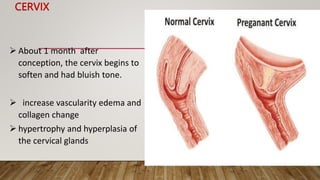
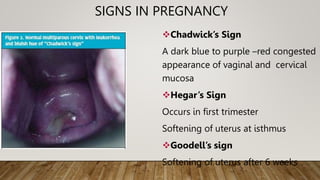
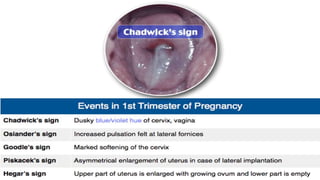
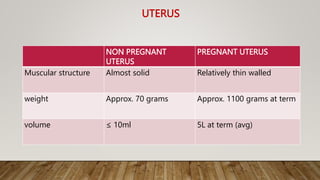
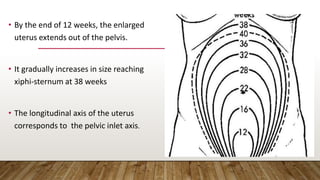
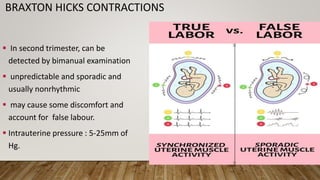
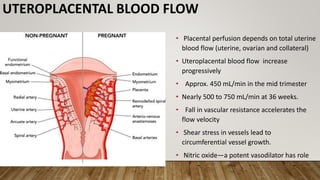
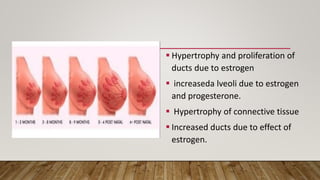
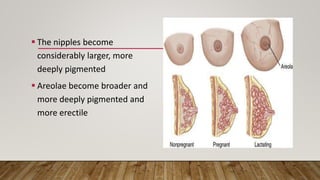
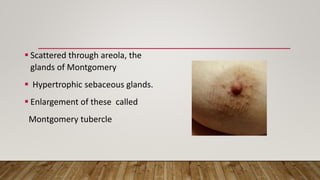
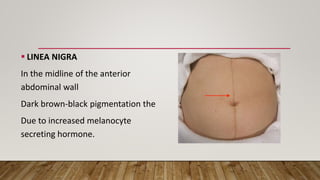
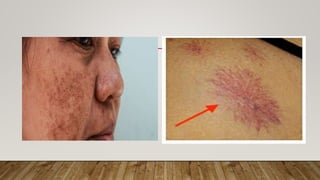
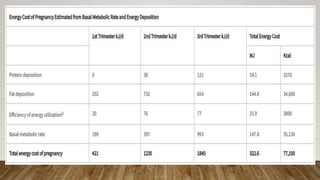
Physiological changes in pregnancy affect many body systems. The reproductive tract undergoes changes like increased vascularity in the vulva, vagina and cervix to accommodate birth. The breasts enlarge due to ductal and alveolar growth in preparation for lactation. Metabolic changes increase calorie and protein needs to support the growing fetus. The uterus expands dramatically under the influence of hormones to carry the pregnancy.