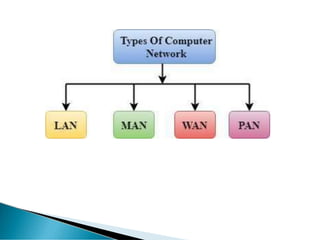
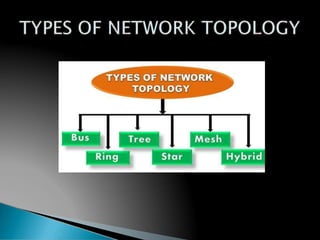
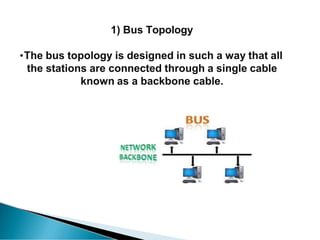
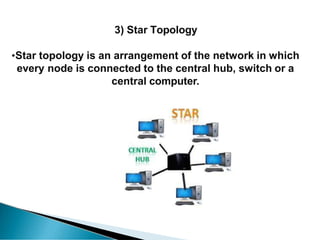
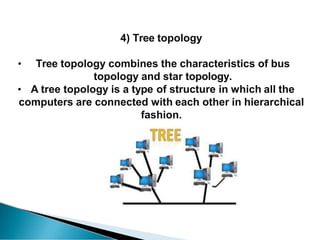
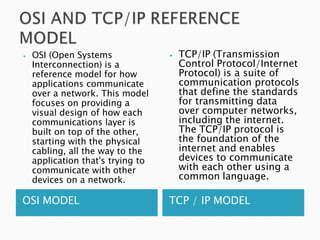
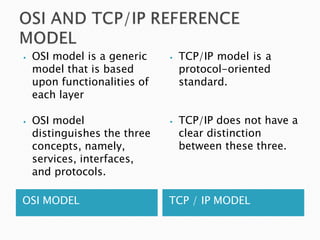
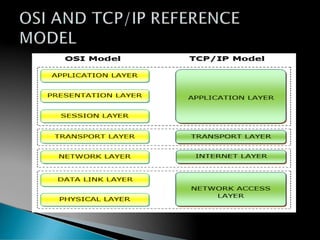
A computer network allows computers to communicate and share resources over a connection. There are different types of networks categorized by size, including local area networks (LANs) within a building, personal area networks (PANs) within 10 meters, metropolitan area networks (MANs) connecting multiple LANs, and wide area networks (WANs) spanning states or countries. Network topology defines how components are interconnected, with common topologies including bus, ring, star, tree, and mesh. The OSI model and TCP/IP model provide standards for network communication layers and protocols.