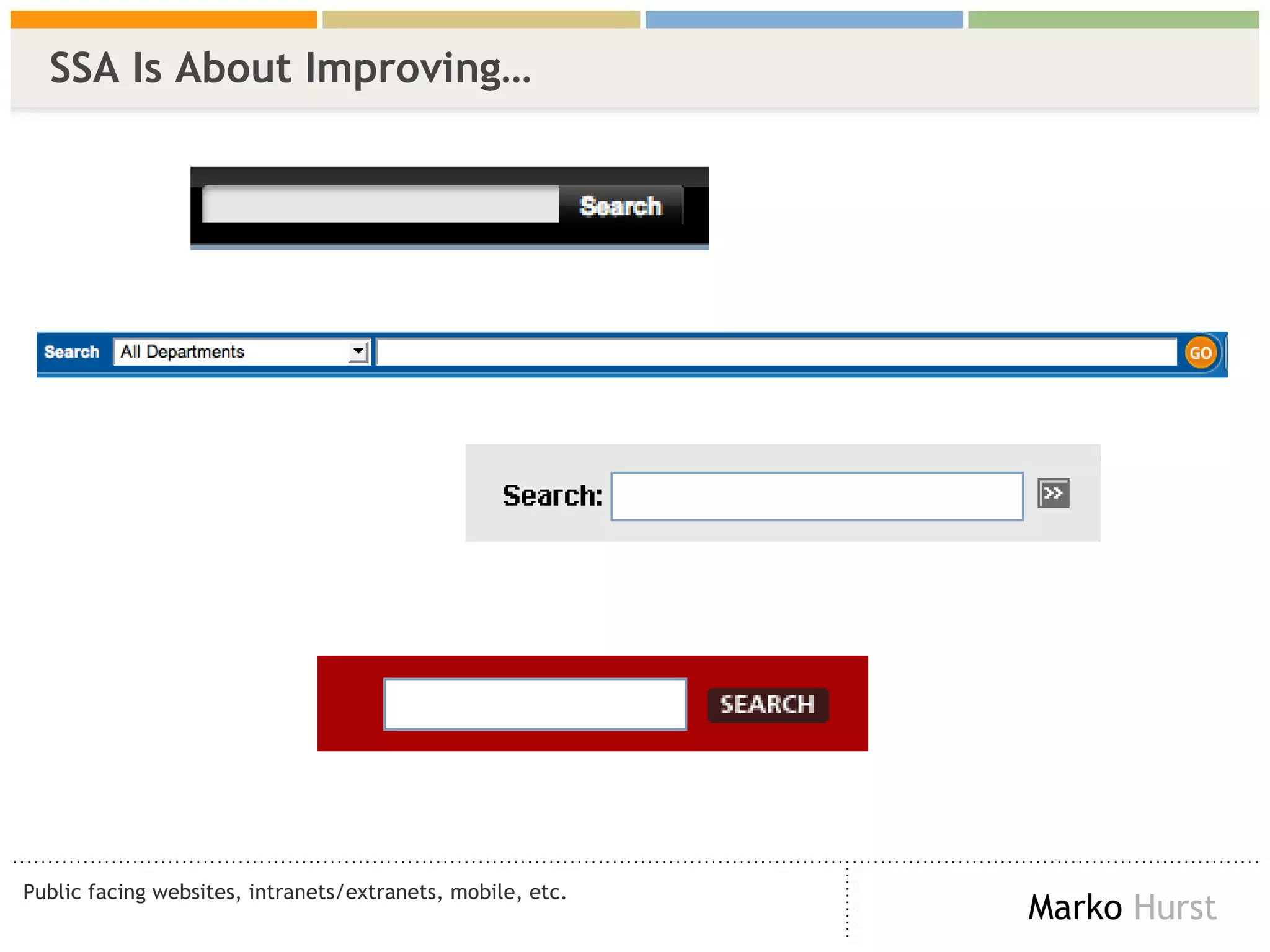
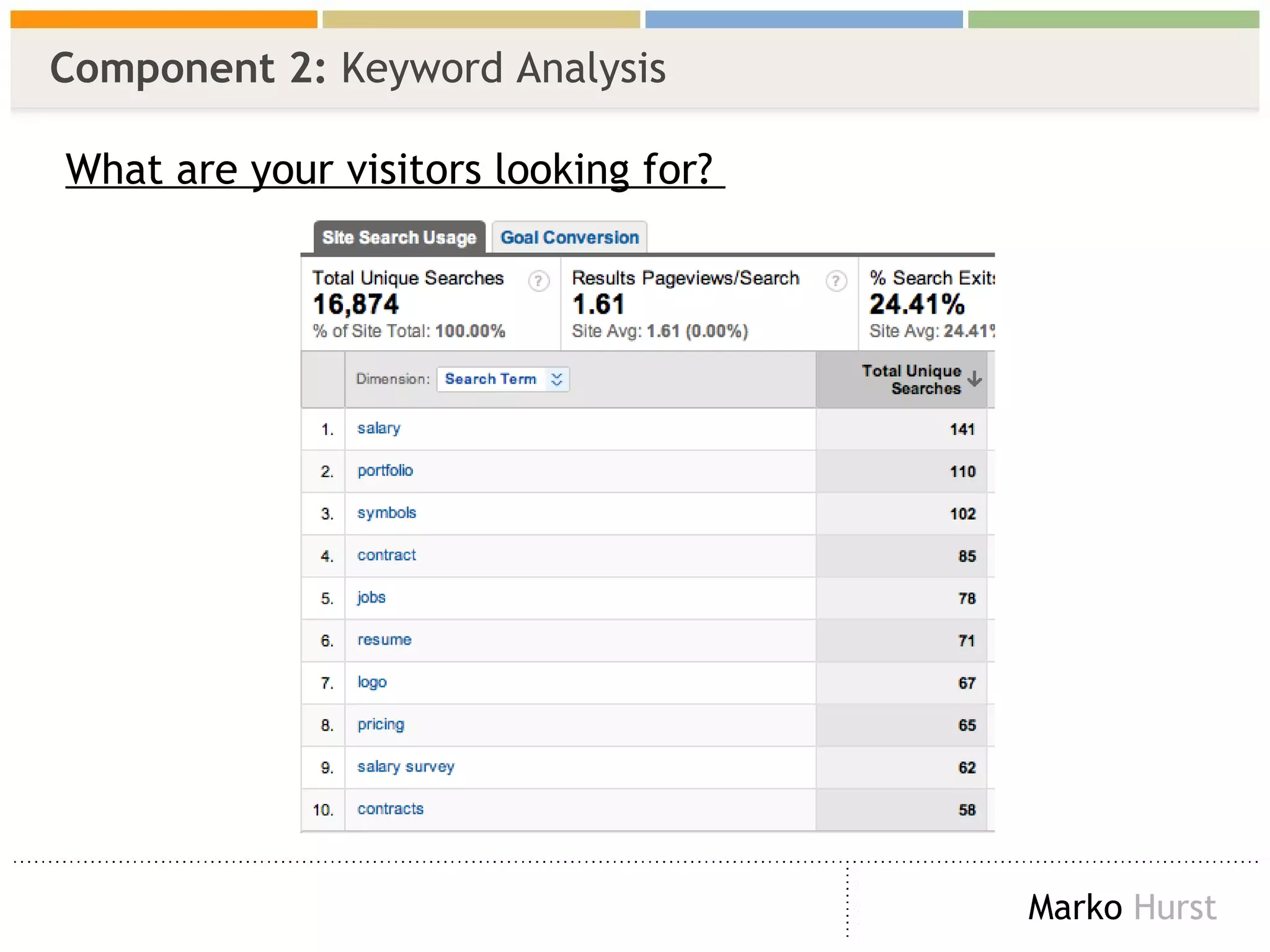
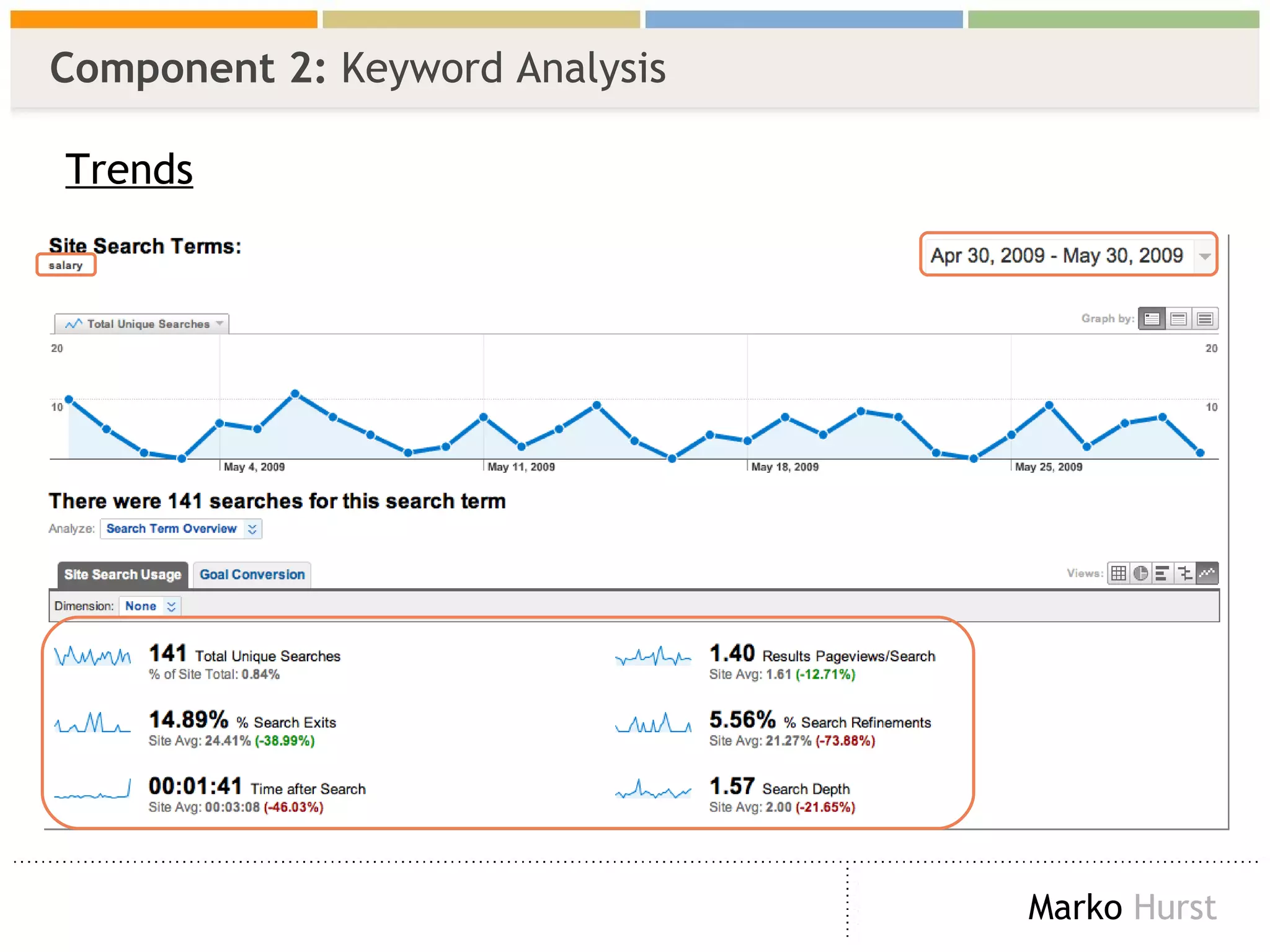
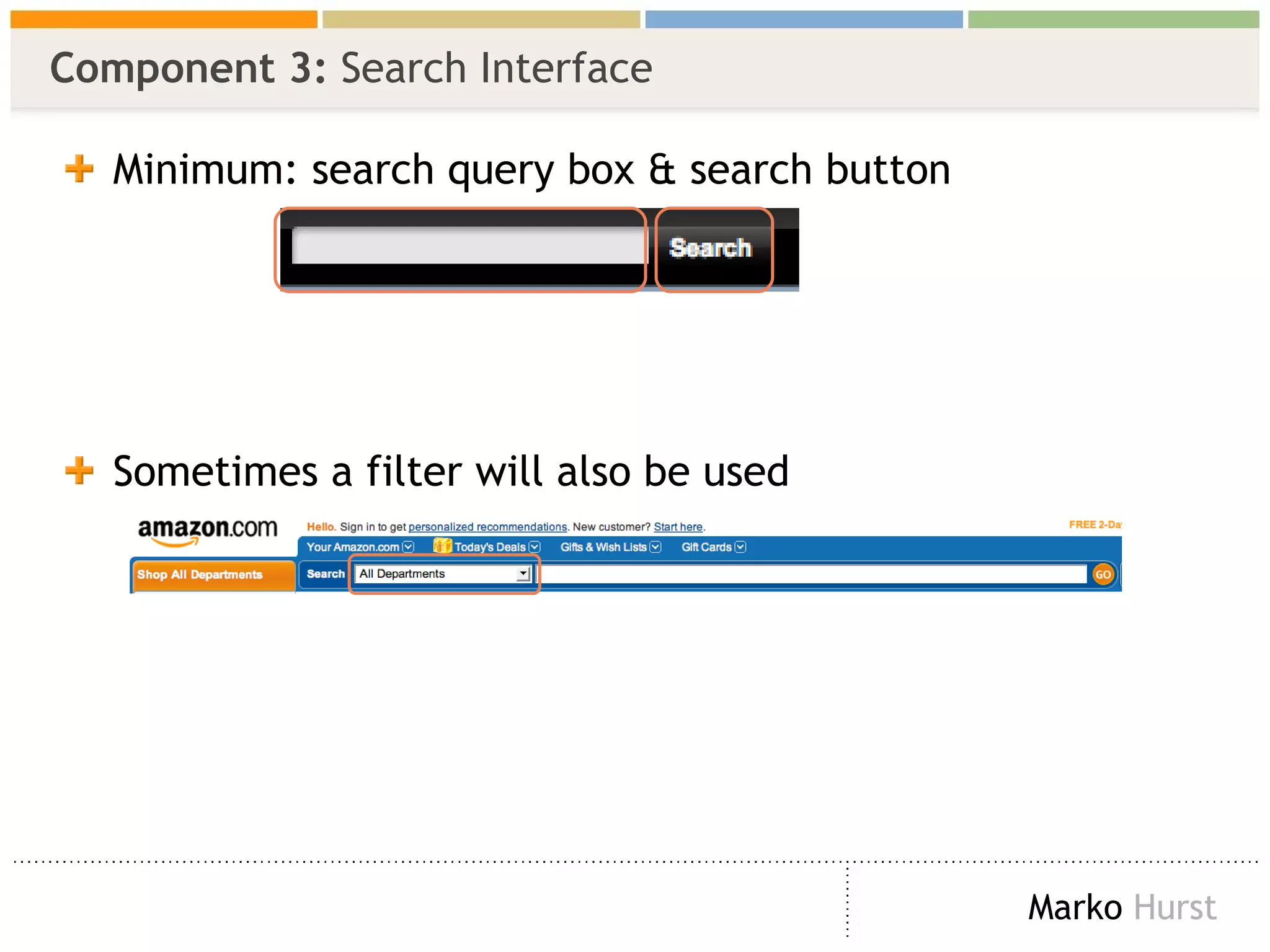
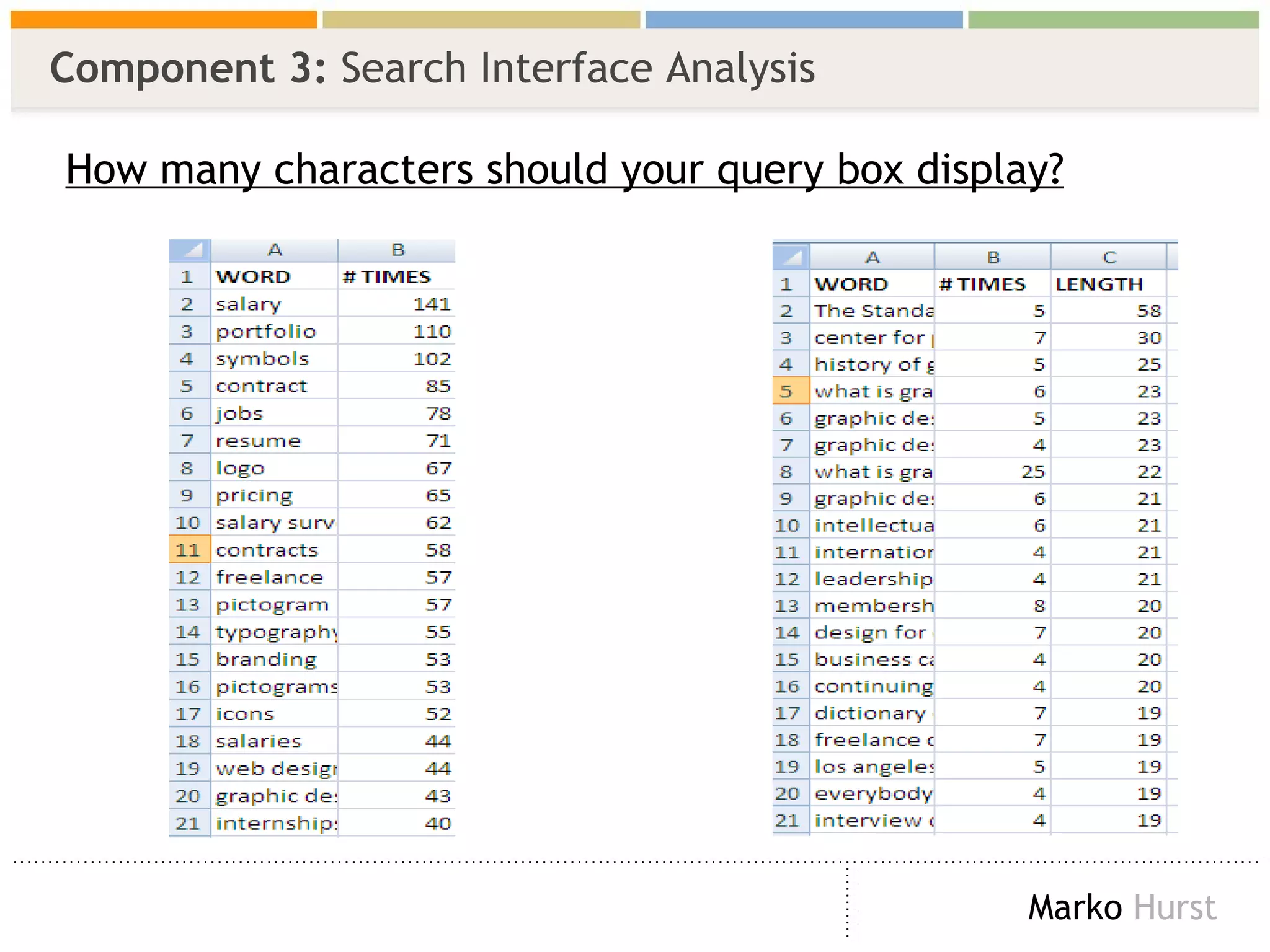
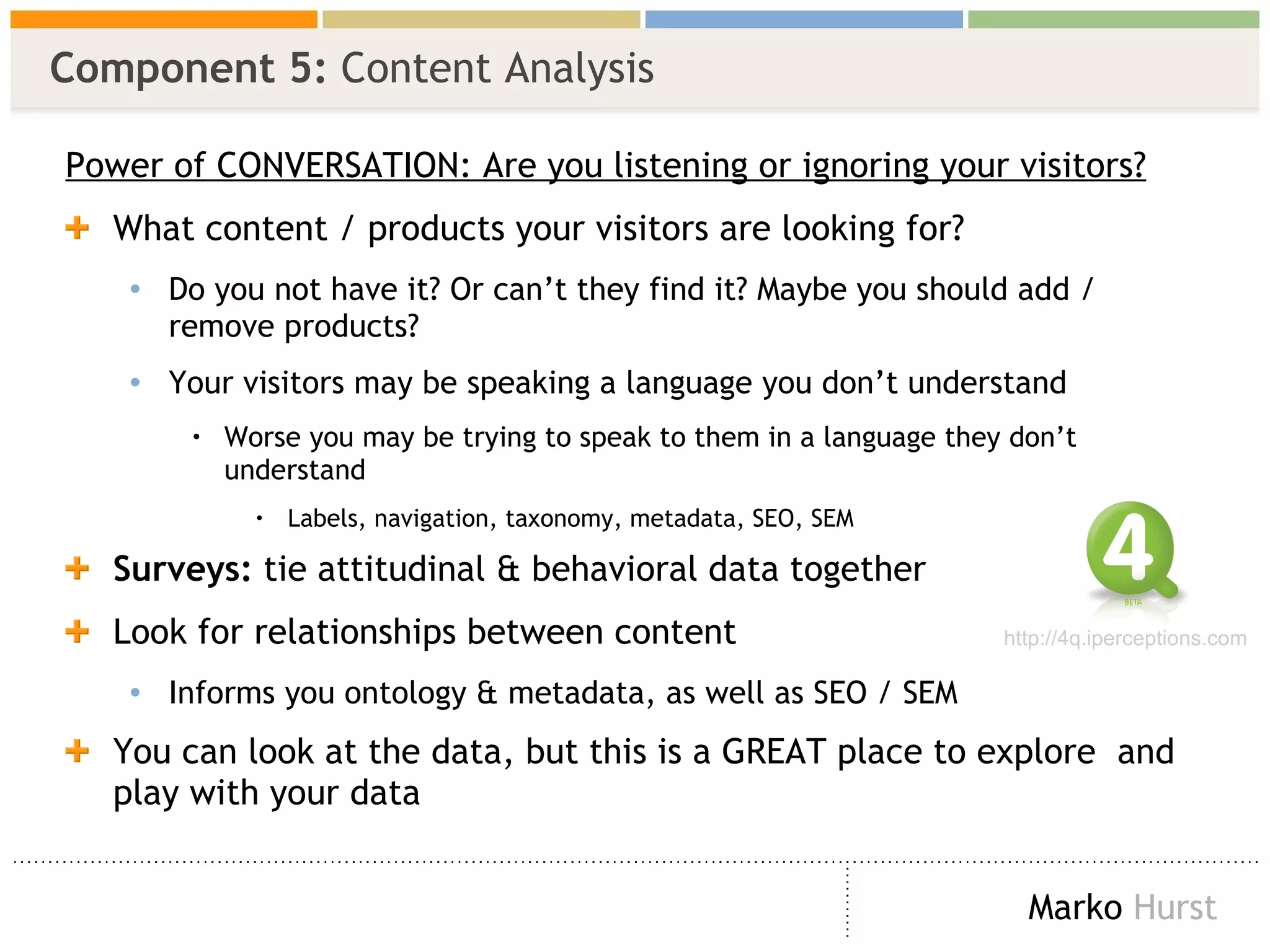
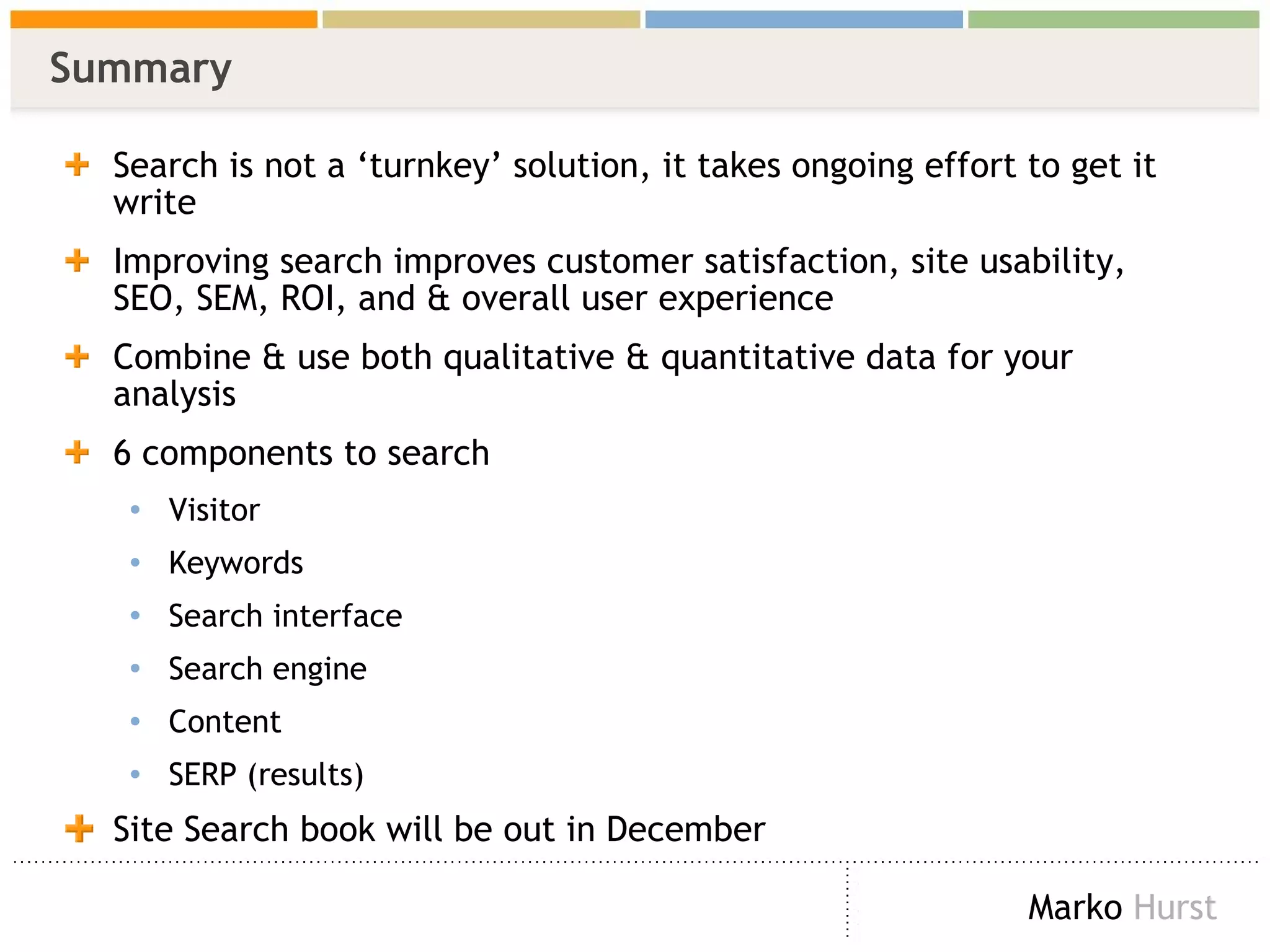
The document discusses the importance of search analytics in enhancing user experience on websites, highlighting