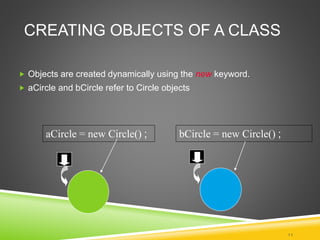
A class defines a template for objects with fields (data) and methods (functions). An object is an instance of a class that exists in memory. The Circle class is defined with double fields for the x and y coordinates of the center and the radius. Methods like circumference() and area() can be declared within the class. Objects are created using the new keyword and access fields and methods using dot notation.