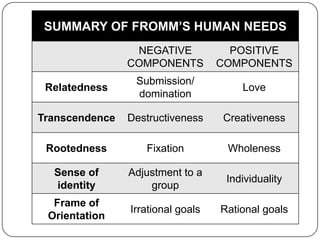
Erich Fromm developed a theory of humanistic psychoanalysis that viewed humans as having been separated from nature, leading to feelings of isolation and basic anxiety. His theory blended Freud's emphasis on the unconscious with Marx's view of socioeconomic determinism. Fromm believed humans have five basic needs - relatedness, transcendence, rootedness, identity, and orientation - and that society influences the development of receptive, exploitative, hoarding, marketing, or productive orientations. He also described personality disorders like necrophilia, malignant narcissism, and incestuous symbiosis.