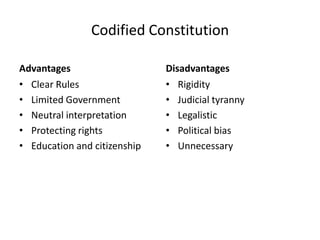
This document defines and provides examples of codified and uncodified constitutions. A codified constitution collects key provisions in a single document, making it authoritative and difficult to amend. Examples include the US and India. An uncodified constitution lacks a single document, so laws have the same status and the constitution can change easily. Examples include the UK and Israel. Codified constitutions are authoritative, entrenched, and allow judicial review, while uncodified constitutions are not and changes are through normal lawmaking. Advantages and disadvantages of each are discussed.