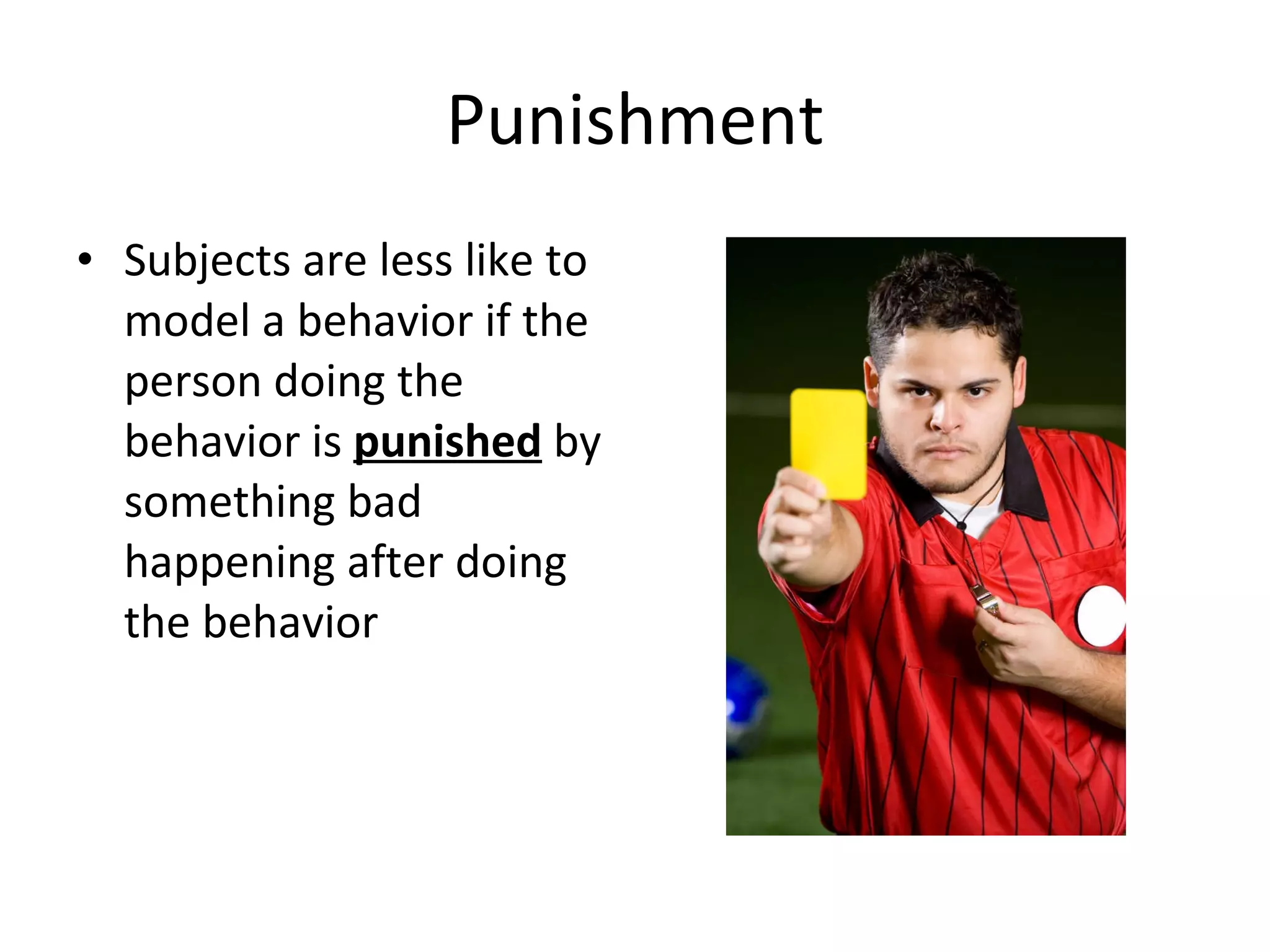
Observational learning plays an important role in advertising. People are more likely to imitate behaviors that are modeled by attractive people and that result in positive reinforcement. Advertisers thus typically use attractive models demonstrating the desired behaviors of using or purchasing a product, with the behavior being rewarded in some way. Negative advertising aims to decrease unwanted behaviors by depicting unattractive models participating in the behavior and being punished as a result.