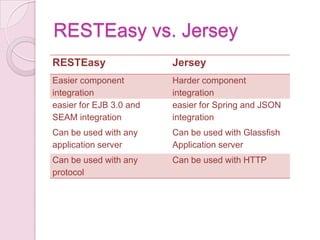
This document provides an overview of RESTEasy, an open source Java framework for building RESTful web services. It discusses what REST is and why it is used, highlights key features of RESTEasy like portability and annotations, compares RESTEasy to Jersey, demonstrates how to use JAX-RS annotations to define RESTful resources and services, and provides references for additional information.