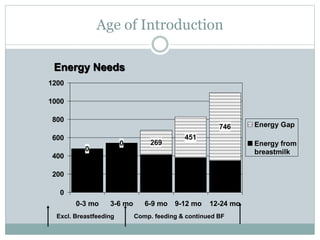
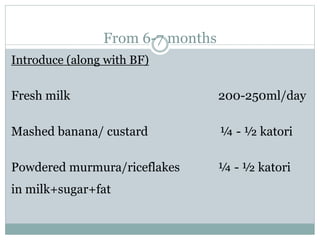
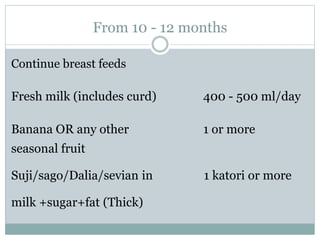
This document defines complementary feeding as providing other foods and liquids to an infant along with breast milk after 6 months when breast milk alone is no longer sufficient. Complementary foods should be introduced timely, adequately in terms of nutrients, and properly through active feeding. Continued breastfeeding for 2 years is important as breast milk provides significant energy and nutrients. Complementary foods should be of appropriate consistency, nutrient-dense, varied, and hygienically prepared and fed to support growth and development from 6 months onwards.