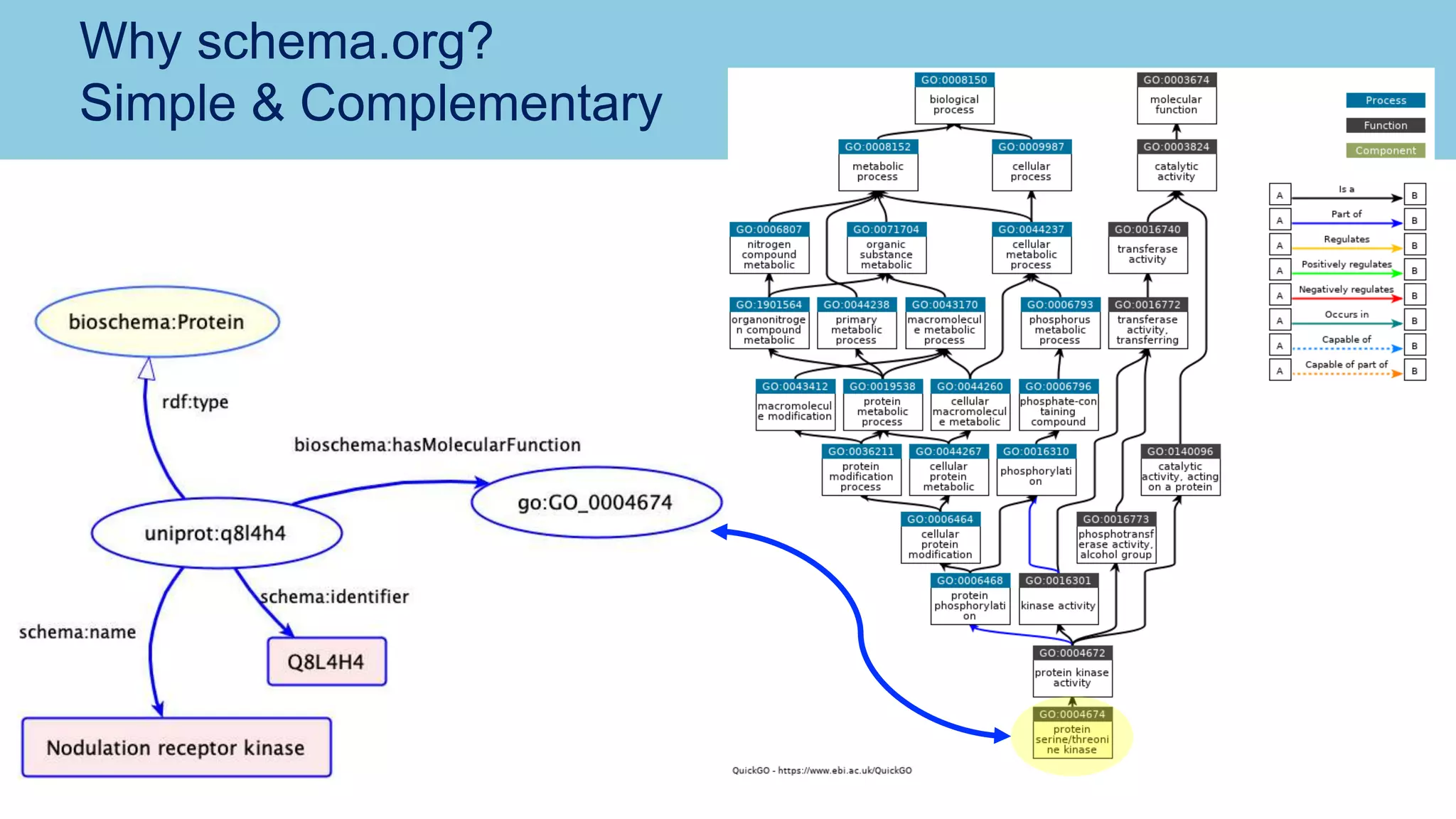
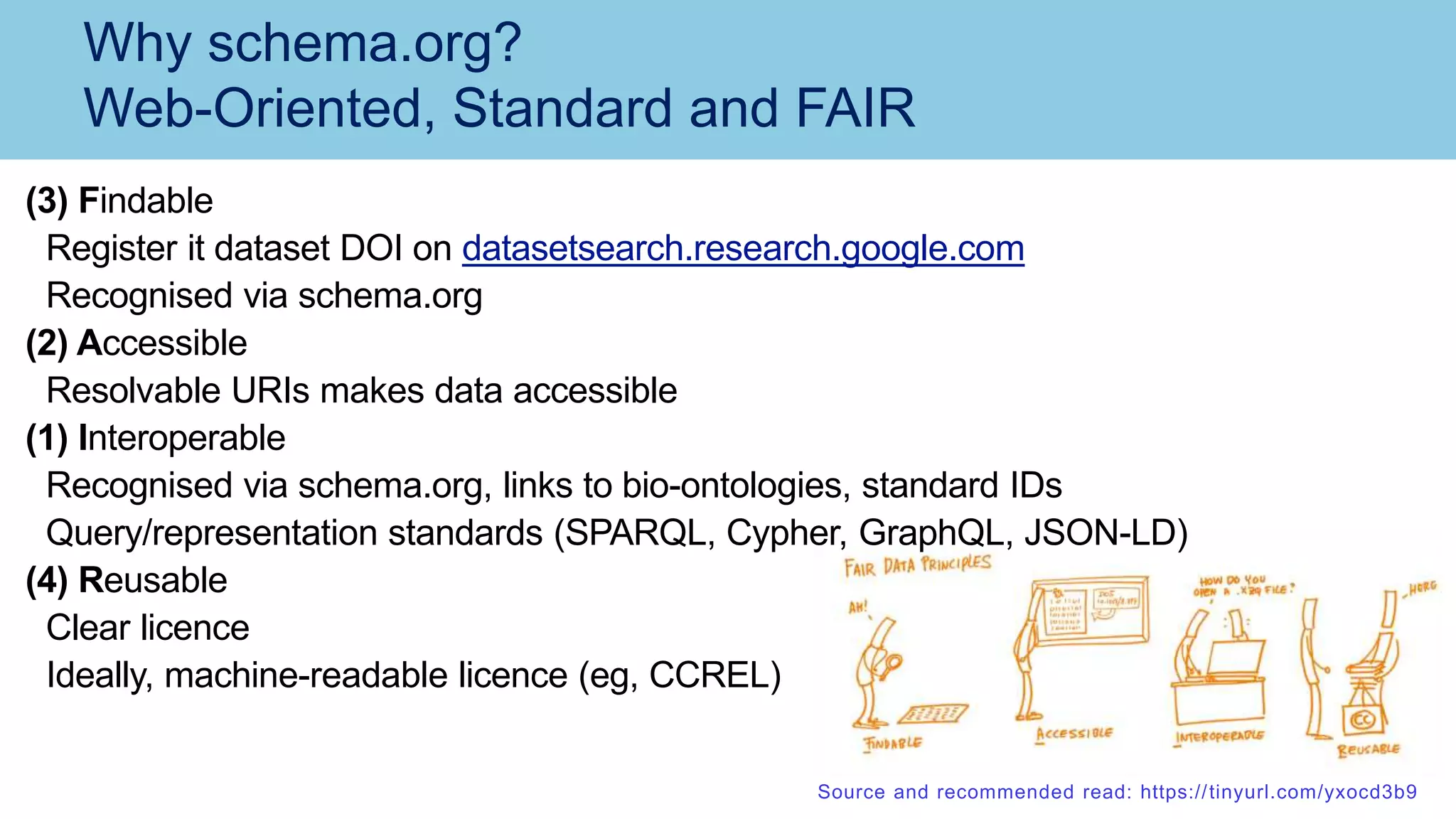
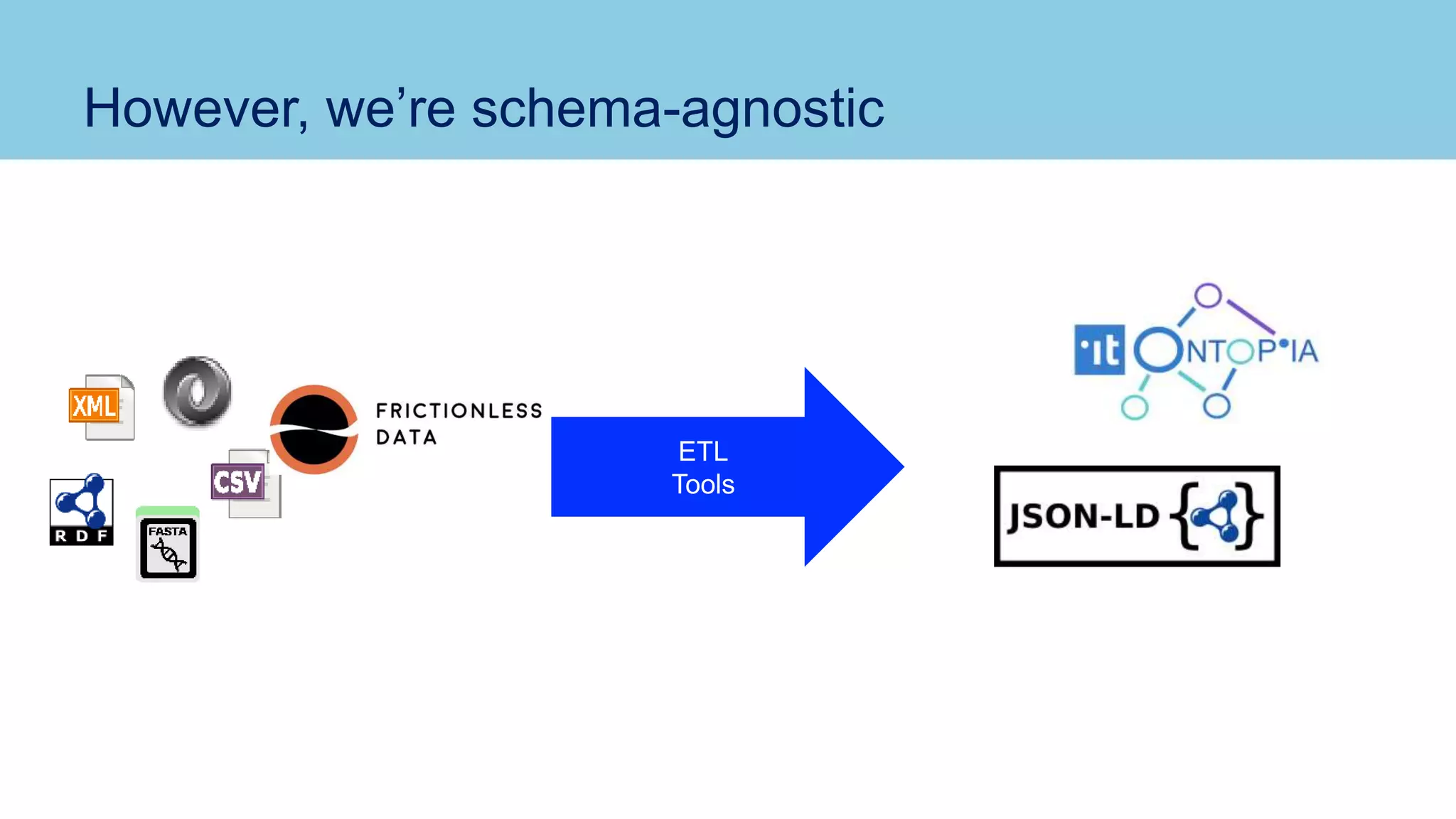
