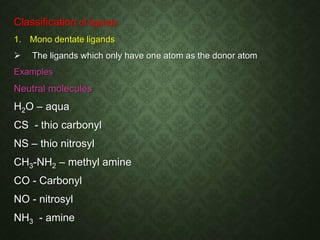
This document discusses coordination chemistry and coordination compounds. It defines coordination chemistry as the study of compounds formed between metals and ligands. Coordinate covalent bonds are observed in these complexes. Coordination compounds can exist as either double salts, which fully ionize in polar solvents, or complex compounds, which partially ionize. Ligands are classified as monodentate, bidentate, or polydentate based on the number of donor atoms bonding to the central metal atom. Common examples of various types of ligands are provided.


![Continue…..
The addition compound which is undergoing
complete ionisation (called double salt) in polar solvent
partial ionisation ( called complex compounds) in polar
solvent
Ex: double salt: KCl MgCl2 KCl.MgCl2.6H2O
H2O
H3O+ K+Mg2+Cl-
polar solvent complete
dissociation
Complex compounds:
K3[Fe(CN)6] K+ + [Fe(CN)6]-
polar solvent partial ionisation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coordinationchemistry-introduction-200714095953/85/Coordination-chemistry-part-1-3-320.jpg)
![Continue ……
[ M Lx ] y ionisation sphere
Central metal atom coordination number
ligand
co-ordination sphere
In complex form central metal atom acts as lewis
acid(electron pair acceptor )
Ligand acts as lewis base (electron pair donar)
Transfer of C-H σ bonding electrons is called agostic
interaction M C
H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coordinationchemistry-introduction-200714095953/85/Coordination-chemistry-part-1-4-320.jpg)