1) Light travels in straight lines and is a form of energy that moves much faster than sound.
2) Mirrors come in different shapes - plane, convex, and concave - and each type produces distinct image types, whether virtual or real.
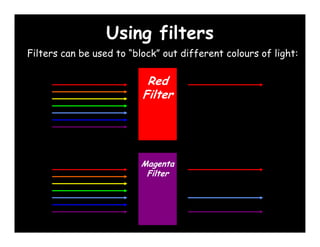
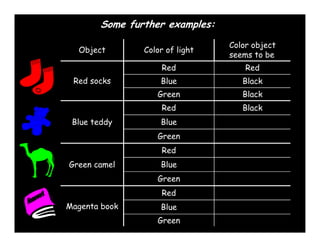
3) Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, while refraction is when light changes speed as it passes from one medium to another, such as from water to air, causing the bending of light rays.