the gap between visitor expectations and actual search results. It emphasizes that effective site search cannot be treated as a simple plug-and-play solution and requires continuous improvement and data analysis. The overarching message is to listen to visitors and make informed changes to enhance satisfaction, usability, and overall site performance.

![Me Book: Search Analytics - Conversations With Your Customers Anticipated release: December 2009 Book website: RosenfeldMedia . com/books/SearchAnalytics Co-Author: Lou Rosenfeld Consultant, Author, & Speaker User Experience Web Analytics Behavioral Targeting: (Machine Learning & Neuroscience) Blog: MarkoHurst .com “Insightful Analytics” Twitter: MarkoHurst Contact: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markohurstsitesearchanalyticsemetricsmadrid-090603105621-phpapp01/75/Site-Search-Analytics-eMetrics-Madrid-2009-2-2048.jpg)











![Data: Search Logs (Google Search Appliance) Critical elements in red IP address, time/date stamp, query, and # of results XXX.XXX.XX.130 - - [ 10/Jul/2006:10:24:38 -0800 ] "GET /search? access=p&entqr=0&output=xml_no_dtd&sort=date%3AD%3AL %3Ad1&ud=1&site=AllSites&ie=UTF-8&client=www&oe=UTF-8&proxystyleshe et=www&q= regional+transportation+governance +commission&ip=XXX.XXX.X.130 HTTP/1.1" 200 9718 62 0.17 XXX.XXX.X.104 - - [ 10/Jul/2006:10:25:46 -0800 ] "GET /search? access=p&entqr=0&output=xml_no_dtd&sort=date%3AD%3AL %3Ad1&ud=1&site=AllSites&ie=UTF-8&client=www&oe=UTF-8&proxystyleshe et=www&q= lincense+plate &ip=XXX.XXX.X.104 HTTP/1.1" 200 971 0 0.02 XXX.XXX.X.104 - - [ 10/Jul/2006:10:25:48 -0800 ] "GET /search? access=p&entqr=0&output=xml_no_dtd&sort=date%3AD%3AL %3Ad1&ie=UTF-8&client=www&q= license+plate &ud=1&site=AllSites&spell=1&oe=UTF-8&proxystylesheet=www&ip=XXX.XXX. X.104 HTTP/1.1" 200 8283 146 0.16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markohurstsitesearchanalyticsemetricsmadrid-090603105621-phpapp01/75/Site-Search-Analytics-eMetrics-Madrid-2009-26-2048.jpg)





![Muchas Gracias! Book: RosenfeldMedia . com/books/SearchAnalytics Blog: MarkoHurst .com Contact: [email_address] .com Twitter: MarkoHurst](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markohurstsitesearchanalyticsemetricsmadrid-090603105621-phpapp01/75/Site-Search-Analytics-eMetrics-Madrid-2009-46-2048.jpg)