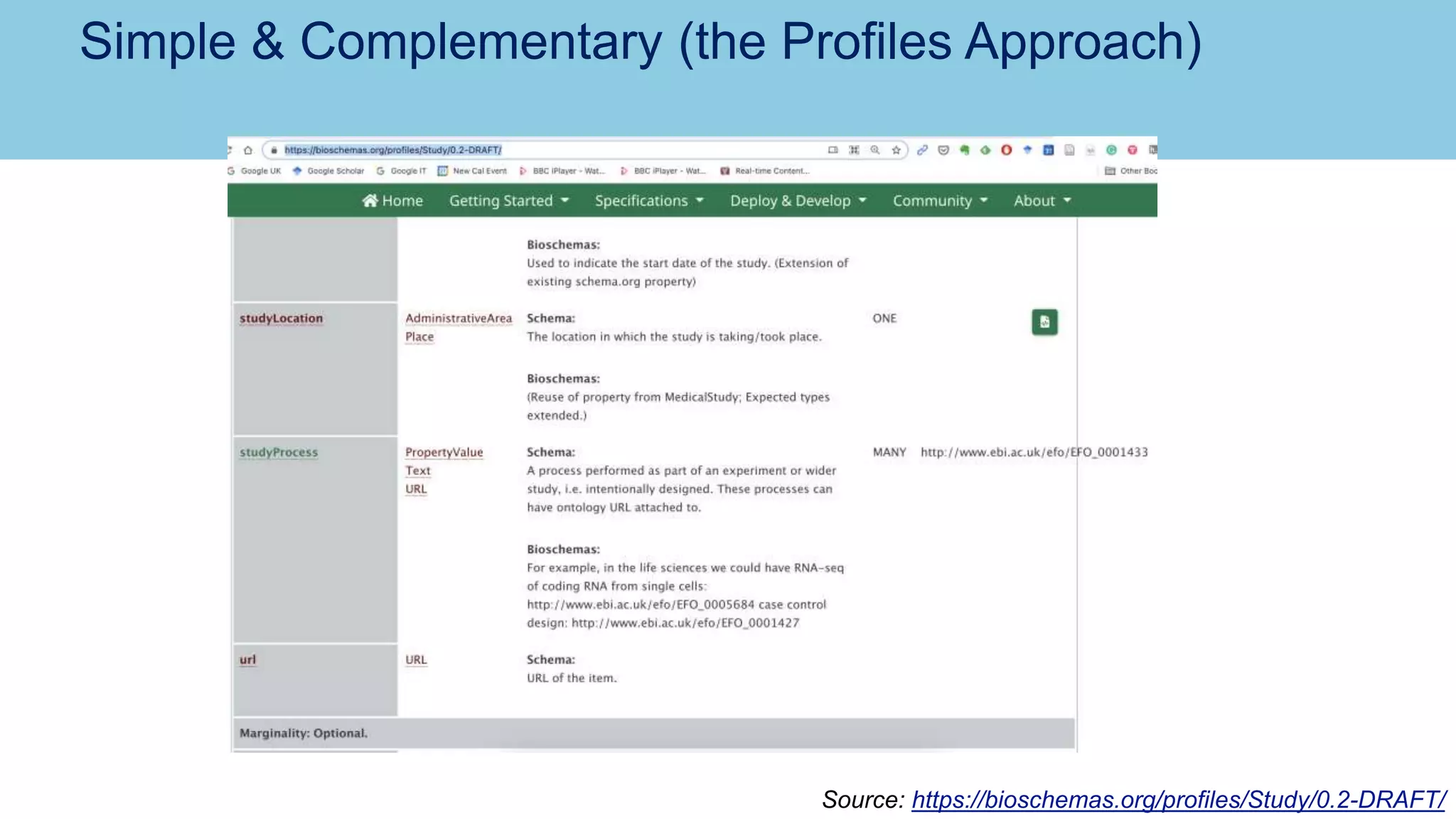
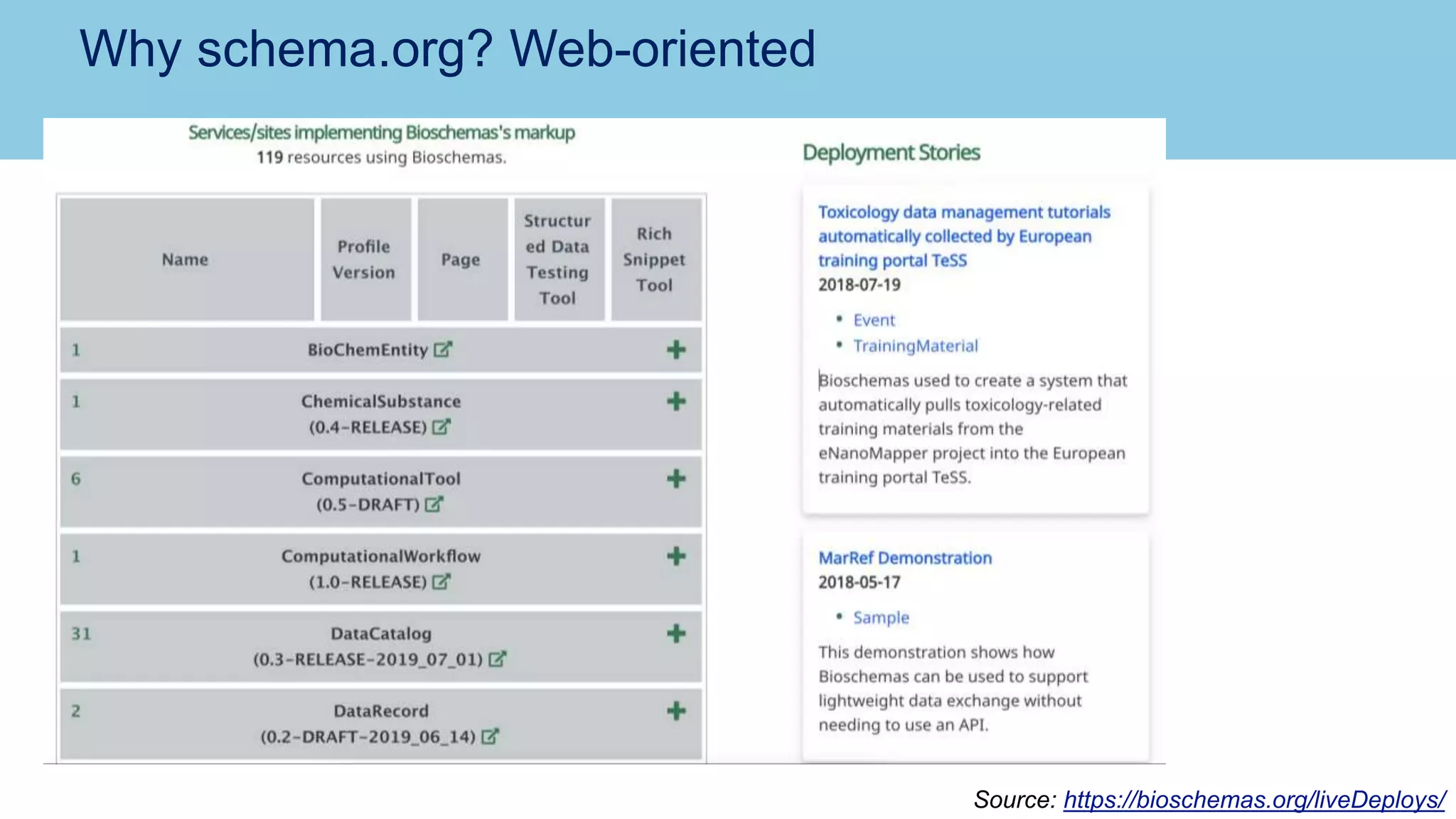
The document discusses the challenges and solutions related to publishing and consuming FAIR data in the agri-food domain. It emphasizes the need for standardized data integration, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability, particularly through the use of schema.org and various ETL tools. It also invites collaboration on data integration projects in agriculture, life sciences, and related fields.