Spine- Anatomy
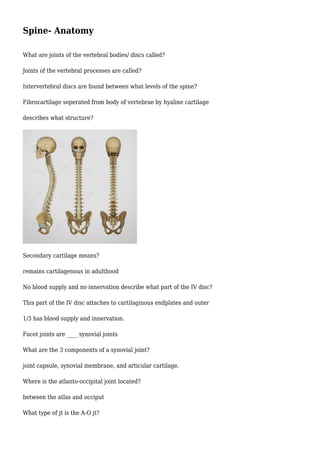
- 1. Spine- Anatomy What are joints of the vertebral bodies/ discs called? Joints of the vertebral processes are called? Intervertebral discs are found between what levels of the spine? Fibrocartilage seperated from body of vertebrae by hyaline cartilage describes what structure? Secondary cartilage means? remains cartilagenous in adulthood No blood supply and no innervation describe what part of the IV disc? This part of the IV disc attaches to cartilaginous endplates and outer 1/3 has blood supply and innervation. Facet joints are ____ synovial joints What are the 3 components of a synovial joint? joint capsule, synovial membrane, and articular cartilage. Where is the atlanto-occipital joint located? between the atlas and occiput What type of jt is the A-O jt?
- 2. What mvmt does the A-O jt allow for? Where is the atlanto-axial jt located? The A-A has ___ median and ___ lateral joint. What cervicle jt allows for 55-58% of head rotation? This atlanto axial jt is a synovial pivot jt. This atlanto axial jt is a synovial plane jt. The medial atlanto-axial jt is made up of what vertebral structures? anterior arch of atlas C1 and dens of C2 What vertebral structures make up the lateral jt of the A-A jt? lateral masses of C1 and superior facet of C2 This lig runs from the atlas' ant tubercle to the sacrum anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL) The ALL attaches to the ____ surface of the vertebral ___ and ___. anterior, bodies and discs What mvmt is the ALL designed to limit Which is stronger the AlL or the PLL and by how much? This ligament is continuos superiorly as the anterior atlanto-occipital membrane. The A-O membrane attaches to what? anterior arch of atlas, and anterior margin of foramen magnum This ligament attaches to the posterior vertebral bodies from C2-S1. posterior ongitudinal ligament (PLL) This ligament continues superiorly as the tectorial membrane. Which ligament ALL or PLL is designed to resist flexion? The tectorial membrane attaches to what? posterior surface of dens, and anterior edge of foramen magnum
- 3. What are the ligaments of the vertebral arches (5)? ligamentum flavum, supraspinous ligament, ligamentum nuchae, interspinous ligament, and intertransverse ligaments This ligament connects to lamina from C2-C5, is 80% elastin and 20% collagen. What gives the ligamentum flavum its yellow color? the 80% elastin component The yellow ligament countiues superiorly as what? the posterior O-A membrane and the posterior A-A membrane. The posterior A-O membrane attaches to what? the posterior arch of the atlas and posterior margin of foramen magnum. This ligament connects to the tips of SPs C7 to approx L3/4 and is well developed in the lumbar spine. The supraspinous lig countinues superiorly as the ___ ____. This lig offers little resistance fo seperation of SPs, however there is little consensus on this information. This lig extends from C7 to external occipital protuberance and its exact role is not yet determined. Thought to be involved with A/P stability. This ligament connects the vertebral spines and offers litle resistance to fexion. This ligament connects to the TPs, is well developed in the lumbar spine, seperates ant and post mm of spine, and ability to limit lateral flexion is thought but questionable. intertransverse ligaments Where are the jt capsules strongest in the spine?
- 4. at the transition regions of the spine What lig is found at the A-A median jt? Cruciform (cruciate) ligament, transverse and longitudinal. The transverse component of the cruciform lig goes around the ____. The longitudinal bands of the cruciform lig attach to. foramen magnum and the axis This component of the cruciform lig prevents anterior displacement of C1 and C2. What two populations have to be considered when treating area of upper spine? Loss of integrity of this lig in an absolute referal with not treatment in cervical spine. Which would be damaged first if there were an injury at C1 C2 juncion, the dens or the trans lig? The alar ligaments attach where? the dens to the medial surface of occipital condyles. Alar lig limits A-A ____. What structures in the vertebral column limit ROM and need to be considered when assessing motion? IV discs, shape/orientation of jt, capsule, and ligaments.