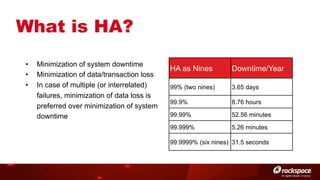
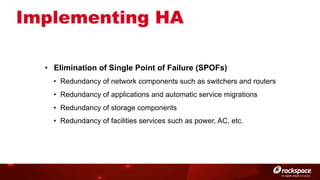
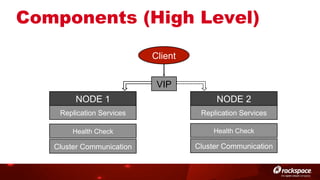
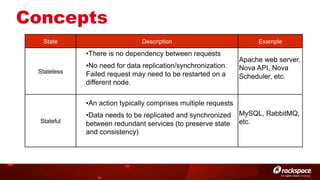
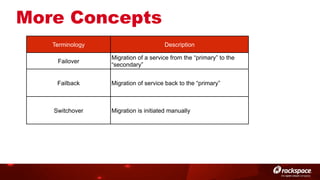
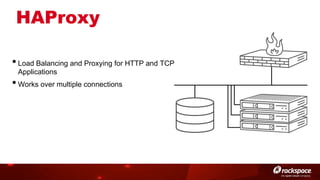
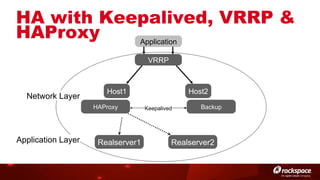
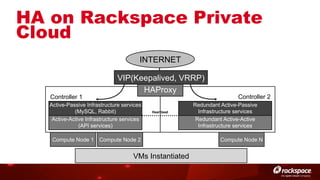
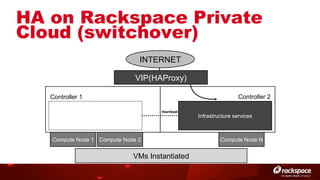
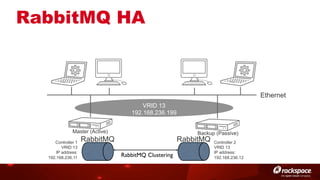
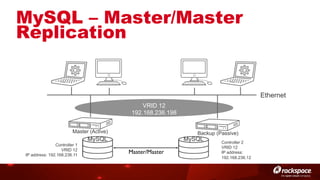
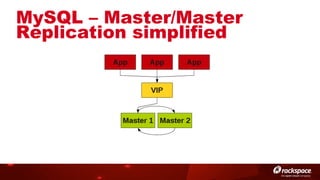
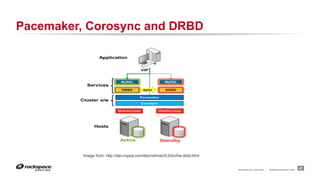
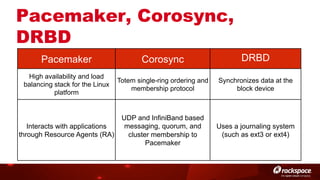
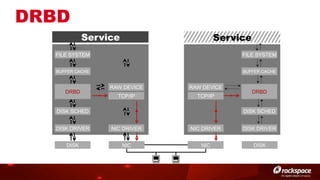
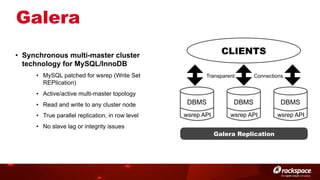
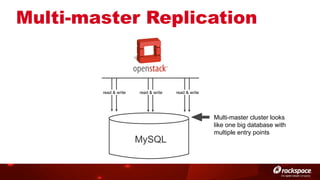
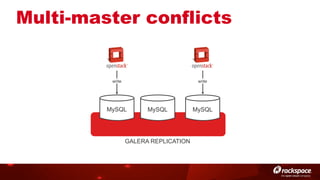
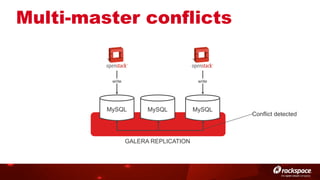
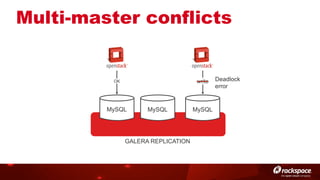
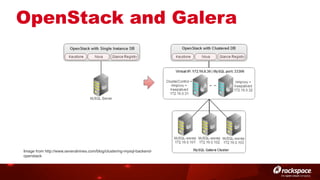
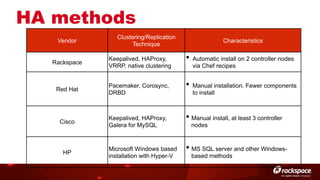
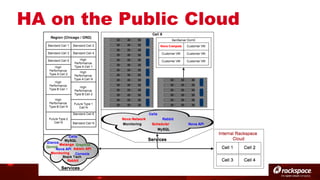
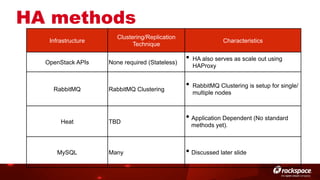
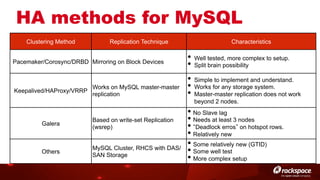
The document discusses high availability (HA) in OpenStack, emphasizing the significance of minimizing system downtime and data loss during failures. It outlines various HA methods and components, including redundancy strategies for services like MySQL and RabbitMQ, along with recommended practices such as utilizing keepalived and HAProxy. Special attention is given to Galera for MySQL, noting its active/active capabilities and the complexity of different clustering techniques.